Abstract
Purpose
To Carry out a low vision quality of life questionnaire and to evaluate subjective quality of life of low-vision patients.
Methods
The subject were 250 patients whose visual acuity was between hand motion and 0.3 among the patients at our clinic. The normal control group included 60 patients. After a review of the literature, we selected a useful questionnaire to assess quality of life in low vision patients and translated the questionnaire into Korean. The questionnaire used had 25 items concerning low vision and each question was multiple-choice, and the sum of the total points was used to assess of the quality of life.
Results
The range of scores was from 0 to 125 points (the higher the score, the higher the quality of life). Fifty-one patients among 250 patients in the low vision group replied to our questionnaire. Fifty patients among 60 patients in the control group replied. The average low vision quality of life (LVQOL) score for patients with low vision (67.3±26.7) was significantly lower than the average score of those with normal vision (114±9.72). There was no statistically significant difference between the average score of patients questioned by mail versus telephone
Conclusions
The score of low vision patients was significantly lower than that of the control group, so this questionnaire can be applied to low vision patients specifically to evaluate quality of life. Optimally, the the questionnaire shoud be administered before and after the low vision consultation. The comparision of prerehabilitation score with postrehabilitation score might be helpful to evaluate the quality of life in a post rehabilitation state.
Go to : 
References
1. American Academy of Ophthalmology. The Eye M.D. Association. Basic and Clinical Science. Section 3. 2005-2006, optic, refraction, and contact lenses. San Francisco: American Academy of Ophthalmologt;2005. p. 347.
2. Strong JG, Pace RJ, Plotkin AD. Low vision services: a model for sequential intervention and rehabilitation. Can J Public Health. 1988; 79:50–4.
4. Byon YC, Kim SH, Yoon SY, et al. 2005 Research on the actual condition of the disabled. Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs. 2006; 04:363–8.
5. Park JH, Moon NJ. Clinical Analysis of 500 Low Vision Patients. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:345–52.
6. Lee HI, Song KS, Moon NJ. Clinical Analysis of 350 Low Vision Patients. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2000; 41:2391–400.
7. Oh SY, Ham DI, Ji YH. Clinical effect of low vision aids. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 38:281–5.
8. Kim KH, Moon NJ. Clinical effect of low vision aids. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1997; 38:141–8.
9. Mangione CM, Phillips RS, Seddon JM, et al. Development of the “activities of daily vision scale.” A measure of visual functional status. Med Care. 1992; 30:1111–26.
10. Steinberg EP, Tielsch JM, Schein OD, et al. National study of cataract surgery outcomes: variation in 4-month postoperative outcomes as reflected in multiple outcome measures. Ophthalmology. 1994; 100:1131–41.
11. Steinberg EP, Tielsch JM, Schein OD, et al. The VF-14. An index of functional impairment in patients with cataract. Arch Ophthalmol. 1994; 112:630–8.
Go to : 
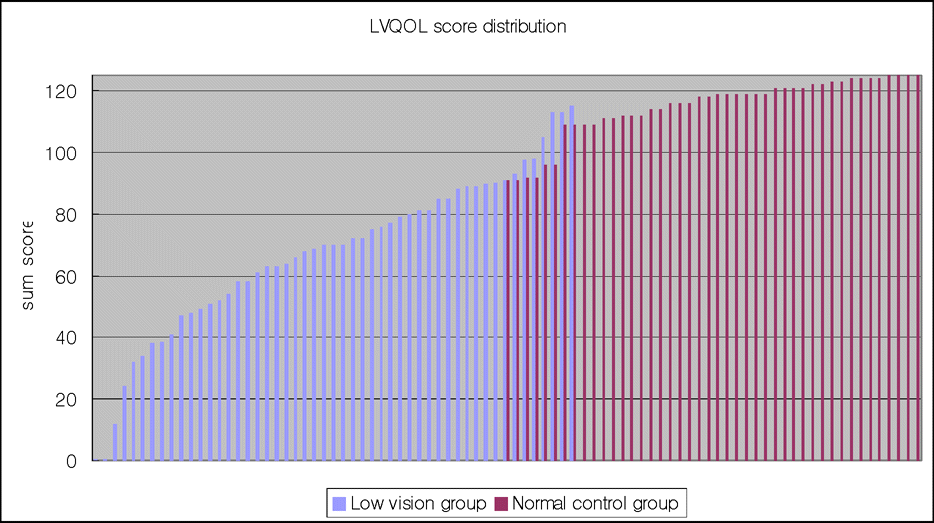 | Figure 2.The distribution of LVQOL score of low vision patiets and normal control group. The summed score were from 0 to 115point in low vision group, and from 91 to 125 point in normal control group. |
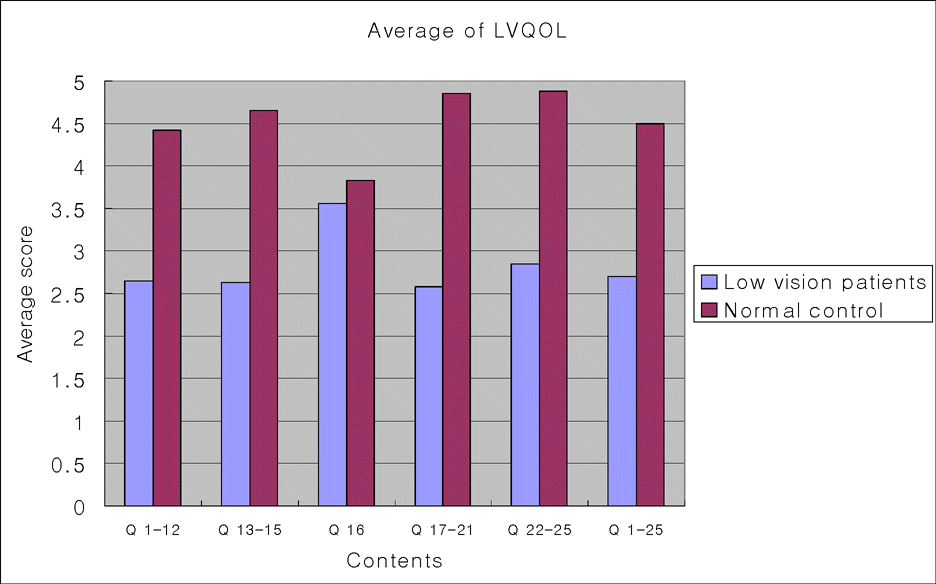 | Figure 3.Average score of each questionnaire contents and question in LVQOL patients and normal control group. All the score of low vision group was lower than normal control group. And score of 16 th question (Insight about eye condition) was higher than score of other questions. |
Table 1.
Demographic characteristics, Best corrected visual acuity and LVQOL score of Low vision patients and normal control
Table 2.
Questionnaire trial number, reply, reply percentage and LVQOL score 51 patients among 200 patients in low vision group replied our questionnaire. 50 patients among 60 patients in control group replied. The average LVQOL score for patients with low vision (67.3±26.7) was significantly lower than the average score of those with normal vision (114±9.72) (p<0.05). Average score of group quested by telephone is 68.1±4.11, by mail 65.3±31.7 and there was no stastically significant difference (p=.741).
|
No. of patient |
Reply percentage | LVQOL score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Questionnaire | Reply | |||
| By telephone | 50 | 37 | 74% | 68.1±4.11 |
| By mail | 200 | 14 | 7% | 65.3±31.7 |
| Total | 250 | 51 | 20% | 67.3±26.7 |
| Normal control | 50 | 44 | 88% | 114±9.7 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download