Abstract
The hematogenous spreading of an infectious pathogen via the portal vein from a mucosal injury in the gastrointestinal tract has been considered as one of the pathologic mechanisms of pyogenic liver abscess. Several studies have presented the association between colorectal cancer and pyogenic liver abscess. However, the cases of stomach cancer concomitant with pyogenic liver abscess have rarely been reported in the world. Herein, we present a case of advanced gastric cancer concomitant with pyogenic liver abscess in a patient who previously underwent subtotal gastrectomy due to peptic ulcer perforation.
Go to : 
References
1. Jeong SW, Jang JY, Lee TH, et al. Cryptogenic pyogenic liver abscess as the herald of colon cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 27:248–255.

2. Cho AR, Lee TH, Park MJ, et al. Septic shock in pyogenic liver abscess: Clinical considerations. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2016; 67:245–252.

3. Choi CS, Seo GS, Cho EY, et al. Comparison of pyogenic liver abscesses based on the origin of infection. Korean J Med. 2008; 75:60–67.
4. Knowles R, Rinaldo JA. Pyogenic liver abscess probably secondary to sigmoid diverticulitis: report of two cases. Gastroenterology. 1960; 38:262–266.
5. Heo NY, Park SH, Park J, et al. Pyogenic liver abscess with complicating intestinal tuberculosis. J Med Cases. 2012; 3:370–372.

6. Margalit M, Elinav H, Ilan Y, Shalit M. Liver abscess in inflammatory bowel disease: Report of two cases and review of the literature. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004; 19:1338–1342.

7. Lai HC, Lin CC, Cheng KS, et al. Increased incidence of gastrointestinal cancers among patients with pyogenic liver abscess: a population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology. 2014; 146:129–137.e1.

8. Nakatani M, Shibaji T, Hisanaga M, Segawa M. A case of pyogenic liver abscess caused by advanced gastric cancer invading hepatic capsule directly, and operated for in emergency. J Jpn Coll Surg. 2014; 39:119–124.

9. Kim DH, Lee CH, Jung HG. A case of subcapsular liver abscess secondary to perforating ulcer of gastric cancer. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2010; 56:109–112.

10. Youn GJ, Choi Y, Kim MJ, Lee JS, Ko UW, Joo YH. Liver abscess and septic complications associated with advanced gastric cancer. Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2015; 32:38–41.

11. Shigefuku R, Matsunaga K, Tamura T, et al. Detection of early gastric cancer facilitated by surveillance for a pyogenic liver abscess caused by streptococcus intermedius. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2016; 113:263–272.
12. Kim YH, Park KS. A clinical study of liver abscess. J Korean Surg Soc. 1980; 22:51–61.
13. Seo TJ, Park CH, Lee SH, et al. A clinical study on liver abscess for recent 15 years in gwangju-chonnam province. Korean J Med. 2005; 68:26–38.
Go to : 
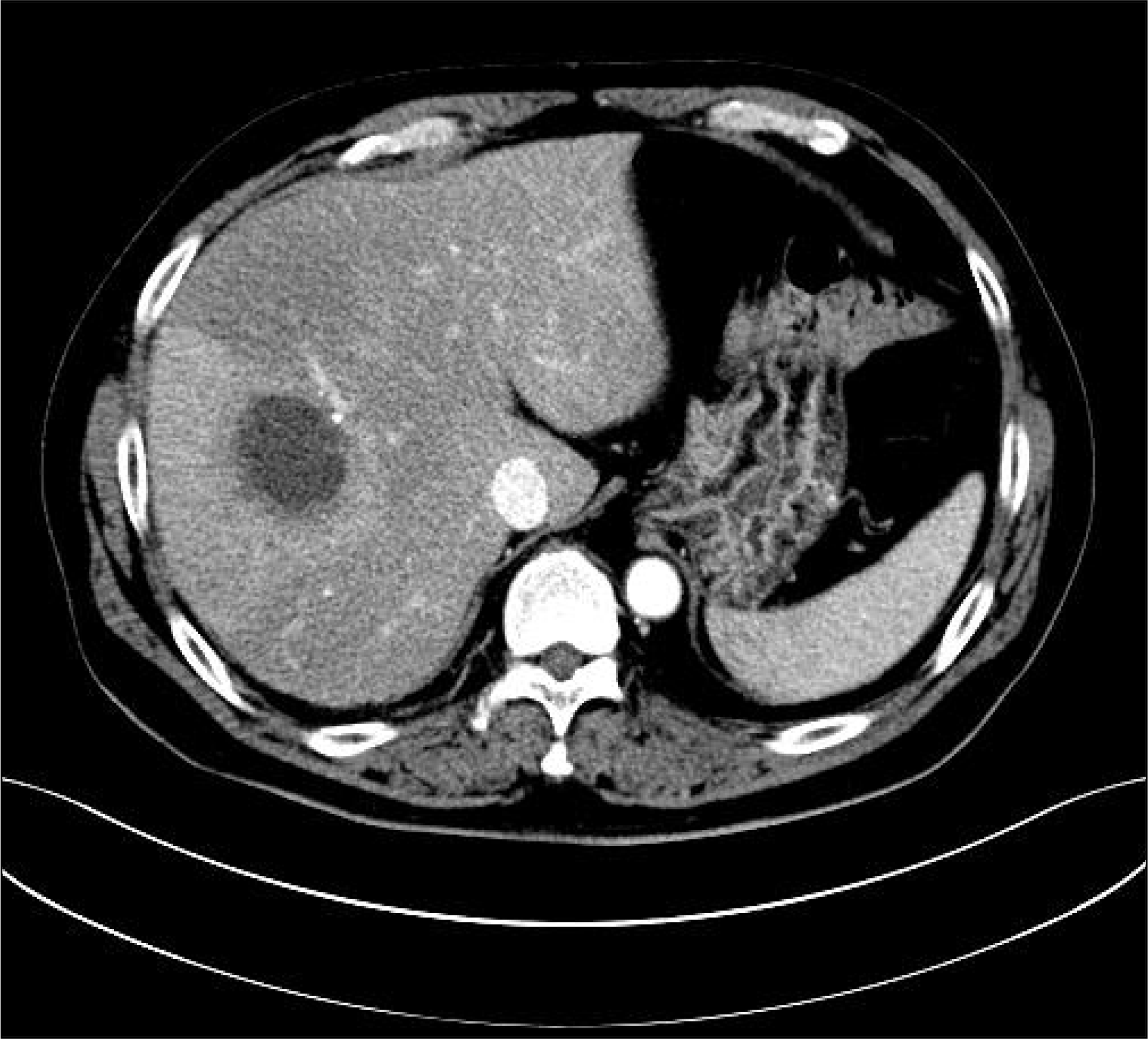 | Fig. 1.Initial abdominal CT showed a 4.1×4.8 cm sized low attenuated lesion with peripheral hyperemic change in the right lobe of the liver in the portal phase. CT, computed tomography. |
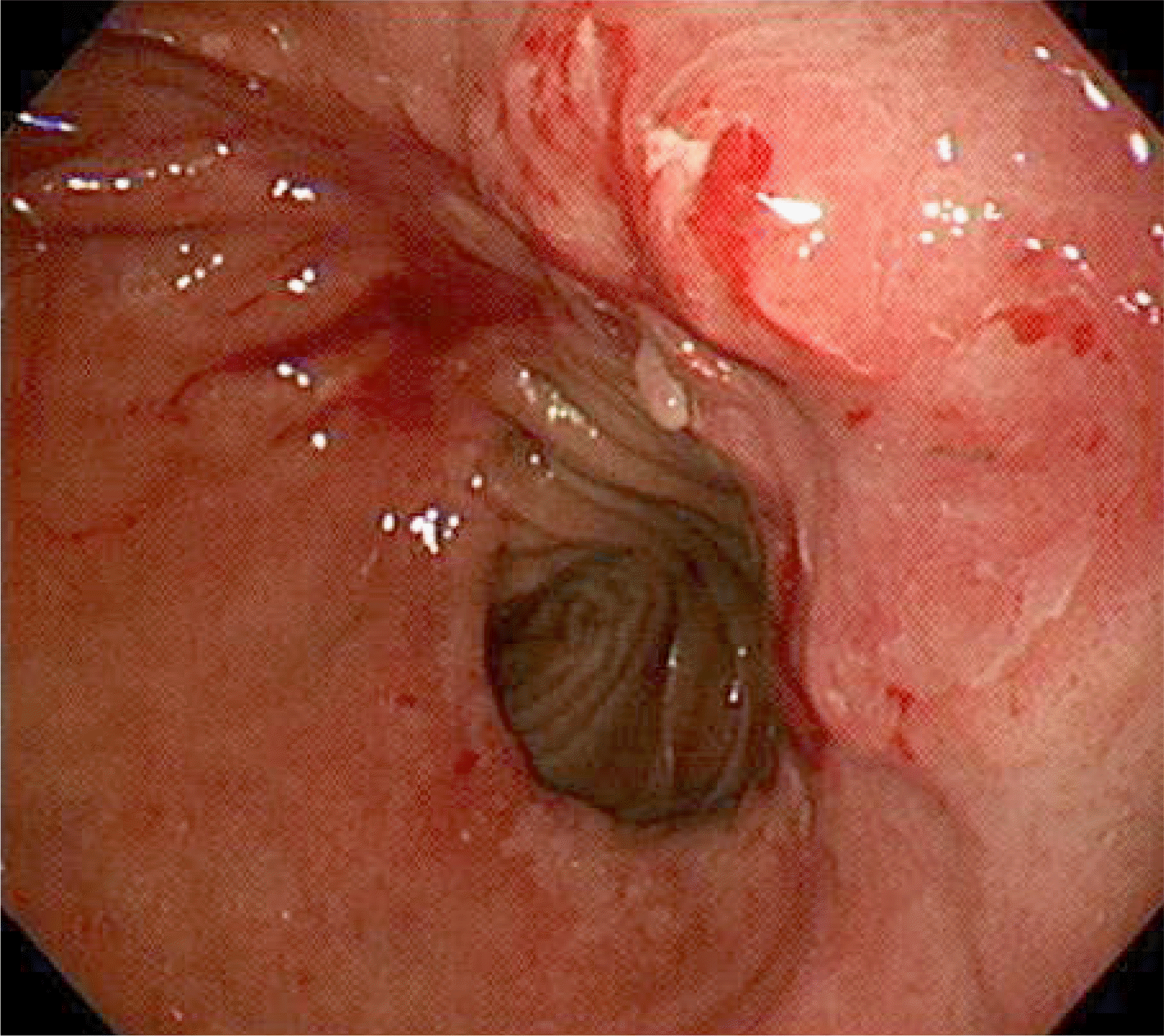 | Fig. 2.Esophagogastroduodenoscopy showed an ulcero-fungating mass on the anterior wall of the middle body of the remnant stomach. |
 | Fig. 3.(A) In the surgical pathology of the resected stomach, a luminal surface was replaced by the protruding tumor mass on the right side of the arrow (H&E stain, ×40). (B) On the magnfied view for the tumor mass, the poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma with distorted glandular formation (H&E stain, ×100). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download