Abstract
Background/Aims
Several previous studies suggest that eradication of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) leads to the disappearance of gastric hyperplastic polyps. However, little is known about the effect of H. pylori status and eradication on the recurrence of gastric polyps after endoscopic removal. Here, we investigated the recurrence of gastric polyps according to the final H. pylori status in patients who underwent endoscopic removal of gastric hyperplastic polyps.
Methods
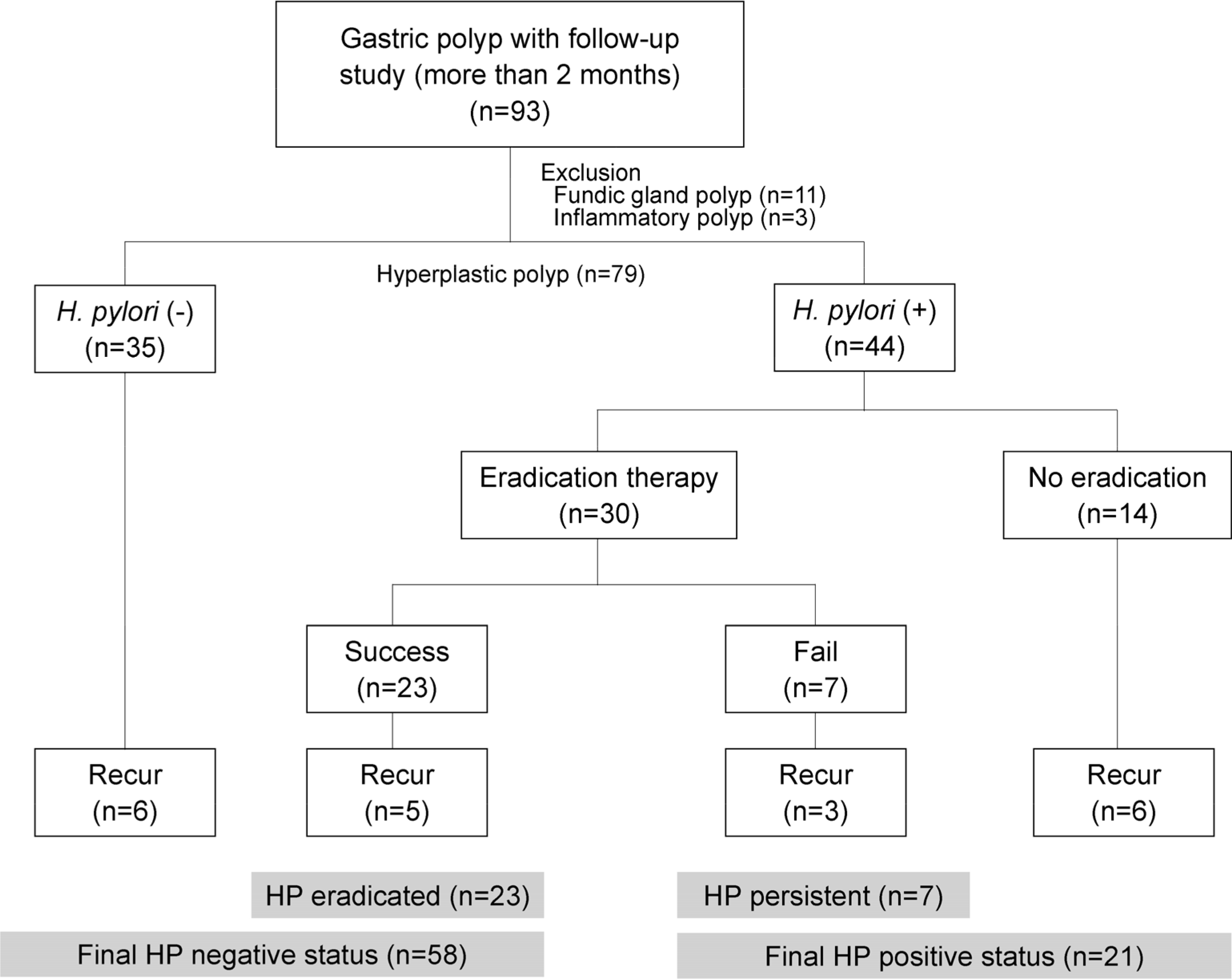
Between January 2011 and December 2016, patients who underwent endoscopic removal of gastric hyperplastic polyps and were followed-up for more than two months were enrolled. The success of H. pylori eradication was assessed by histology and rapid urease test or urea breath test, at least 4 weeks after the completion of eradication treatment. At follow-up, the recurrence of gastric polyp was evaluated via esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
Results
Seventy-nine patients were enrolled. During the mean follow-up period of 16.4 months, the recurrence rate of gastric polyp was 25.3%. Among those who received H. pylori eradication therapy, the H. pylori persistent group showed a higher recurrence of polyp than the H. pylori eradicated group; but there was no statistical significance (42.9% vs. 21.7%, p=0.269). Regarding the final H. pylori infection status, the recurrence rate of gastric polyps was significantly higher in the H. pylori positive group than in the H. pylori negative group (42.9% vs. 18.9%, p=0.031). In multivariate analysis, the final H. pylori infection status was a significant risk factor for gastric polyp recurrence after endoscopic removal.
Go to : 
References
1. Park DY, Lauwers GY. Gastric polyps: classification and management. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008; 132:633–640.

2. Goddard AF, Badreldin R, Pritchard DM, Walker MM, Warren B. British Society of Gastroenterology. The management of gastric polyps. Gut. 2010; 59:1270–1276.

3. Nam SY, Park BJ, Ryu KH, Nam JH. Effect of Helicobacter pylori infection and its eradication on the fate of gastric polyps. Eur J Gastroenterol. 2016; 28:449–454.

4. Kume K, Hirakoba M, Murata I, Yoshikawa I, Otsuki M. Disappearance of both MALT lymphoma and hyperplastic polyps in the stomach after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001; 96:2796–2797.

5. Saccá N. Hyperplastic gastric polyps and Helicobacter pylori. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2003; 38:904.
6. Ohkusa T, Miwa H, Hojo M, et al. Endoscopic, histological and serologic findings of gastric hyperplastic polyps after eradication of Helicobacter pylori: comparison between responder and non-responder cases. Digestion. 2003; 68:57–62.
7. Abraham SC, Nobukawa B, Giardiello FM, Hamilton SR, Wu TT. Sporadic fundic gland polyps: common gastric polyps arising through activating mutations in the β-catenin gene. Am J Pathol. 2001; 158:1005–1010.
8. Malfertheiner P, Megraud F, O'Morain CA, et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection-the Maastricht V/Florence consensus report. Gut. 2017; 66:6–30.
9. Davis GR. Gastric polyps. Sleisenger MH, Fordtran JS, editors. Gastrointestinal disease. 10th ed.Philadelphia: WB Saunders;2015. p. 763–764.
10. Carmack SW, Genta RM, Schuler CM, Saboorian MH. The current spectrum of gastric polyps: a 1-year national study of over 120,000 patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009; 104:1524–1532.

11. Kamiya T, Morishita T, Asakura H, Munakata Y, Miura S, Tsuchiya M. Histoclinical long-standing follow-up study of hyperplastic polyps of the stomach. Am J Gastroenterol. 1981; 75:275–281.
12. Fan NN, Yang J, Sun G, et al. Changes in the spectrum of gastric polyps in the Chinese population. World J Gastroenterol. 2015; 21:9758–9764.

13. Morais DJ, Yamanaka A, Zeitune JM, Andreollo NA. Gastric polyps: a retrospective analysis of 26,000 digestive endoscopies. Arq Gastroenterol. 2007; 44:14–17.

14. Yasunaga Y, Shinomura Y, Kanayama S, et al. Increased production of interleukin 1 beta and hepatocyte growth factor may contribute to foveolar hyperplasia in enlarged fold gastritis. Gut. 1996; 39:787–794.

15. Lipkin M, Enker WE, Winawer SJ. Tritiated-thymidine labeling of rectal epithelial cells in ‘non-prep'biopsies of individuals at increased risk for colonic neoplasia. Cancer Lett. 1987; 37:153–161.
16. Bechi P, Balzi M, Becciolini A, et al. Helicobacter pylori and cell proliferation of the gastric mucosa: possible implications for gastric carcinogenesis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996; 91:271–276.
17. Archimandritis A, Spiliadis C, Tzivras M, et al. Gastric epithelial polyps: a retrospective endoscopic study of 12974 symptomatic patients. Ital J Gastroenterol. 1996; 28:387–390.
18. Jalving M, Koornstra JJ, Wesseling J, Boezen H, DE Jong S, Kleibeuker JH. Increased risk of fundic gland polyps during long‐term proton pump inhibitor therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006; 24:1341–1348.

19. Oberhuber G, Stolte M. Gastric polyps: an update of their pathology and biological significance. Virchows Arch. 2000; 437:581–590.

20. Ahn JY, Son DH, Choi KD, et al. Neoplasms arising in large gastric hyperplastic polyps: endoscopic and pathologic features. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014; 80:1005–1013.e2.

Go to : 
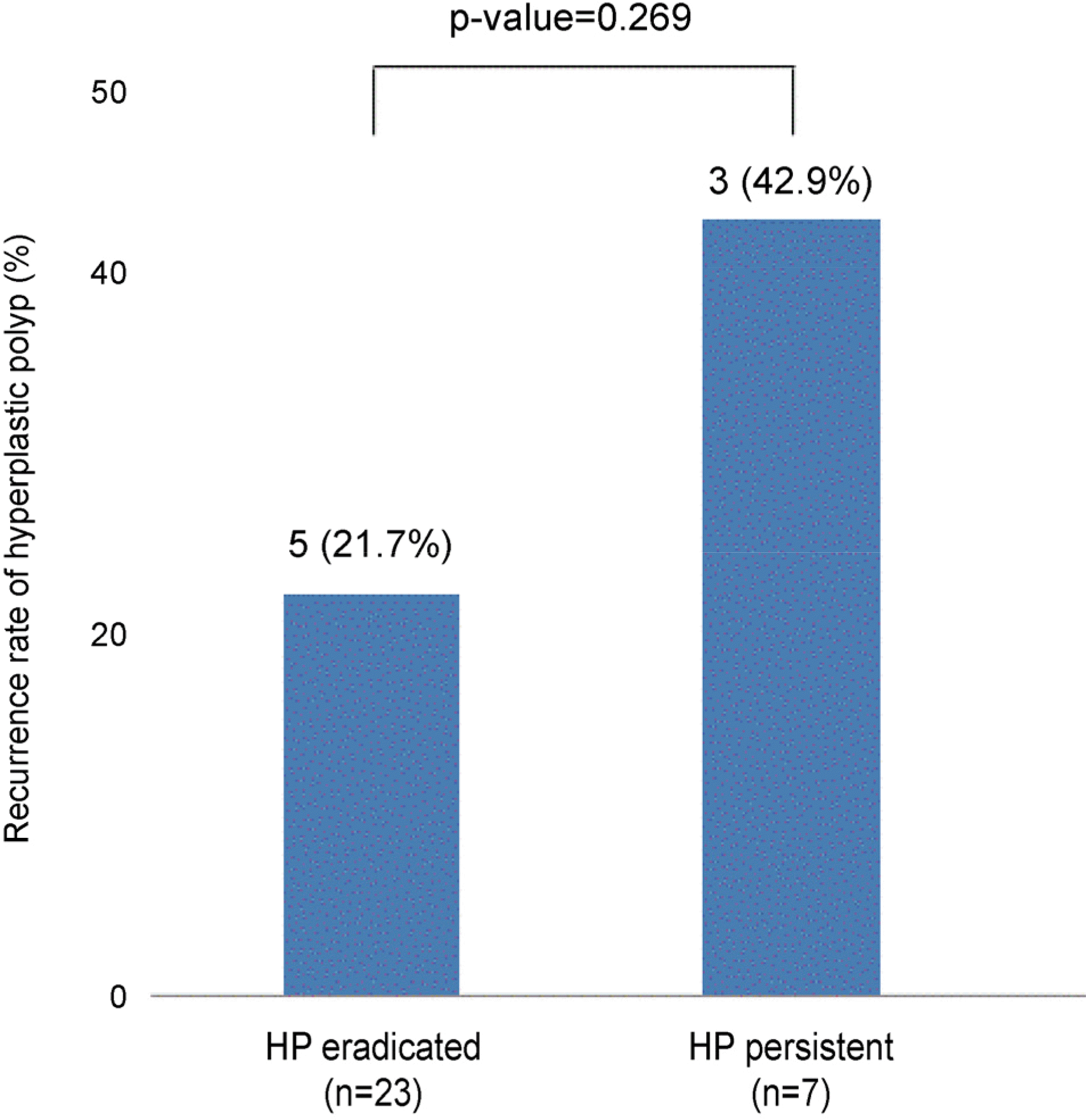 | Fig. 2.Comparison of gastric hyperplastic polyp recurrence according to HP eradication status (HP eradicated vs. HP persistent). HP, Helicobacter pylori. |
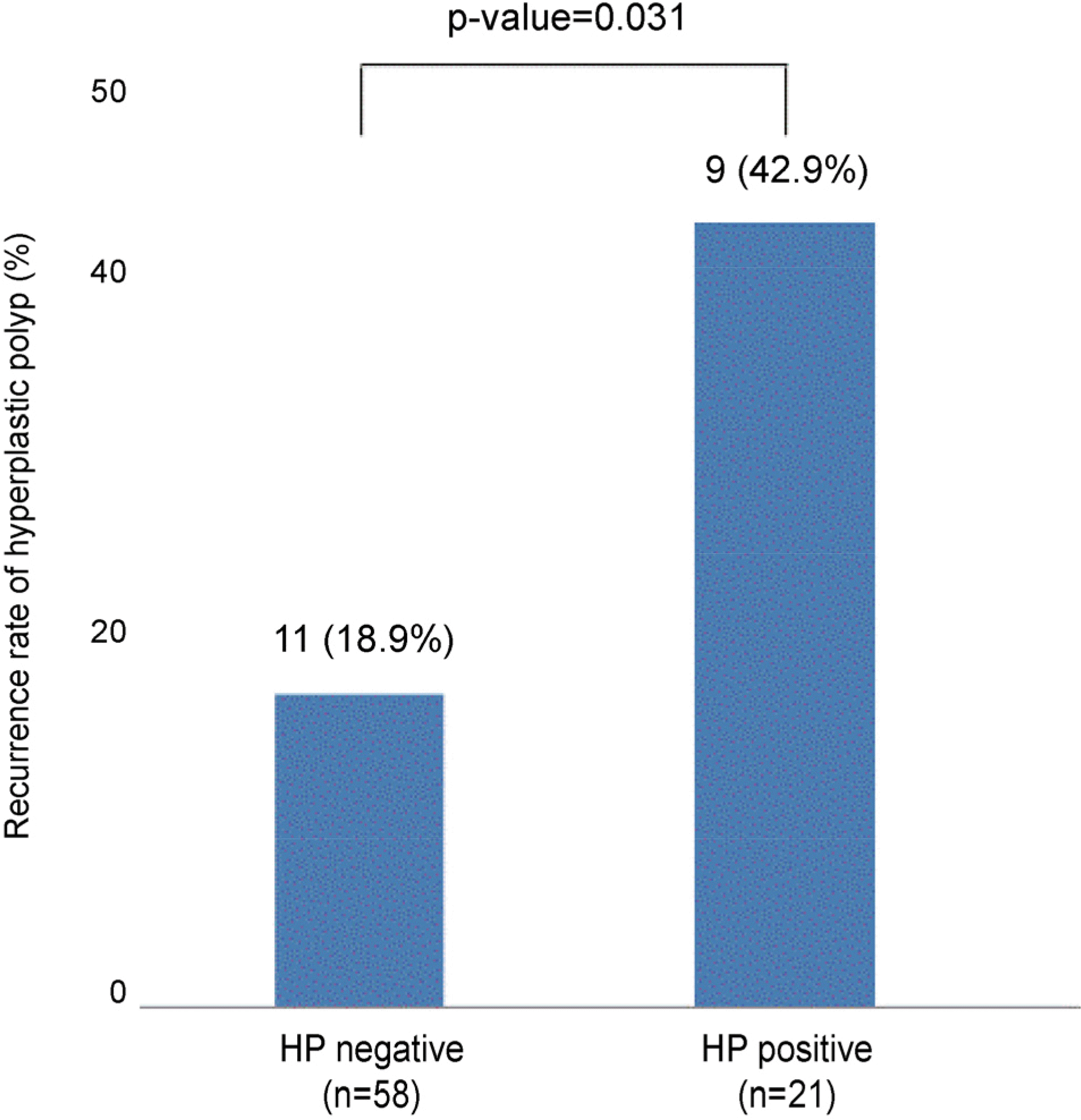 | Fig. 3.Comparison of gastric hyperplastic polyp recurrence according to final HP status (HP negative status vs. HP positive status). HP, Helicobacter pylori. |
Table 1.
Baseline Clinical Characteristics of Study Population according to H. pylori Infection
Table 2.
Characteristics of Gastric Hyperplastic Polyps
Table 3.
Risk Factors of Gastric Hyperplastic Polyp Recurrence (Univariate and Multivariate Logistic Regression Analysis)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download