Abstract
Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis (LMC) is rare metastatic form of gastric cancer. Most cases are diagnosed in the final stage after multiple distant metastasis. An 84-year-old woman was admitted with melena, headache and vomiting. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy showed an ulceroinfiltrating lesion at the stomach (Borrmann class III), and biopsy revealed a signet ring cell carcinoma. The abdominal-pelvic CT showed no evidence of metastasis. A sudden decrease of consciousness was noted, but the brain CT showed no active lesion while the brain MRI revealed enhancement of leptomeninges. A lumbar puncture was performed and the cerebrospinal fluid study revealed malignant neoplastic cells. With family consent, no further evaluation and treatment were administered and she died six weeks after the diagnosis of gastric cancer. We report an extremely rare case of a patient who initially presented with neurologic symptoms, and was diagnosed LMC from advanced gastric cancer without any evidence of metastasis in abdomen and pelvis.
Go to : 
References
1. Lee JL, Kang YK, Kim TW, et al. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis in gastric cancer. J Neurooncol. 2004; 66:167–174.

2. Lisenko Y, Kumar AJ, Yao J, Ajani J, Ho L. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis originating from gastric cancer: report of eight cases and review of the literature. Am J Clin Oncol. 2003; 26:165–170.
3. Kim NH, Kim JH, Chin HM, Jun KH. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis from gastric cancer: single institute retrospective analysis of 9 cases. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2014; 86:16–21.

4. Oh SY, Lee SJ, Lee J, et al. Gastric leptomeningeal carcinomatosis: multicenter retrospective analysis of 54 cases. World J Gastroenterol. 2009; 15:5086–5090.

5. Emoto S, Ishigami H, Yamaguchi H, Yamashita H, Kaisaki S, Kitayama J. Frequent development of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis in patients with peritoneal dissemination of gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2011; 14:390–395.

6. Kim KW, Kim SM, Kim JS. Clinical features and prognosis of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1989; 7:210–217.
7. Lee HG, Lee B, Kim SM, Suh BJ, Yu HJ. A case of gastric adenocarcinoma presenting as meningeal carcinomatosis. Korean J Intern Med. 2007; 22:304–307.

8. Guo JW, Zhang XT, Chen XS, et al. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis as the initial manifestation of gastric adenocarcinoma: a case report. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:2120–2126.

9. Tomita H, Yasui H, Boku N, et al. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis associated with gastric cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 2012; 17:361–366.

10. Grove A. Meningeal carcinomatosis from a clinically undiagnosed early gastric cancer. Pathol Res Pract. 1991; 187:341–345.

11. Park KK, Yang SI, Seo KW, Kim YO, Yoon KY. A case of metastatic leptomeningeal carcinomatosis from early gastric carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol. 2012; 10:74.

12. Yamada T, Furukawa K, Yokoi K, Ohaki Y, Okada S, Tajiri T. Case of meningeal carcinomatosis with gastric cancer which manifested meningeal signs as the initial symptom; the palliative benefit of radiotherapy. J Nippon Med Sch. 2008; 75:216–220.
13. Deeb LS, Yamout BI, Shamseddine AI, Shabb NS, Uthman SM. Meningeal carcinomatosis as the presenting manifestation of gastric adenocarcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997; 92:329331.
14. Rakusic Z, Misir Krpan A, Stupin Polancec D, Jakovcevic A, Bisof V. Sudden bilateral hearing loss in gastric cancer as the only symptom of disease. Onco Targets Ther. 2015; 8:1285–1289.

15. Kawasaki A, Suzuki K, Takekawa H, et al. Co-occurrence of multiple cerebral infarctions due to hypercoagulability associated with malignancy and meningeal carcinomatosis as the initial manifestation of gastric cancer. BMC Neurol. 2014; 14:160.

16. Straathof CS, de Bruin HG, Dippel DW, Vecht CJ. The diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging and cerebrospinal fluid cytology in leptomeningeal metastasis. J Neurol. 1999; 246:810–814.

Go to : 
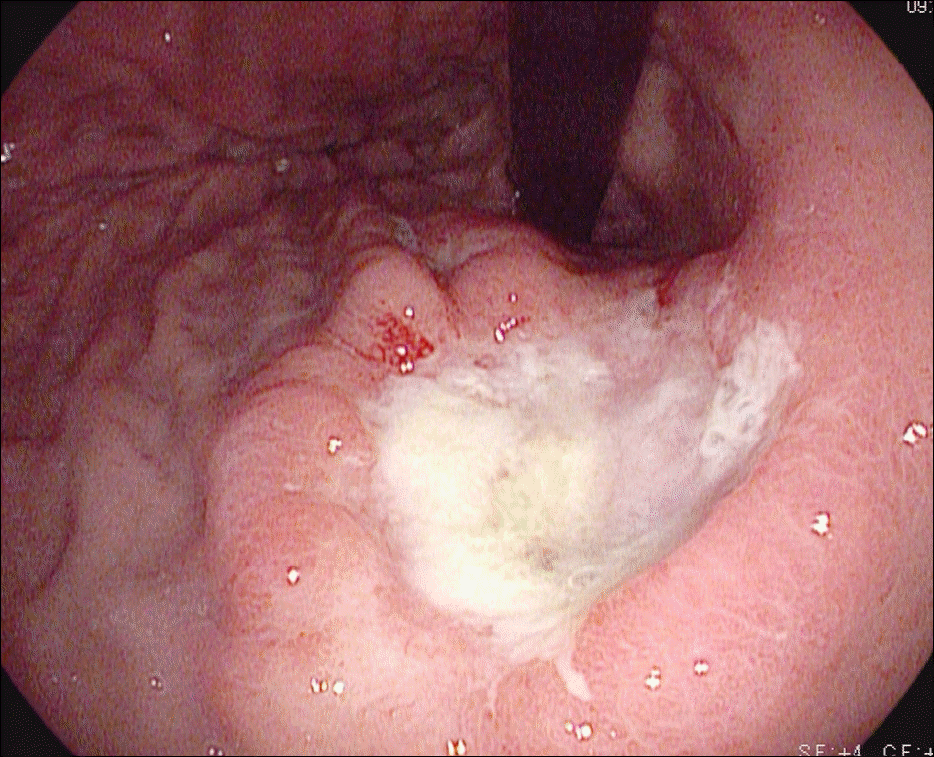 | Fig. 1.Endoscopic finding. Endoscopy shows a 3 cm ulceroinfiltrative lesion with irregular base, nodular elevated margin, and abnormalities of surrounding folds (Borrmann class III) at the posterior wall of the upper body. |
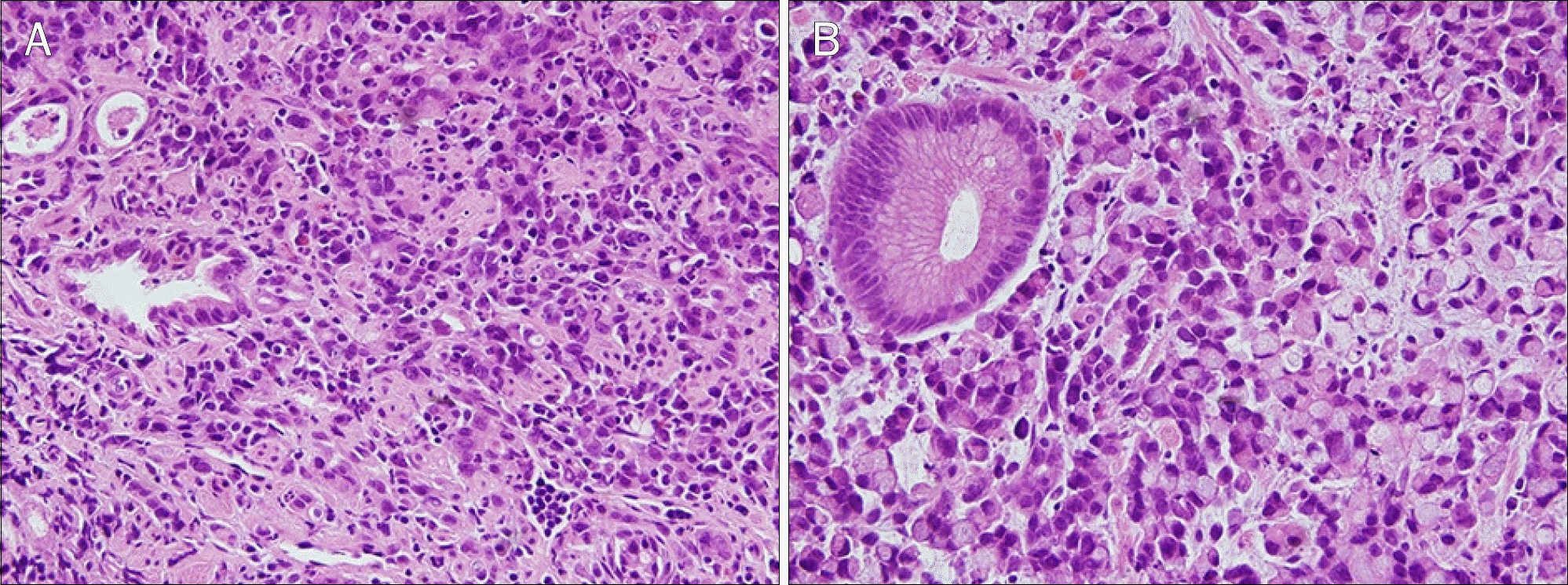 | Fig. 2.Pathologic findings (H&E). (A) The biopsy of stomach shows cellular infiltration with poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma, bizarre/ pleomorphic cells and few eosinophilic cells (×100). (B) Signet ring cells, characterized by a central optical clearing and globoid droplet of cytoplasmic mucin with an eccentrically placed nucleus, are observed (×400). |
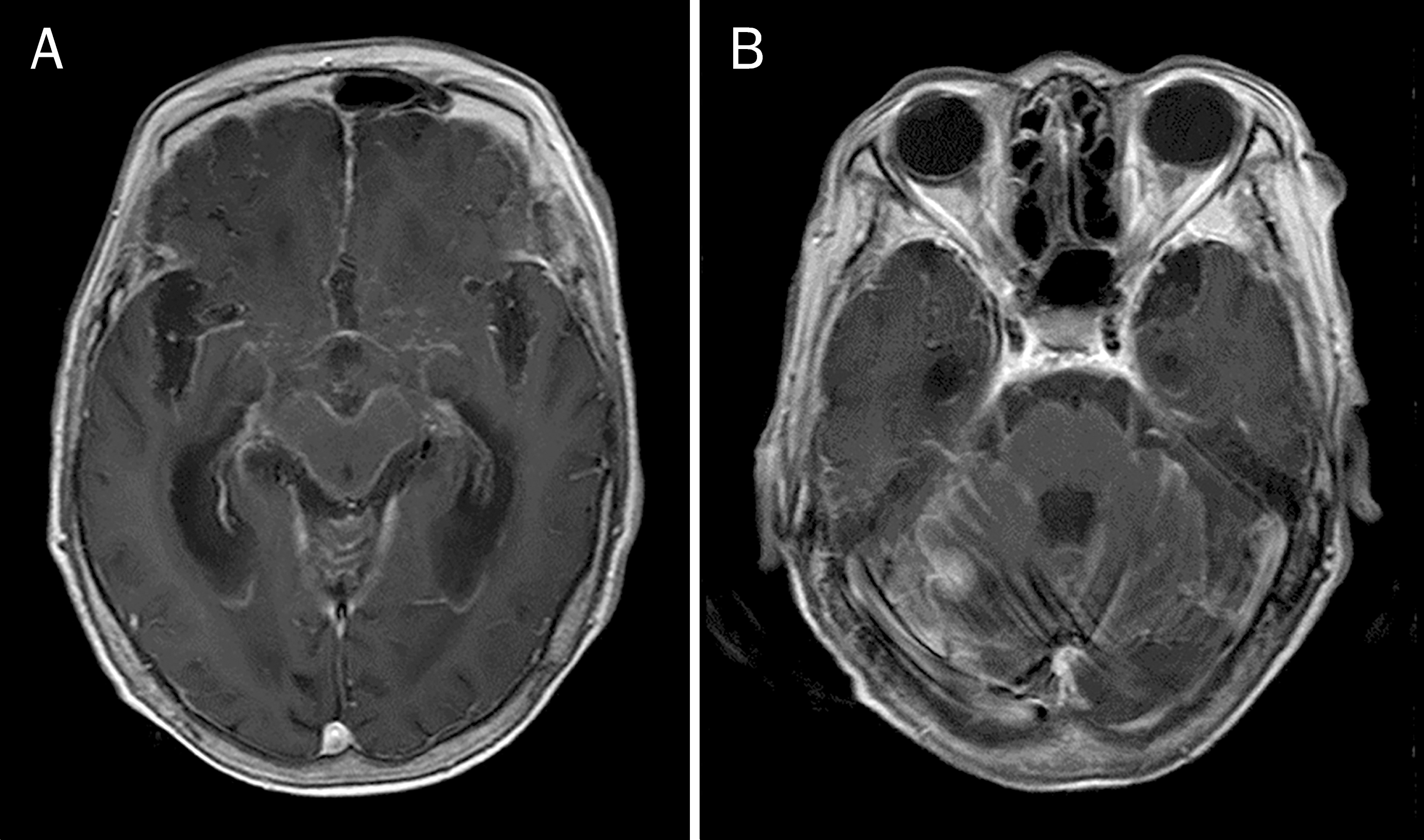 | Fig. 3.MRI findings. (A) Brain MRI with gadolinium-enhanced, T1-weighted axial image shows multifocal diffuse leptomeningeal enhancement at cerebrum and cerebellum. (B) Focal enhancing nodule of 1 cm is noted on right infratentorium. |
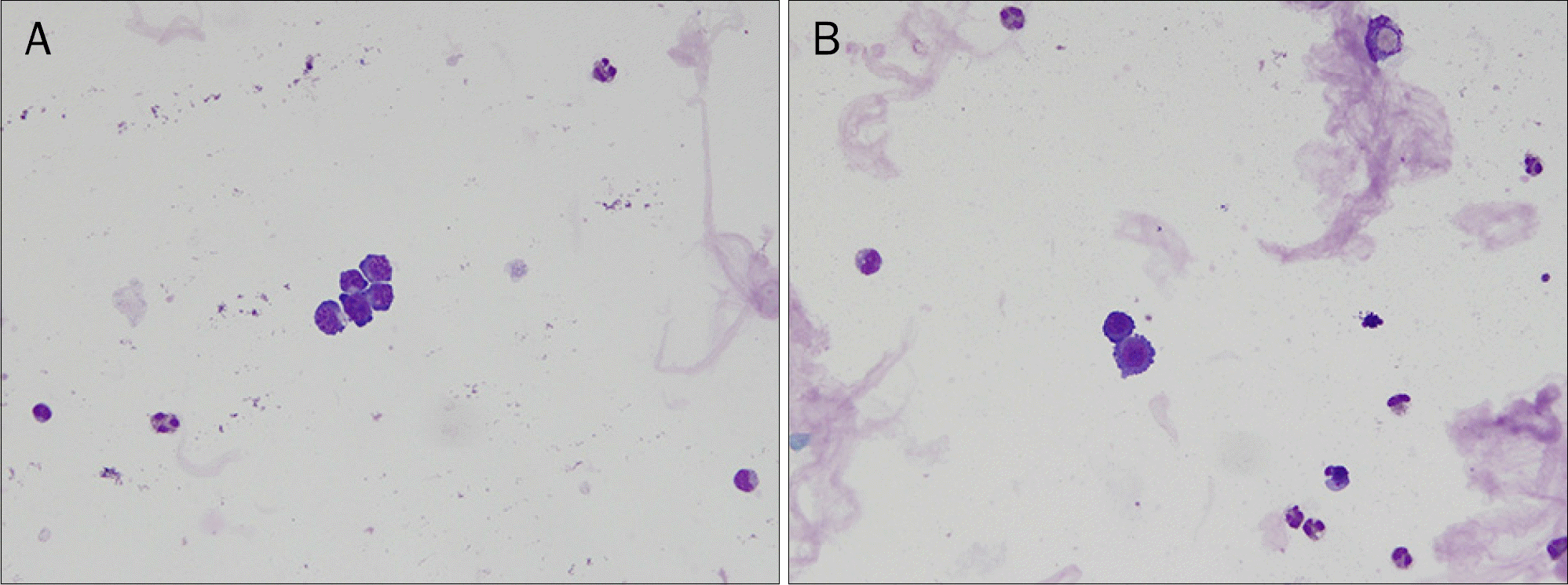 | Fig. 4.Cytological findings (Wright's stain). (A) The cerebrospinal fluid shows a few large malignant cells with high nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio, 2–3 nucleoli, and basophilic cytoplasms (×400). (B) Adenocarcinoma includes small vacuoles and protoplasmic projection (×400). |
Table 1.
Summary of Six Retrospective Studies of Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis in Gastric Cancer
Table 2.
Cases of Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis from Gastric Cancer without Involvement of Any Other Sites




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download