Abstract
Background/Aims
Although polypoid leiomyomas in the colon and rectum are rare, they are increasingly detected during colonoscopy. The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and clinical outcomes of endoscopic removal for colorectal polypoid leiomyoma.
Methods
Data were retrospectively collected from 22 patients with polypoid leiomyoma arising from the muscularis mucosae in the colon and rectum who underwent endoscopic removal at single referral gastrointestinal endoscopy unit. Colonoscopic findings, endoscopic removal, success rates, complication rates (bleeding or perforation), pathologic characteristics, and recurrence rates were investigated.
Results
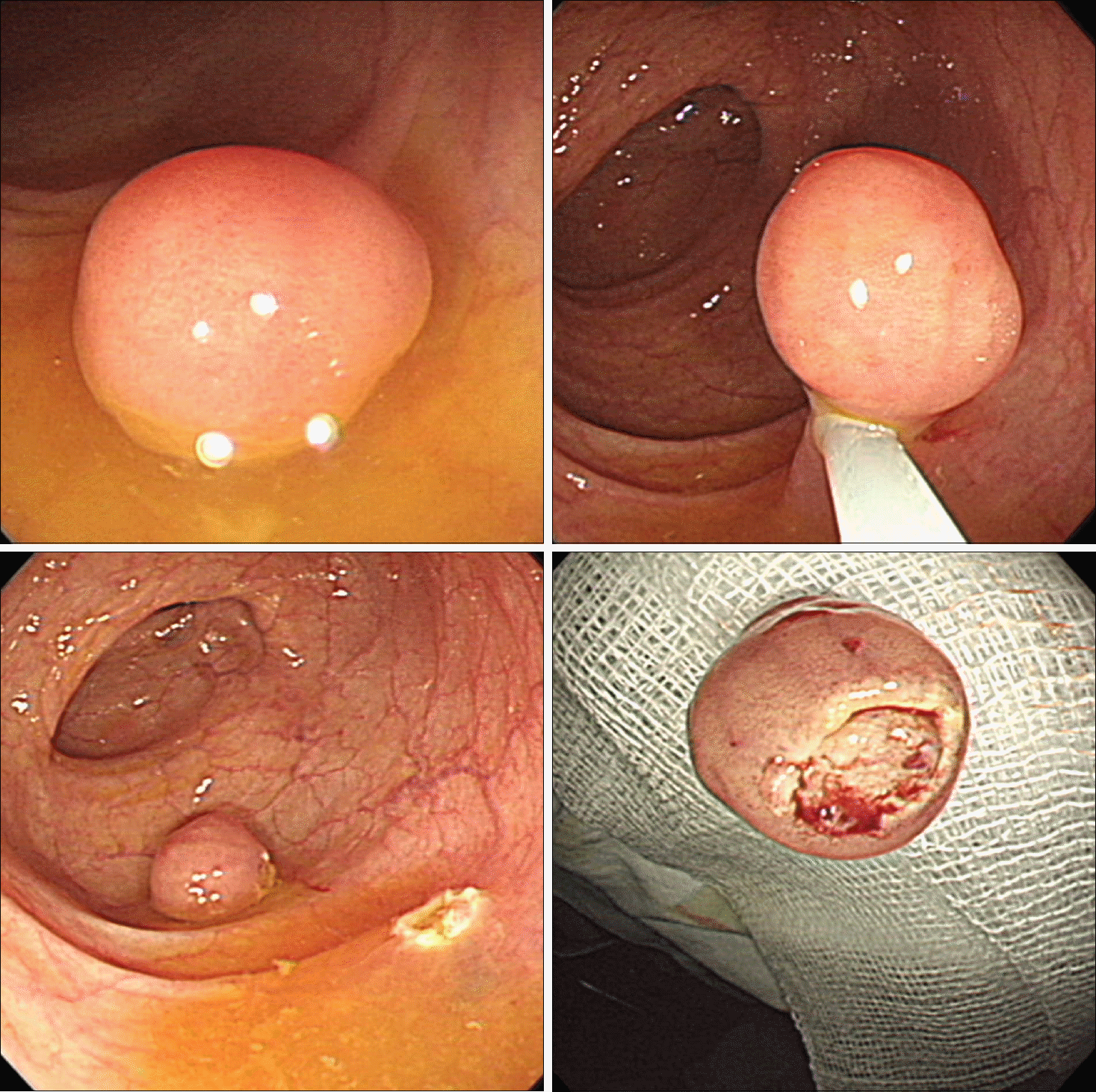
Most polypoid leiomyomas were small asymptomatic lesions less than 1 cm. The tumors were located predominantly in the left colon. Ten leiomyomas were removed using cold biopsy forceps, and 12 were resected by conventional polypectomy or endoscopic mucosal resection. All tumors arose from or involved the muscularis mucosa. There were no complications, such as bleeding or perforation. No local remnant lesions were found in 19 patients who underwent at least one follow-up colonoscopy.
Conclusions
This case series represent cases of small colorectal polypoid leiomyoma that were safely removed endoscopically. An awareness of their endoscopic and clinic-pathological characteristics may provide safe treatment strategy for colonic leiomyomatous tumors of similar size in capable hands.
Go to : 
References
1. Miettinen M, Furlong M, Sarlomo-Rikala M, Burke A, Sobin LH, Lasota J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors, intramural leiomyomas, and leiomyosarcomas in the rectum and anus: a clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic study of 144 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2001; 25:1121–1133.
2. Björnsdóttir H, Björnsson J, Gudjónsson H. Leiomyomatous colonic polyp. Dig Dis Sci. 1993; 38:1945–1947.
3. David SS, Samuel JJ. Pedunculated extraluminal leiomyoma of the sigmoid colon. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1996; 11:299–300.

4. Kadakia SC, Kadakia AS, Seargent K. Endoscopic removal of colonic leiomyoma. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1992; 15:59–62.

5. Chow WH, Kwan WK, Ng WF. Endoscopic removal of leiomyoma of the colon. Hong Kong Med J. 1997; 3:325–327.
6. Jovanovic I, Cvejic T, Popović D, Micev M. Endoscopic removal of pedunculated leiomyoma of the sigmoid colon (case report and literature review of dignostic and treatment options). Acta Chir Iugosl. 2006; 53:87–89.

7. Hirasaki S, Suwaki K, Tada S, Goji T. Pedunculated leiomyomatous polyp (pedunculated leiomyoma) of the transverse colon. Intern Med. 2010; 49:2519–2520.

8. Kemp CD, Arnold CA, Torbenson MS, Stein EM. An unusual polyp: a pedunculated leiomyoma of the sigmoid colon. Endoscopy. 2011; 43(Suppl 2 UCTN):E306–E307.

10. Urgesi R, Pastorelli A, Zampaletta C, et al. Obscure-occult bleeding: resolution of unexplained chronic sideropenic anaemia by colonoscopic removal of a colonic leiomyoma. BMJ Case Rep. 2011. DOI: doi:10.1136/bcr.11.2009.2455.

11. Ishiguro A, Uno Y, Ishiguro Y, Munakata A. Endoscopic removal of rectal leiomyoma: case report. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999; 50:433–436.

12. Lee IL, Tung SY, Lee KF, Chiu CT, Wu CS. Endoscopic resection of a large colonic leiomyoma. Chang Gung Med J. 2002; 25:39–44.
13. Friedman CJ, Cunningham WN, Sperling MH. Colonoscopic removal of a colonic leiomyoma: report of a case. Gastrointest Endosc. 1979; 25:107–108.
14. Agaimy A, Wünsch PH. True smooth muscle neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract: morphological spectrum and classification in a series of 85 cases from a single institute. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2007; 392:75–81.

15. Rubin BP, Fletcher JA, Fletcher CD. Molecular insights into the histogenesis and pathogenesis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Int J Surg Pathol. 2000; 8:5–10.

16. Miettinen M, Sarlomo-Rikala M, Sobin LH, Lasota J. Esophageal stromal tumors: a clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic study of 17 cases and comparison with esophageal leiomyomas and leiomyosarcomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000; 24:211–222.
17. Miettinen M, Sarlomo-Rikala M, Sobin LH. Mesenchymal tumors of muscularis mucosae of colon and rectum are benign leiomyomas that should be separated from gastrointestinal stromal tumors–a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of eighty-eight cases. Mod Pathol. 2001; 14:950–956.

18. Heidet L, Boye E, Cai Y, et al. Somatic deletion of the 5' ends of both the COL4A5 and COL4A6 genes in a sporadic leiomyoma of the esophagus. Am J Pathol. 1998; 152:673–678.
19. Ueki Y, Naito I, Oohashi T, et al. Topoisomerase I and II consensus sequences in a 17-kb deletion junction of the COL4A5 and COL4A6 genes and immunohistochemical analysis of esophageal leiomyomatosis associated with Alport syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1998; 62:253–261.

20. Waxman I, Saitoh Y, Raju GS, et al. High-frequency probe EUS-as-sisted endoscopic mucosal resection: a therapeutic strategy for submucosal tumors of the GI tract. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 55:44–49.

21. Kusminsky RE, Bailey W. Leiomyomas of the rectum and anal canal: report of six cases and review of the literature. Dis Colon Rectum. 1977; 20:580–599.
22. Mansoor S, Dolkar T, El-Fanek H. Polyps and polypoid lesions of the colon. Int J Surg Pathol. 2013; 21:215–223.

23. Matsukuma S, Takeo H, Ohara I, Sakai Y. Endoscopically resected colorectal leiomyomas often containing eosinophilic globules. Histopathology. 2004; 45:302–303.

Go to : 
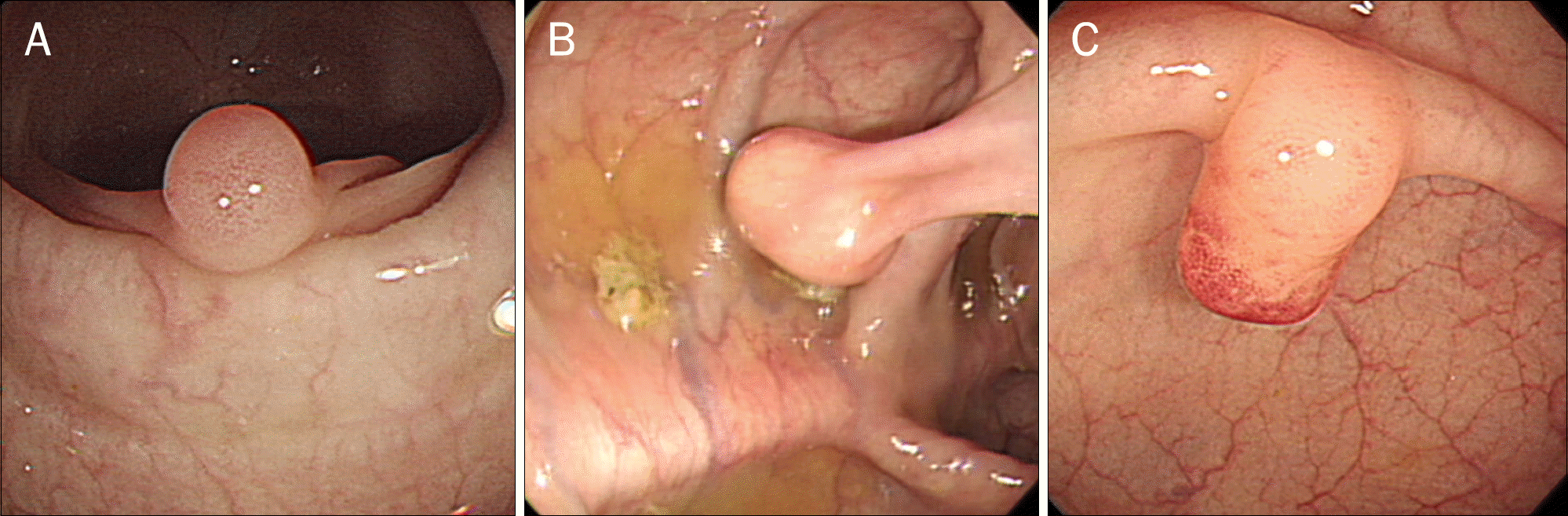 | Fig. 1.Colonoscopic findings of polypoid leiomyomas. A typical leiomyoma (approximately 5-mm) presenting as smooth round sessile polyp (A), a 13-mm leiomyoma presenting as pedunculated polyp (B), and a 7-mm leiomyoma resembling a hyperplastic polyp (C). |
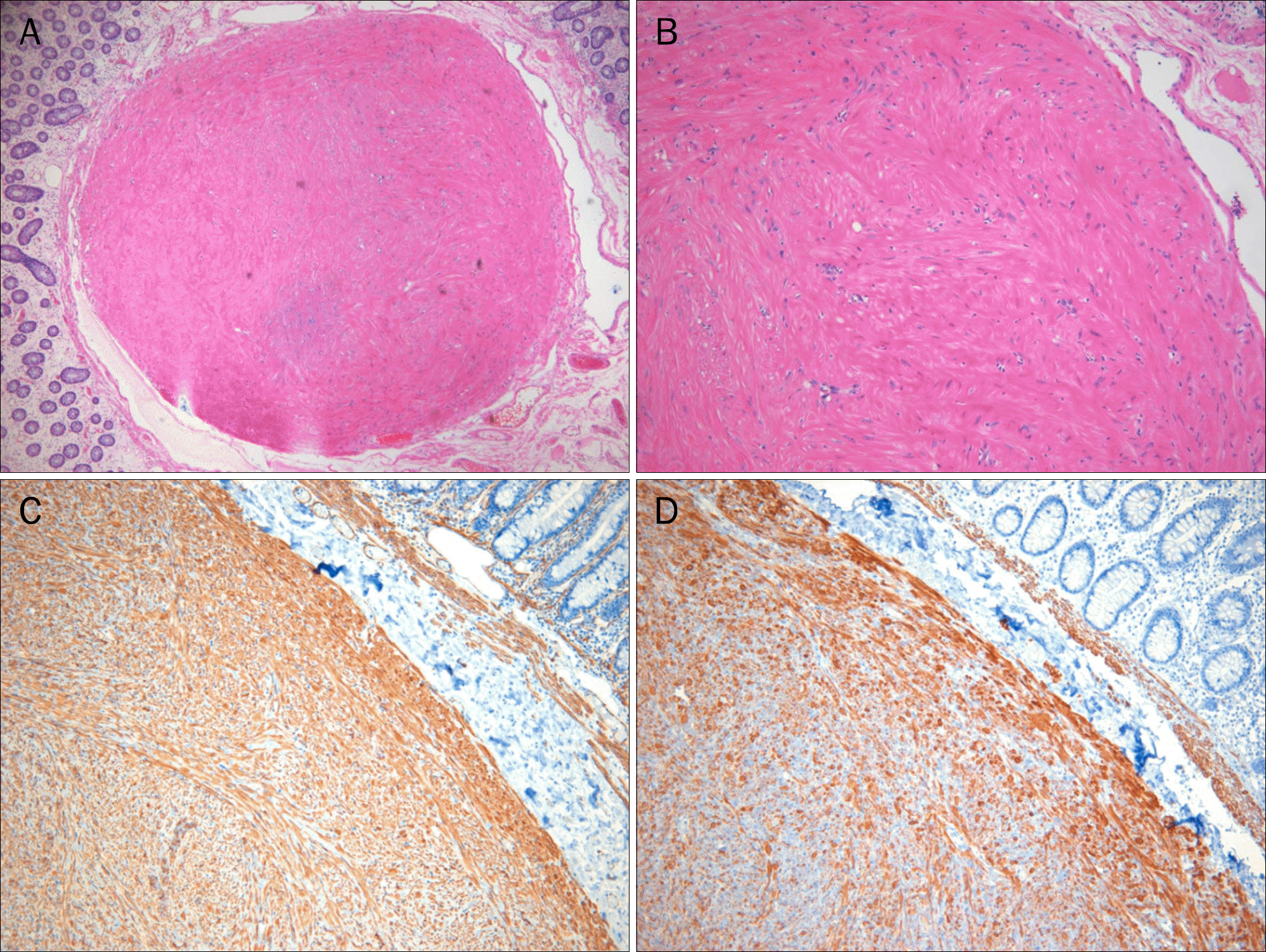 | Fig. 3.Histologic findings (H&E) showing well-circumscribed nodule arising from the muscularis mucosae (A, ×40) composed of well-differentiated smooth muscle cells (B, ×100). On immunohistochemistry, the tumor is positive for smooth muscle actin (C, ×100) and desmin (D, ×100). |
Table 1.
Patient Demographics and Colonoscopic Findings




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download