Abstract
Gastric adenoma (dysplasia) is a precancerous lesion. Therefore, managements of gastric adenomas are important for preventing the development of gastric cancers and for detecting gastric cancers at earlier stages. The Vienna classification divides gastric adenomas into two categories: high-grade dysplasia and low-grade dysplasia. Generally, endoscopic resection is performed for adenoma with high-grade dysplasia due to the coexistence of carcinoma and the potential of progression to carcinomas. However, the treatments of adenoma with low-grade dysplasia remain controversial. Currently two treatment strategies for the low-grade type have been suggested; First is the ‘wait and see' strategy; Second is endoscopic treatment (e.g., endoscopic mucosal resection, endoscopic submucosal dissection, or argon plasma coagulation). In this review, we discuss the current optimal strategies for endoscopic management of gastric adenoma.
Go to : 
References
1. Kamangar F, Dores GM, Anderson WF. Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five continents: defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:2137–2150.

3. Lewin KJ. Nomenclature problems of gastrointestinal epithelial neoplasia. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998; 22:1043–1047.

4. Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Montgomery EA. Gastrointestinal and liver pathology. 2nd ed.Philadelphia: Saunders;2012.
5. Schlemper RJ, Kato Y, Stolte M. Review of histological classifications of gastrointestinal epithelial neoplasia: differences in diagnosis of early carcinomas between Japanese and Western pathologists. J Gastroenterol. 2001; 36:445–456.

6. Stolte M. The new Vienna classification of epithelial neoplasia of the gastrointestinal tract: advantages and disadvantages. Virchows Arch. 2003; 442:99–106.

7. Schlemper RJ, Riddell RH, Kato Y, et al. The Vienna classification of gastrointestinal epithelial neoplasia. Gut. 2000; 47:251–255.

8. Yamada H, Ikegami M, Shimoda T, Takagi N, Maruyama M. Longterm follow-up study of gastric adenoma/dysplasia. Endoscopy. 2004; 36:390–396.

9. Kokkola A, Haapiainen R, Laxén F, et al. Risk of gastric carcinoma in patients with mucosal dysplasia associated with atrophic gastritis: a follow up study. J Clin Pathol. 1996; 49:979–984.

10. Fertitta AM, Comin U, Terruzzi V, et al. Clinical significance of gastric dysplasia: a multicenter follow-up study. Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Pathology Study Group. Endoscopy. 1993; 25:265–268.
11. Di Gregorio C, Morandi P, Fante R, De Gaetani C. Gastric dysplasia. A follow-up study. Am J Gastroenterol. 1993; 88:1714–1719.
12. Rugge M, Farinati F, Di Mario F, Baffa R, Valiante F, Cardin F. Gastric epithelial dysplasia: a prospective multicenter follow-up study from the Interdisciplinary Group on Gastric Epithelial Dysplasia. Hum Pathol. 1991; 22:1002–1008.

13. Lansdown M, Quirke P, Dixon MF, Axon AT, Johnston D. High grade dysplasia of the gastric mucosa: a marker for gastric carcinoma. Gut. 1990; 31:977–983.

14. Saraga EP, Gardiol D, Costa J. Gastric dysplasia. A histological fol-low-up study. Am J Surg Pathol. 1987; 11:788–796.
16. Rugge M, Cassaro M, Di Mario F, et al. The long term outcome of gastric noninvasive neoplasia. Gut. 2003; 52:1111–1116.

17. Suzuki S, Gotoda T, Suzuki H, et al. Morphologic and histologic changes in gastric adenomas after helicobacter pylori eradication: a long-term prospective analysis. Helicobacter. 2015; 20:431–437.
18. Srivastava A, Lauwers GY. Gastric epithelial dysplasia: the Western perspective. Dig Liver Dis. 2008; 40:641–649.

19. Bearzi I, Brancorsini D, Santinelli A, Rezai B, Mannello B, Ranaldi R. Gastric dysplasia: a ten-year follow-up study. Pathol Res Pract. 1994; 190:61–68.
20. ASGE Standards of Practice Committee. Evans JA, Chandrasekhara V, et al. The role of endoscopy in the management of premalignant and malignant conditions of the stomach. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 82:1–8.

21. Goddard AF, Badreldin R, Pritchard DM, Walker MM, Warren B. British Society of Gastroenterology. The management of gastric polyps. Gut. 2010; 59:1270–1276.

22. Dinis-Ribeiro M, Areia M, de Vries AC, et al. Management of precancerous conditions and lesions in the stomach (MAPS): guideline from the European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE), European Helicobacter Study Group (EHSG), European Society of Pathology (ESP), and the Sociedade Portuguesa de Endoscopia Digestiva (SPED). Endoscopy. 2012; 44:74–94.
23. Zhao G, Xue M, Hu Y, Lai S, Chen S, Wang L. How commonly is the diagnosis of gastric low grade dysplasia upgraded following endoscopic resection? A metaanalysis. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0132699.

24. Kato M, Nishida T, Tsutsui S, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection as a treatment for gastric noninvasive neoplasia: a multicenter study by Osaka University ESD Study Group. J Gastroenterol. 2011; 46:325–331.

25. de Melo SW Jr, Cleveland P, Raimondo M, Wallace MB, Woodward T. Endoscopic mucosal resection with the grasp-and-snare technique through a double-channel endoscope in humans. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 73:349–352.

26. Yamamoto H, Kawata H, Sunada K, et al. Success rate of curative endoscopic mucosal resection with circumferential mucosal incision assisted by submucosal injection of sodium hyaluronate. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 56:507–512.

27. Suzuki Y, Hiraishi H, Kanke K, et al. Treatment of gastric tumors by endoscopic mucosal resection with a ligating device. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999; 49:192–199.

28. Inoue H, Endo M, Takeshita K, Yoshino K, Muraoka Y, Yoneshima H. A new simplified technique of endoscopic esophageal mucosal resection using a cap-fitted panendoscope (EMRC). Surg Endosc. 1992; 6:264–265.

29. Kim JW, Jang JY. Optimal management of biopsy-proven low-grade gastric dysplasia. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 7:396–402.

30. Oka S, Tanaka S, Kaneko I, et al. Advantage of endoscopic submucosal dissection compared with EMR for early gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 64:877–883.

31. Tanabe S, Koizumi W, Kokutou M, et al. Usefulness of endoscopic aspiration mucosectomy as compared with strip biopsy for the treatment of gastric mucosal cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999; 50:819–822.

32. Kojima T, Parra-Blanco A, Takahashi H, Fujita R. Outcome of endoscopic mucosal resection for early gastric cancer: review of the Japanese literature. Gastrointest Endosc. 1998; 48:550–554. discussion 554–555.

33. Inoue H, Takeshita K, Hori H, Muraoka Y, Yoneshima H, Endo M. Endoscopic mucosal resection with a cap-fitted panendoscope for esophagus, stomach, and colon mucosal lesions. Gastrointest Endosc. 1993; 39:58–62.

34. Szalóki T, Tóth V, Tiszlavicz L, Czakó L. Flat gastric polyps: results of forceps biopsy, endoscopic mucosal resection, and long-term follow-up. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2006; 41:1105–1109.

35. Lim H, Jung HY, Park YS, et al. Discrepancy between endoscopic forceps biopsy and endoscopic resection in gastric epithelial neoplasia. Surg Endosc. 2014; 28:1256–1262.

36. Won CS, Cho MY, Kim HS, et al. Upgrade of lesions initially diagnosed as low-grade gastric dysplasia upon forceps biopsy following endoscopic resection. Gut Liver. 2011; 5:187–193.

37. Cho SJ, Choi IJ, Kim CG, et al. Risk of high-grade dysplasia or carcinoma in gastric biopsy-proven low-grade dysplasia: an analysis using the Vienna classification. Endoscopy. 2011; 43:465–471.

38. Park DI, Rhee PL, Kim JE, et al. Risk factors suggesting malignant transformation of gastric adenoma: univariate and multivariate analysis. Endoscopy. 2001; 33:501–506.

39. Park YM, Cho E, Kang HY, Kim JM. The effectiveness and safety of endoscopic submucosal dissection compared with endoscopic mucosal resection for early gastric cancer: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Surg Endosc. 2011; 25:2666–2677.

40. Cao Y, Liao C, Tan A, Gao Y, Mo Z, Gao F. Meta-analysis of endoscopic submucosal dissection versus endoscopic mucosal resection for tumors of the gastrointestinal tract. Endoscopy. 2009; 41:751–757.

41. Oda I, Odagaki T, Suzuki H, Nonaka S, Yoshinaga S. Learning curve for endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer based on trainee experience. Dig Endosc. 2012; 24(Suppl 1):129–132.

42. Sakamoto T, Saito Y, Fukunaga S, Nakajima T, Matsuda T. Learning curve associated with colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection for endoscopists experienced in gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection. Dis Colon Rectum. 2011; 54:1307–1312.

43. Grund KE. Argon plasma coagulation (APC): ballyhoo or breakthrough? Endoscopy. 1997; 29:196–198.

44. Grund KE, Storek D, Farin G. Endoscopic argon plasma coagulation (APC) first clinical experiences in flexible endoscopy. Endosc Surg Allied Technol. 1994; 2:42–46.
45. Lee DH, Bae WK, Kim JW, et al. The usefulness of argon plasma coagulation compared with endoscopic submucosal dissection to treat gastric adenoma. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2017; 69:283–290.

46. Jung SJ, Cho SJ, Choi IJ, et al. Argon plasma coagulation is safe and effective for treating smaller gastric lesions with low-grade dysplasia: a comparison with endoscopic submucosal dissection. Surg Endosc. 2013; 27:1211–1218.

47. Ahn JY, Choi KD, Na HK, et al. Clinical outcomes of argon plasma coagulation for the treatment of gastric neoplasm. Surg Endosc. 2013; 27:3146–3152.

48. Lee KM, Kim YB, Sin SJ, et al. Argon plasma coagulation with submucosal saline injection for gastric adenoma on outpatient basis. Dig Dis Sci. 2009; 54:2623–2628.

49. Gotoda T, Saito D, Kondo H, et al. Endoscopic and histological reversibility of gastric adenoma after eradication of helicobacter pylori. J Gastroenterol. 1999; 34(Suppl 11):91–96.
50. Rugge M, Nitti D, Farinati F, di Mario F, Genta RM. Non-invasive neoplasia of the stomach. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005; 17:1191–1196.

51. Weinstein WM, Goldstein NS. Gastric dysplasia and its management. Gastroenterology. 1994; 107:1543–1545.

52. Kim MK, Jang JY, Kim JW, et al. Is lesion size an independent indication for endoscopic resection of biopsy-proven low-grade gastric dysplasia? Dig Dis Sci. 2014; 59:428–435.

53. Shin SH, Jung DH, Kim JH, et al. Helicobacter pylori eradication prevents metachronous gastric neoplasms after endoscopic resection of gastric dysplasia. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0143257.

54. Bae SE, Jung HY, Kang J, et al. Effect of helicobacter pylori eradication on metachronous recurrence after endoscopic resection of gastric neoplasm. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014; 109:60–67.

55. Chon I, Choi C, Shin CM, Park YS, Kim N, Lee DH. Effect of helicobacter pylori eradication on subsequent dysplasia development after endoscopic resection of gastric dysplasia. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2013; 61:307–312.
56. Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma:3rd English edition. Gastric Cancer. 2011; 14:101–112.
57. Yakirevich E, Resnick MB. Pathology of gastric cancer and its precursor lesions. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2013; 42:261–284.

58. Kim SY, Sung JK, Moon HS, et al. Is endoscopic mucosal resection a sufficient treatment for low-grade gastric epithelial dysplasia? Gut Liver. 2012; 6:446–451.

Go to : 
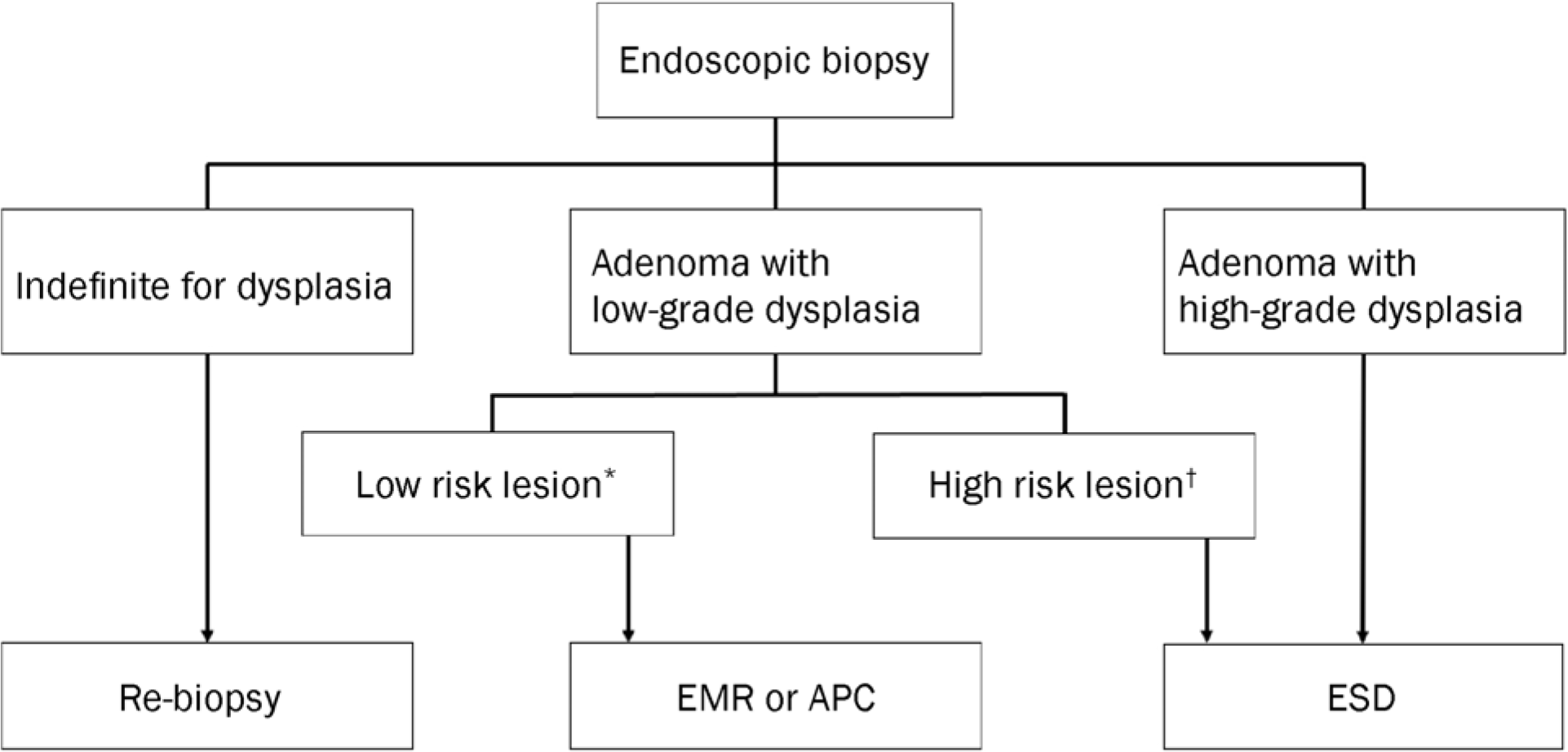 | Fig. 1.Proposed treatment strategy algorithm for gastric adenoma diagnosed by endoscopic biopsy; * low risk lesion: size<2 cm, grossly flat type, whitish color with smooth surface; † high risk lesion: size≥2 cm, grossly depressed type, surface erythema or unevenness, presence of spontaneous bleeding. EMR, endoscopic mucosal resection; APC, argon plasma coagulation; ESD, endoscopic submucosal dissection. |
Table 1.
Classification Systems of Gastric Epithelial Neoplasia
Table 2.
Treatment Outcomes and Complications of Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Gastric Adenoma
Table 3.
Treatment Outcomes and Complications of Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Gastric Adenoma
Table 4.
Treatment Outcomes and Complications of Argon Plasma Coagulation for Gastric Adenoma




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download