Abstract
Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is a common treatment modality to locally manage hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver abscess and bile duct injury are common complications of TACE. However, hepatobronchial fistula is a rare complication. Herein, we report a case of lung abscess due to hepatobronchial fistula after TACE. A 67-year-old man, who had underwent TACE 6 months ago, presented cough and bile-colored sputum. He was diagnosed with lung abscess and hepatobronchial fistula. We performed endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; however, there was no improvement in his symptoms. Thereafter, partial hepatectomy and repair of fistula were successively conducted.
Figures and Tables
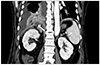
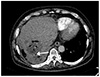 | Fig. 1Contrast-enhanced chest computed tomography at admission day. Hepatic abscess and lung abscess are shown in this image. The arrow indicates fistula between lung abscess and liver abscess. |
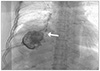 | Fig. 2Cholangiography via hepatic abscess drainage catheter. The arrow indicates contrast dye leakage from hepatic abscess to bronchus. |
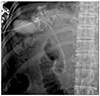 | Fig. 3Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) image. Endoscopic retrograde bile drainage was inserted via ERCP to treat hepatobronchial fistula by decompressing biliary pressure. |
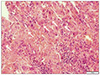
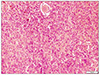 | Fig. 4Microscopic findings of the resected specimen (H&E, ×200). Postoperative pathology shows acute inflammation (neutrophil dominant) and necrosis. |
References
1. The Korean liver cancer study group, National cancer center. 2014 KLCSG-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Seoul (KR): 2014. 06. 14. updated 2014 Jun 14. cited Year 2015 Nov 24. Available from: http://www.klcsg.or.kr/html/sub03_02.asp.
2. Paye F, Farges O, Dahmane M, Vilgrain V, Flejou JF, Belghiti J. Cytolysis following chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Surg. 1999; 86:176–180.
3. Chung JW, Park JH, Han JK, et al. Hepatic tumors: predisposing factors for complications of transcatheter oily chemoembolization. Radiology. 1996; 198:33–40.
4. Kim HK, Chung YH, Song BC, et al. Ischemic bile duct injury as a serious complication after transarterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2001; 32:423–427.
5. Marelli L, Stigliano R, Triantos C, et al. Transarterial therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: which technique is more effective? A systematic review of cohort and randomized studies. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2007; 30:6–25.
6. Song SY, Chung JW, Han JK, et al. Liver abscess after transcatheter oily chemoembolization for hepatic tumors: incidence, predisposing factors, and clinical outcome. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001; 12:313–320.
7. Zhao H, Wang HQ, Fan QQ, Chen XX, Lou JY. Rare pulmonary and cerebral complications after transarterial chemoembolisation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a case report. World J Gastroenterol. 2008; 14:6425–6427.
8. Kontoravdis N, Panagiotopoulos N, Lawrence D. The challenging management of hepatopulmonary fistulas. J Thorac Dis. 2014; 6:1336–1339.
9. Liao GQ, Wang H, Zhu GY, Zhu KB, Lv FX, Tai S. Management of acquired bronchobiliary fistula: a systematic literature review of 68 cases published in 30 years. World J Gastroenterol. 2011; 17:3842–3849.
10. Gulamhussein MA, Patrini D, Pararajasingham J, et al. Hepatopulmonary fistula: a life threatening complication of hydatid disease. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2015; 10:103.
11. Korkmaz M, Bozkaya H, Çınar C, et al. Liver abscess following radioembolization with yttrium-90 microspheres. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2014; 126:785–788.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download