Abstract
Antituberculosis drugs can produce levels of hepatotoxicity ranging from mild elevation of aminotransferase to severe acute hepatitis. A few cases of drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis or the drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptom (DRESS) syndrome by anti-tuberculosis medications have been reported. However, concomitant occurrence of these two disorders has not been reported. Here, we present a case of severe acute hepatitis with DRESS syndrome and autoimmune hepatitis resulting from primary standard anti-tuberculosis drugs. Both conditions were successfully treated with a systemic steroid regimen.
Go to : 
References
1. Tostmann A, Boeree MJ, Aarnoutse RE, de Lange WC, van der Ven AJ, Dekhuijzen R. Antituberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity: concise uptodate review. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008; 23:192–202.

2. Lee JH, Park HK, Heo J, et al. Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) syndrome induced by celecoxib and anti-tuberculosis drugs. J Korean Med Sci. 2008; 23:521–525.

3. Palmero D, Castagnino J, Musella RM, Mosca C, González Montaner P, de Casado GC. Difficult clinical management of anti-tuberculosis DRESS syndrome. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2013; 17:76–78.
4. Kardaun SH, Sidoroff A, Valeyrie-Allanore L, et al. Variability in the clinical pattern of cutaneous side-effects of drugs with systemic symptoms: does a DRESS syndrome really exist? Br J Dermatol. 2007; 156:609–611.

6. Manns MP, Czaja AJ, Gorham JD, et al. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology. 2010; 51:2193–2213.

7. Rothfield NF, Bierer WF, Garfield JW. Isoniazid induction of antinuclear antibodies: a prospective study. Ann Intern Med. 1978; 88:650–652.
Go to : 
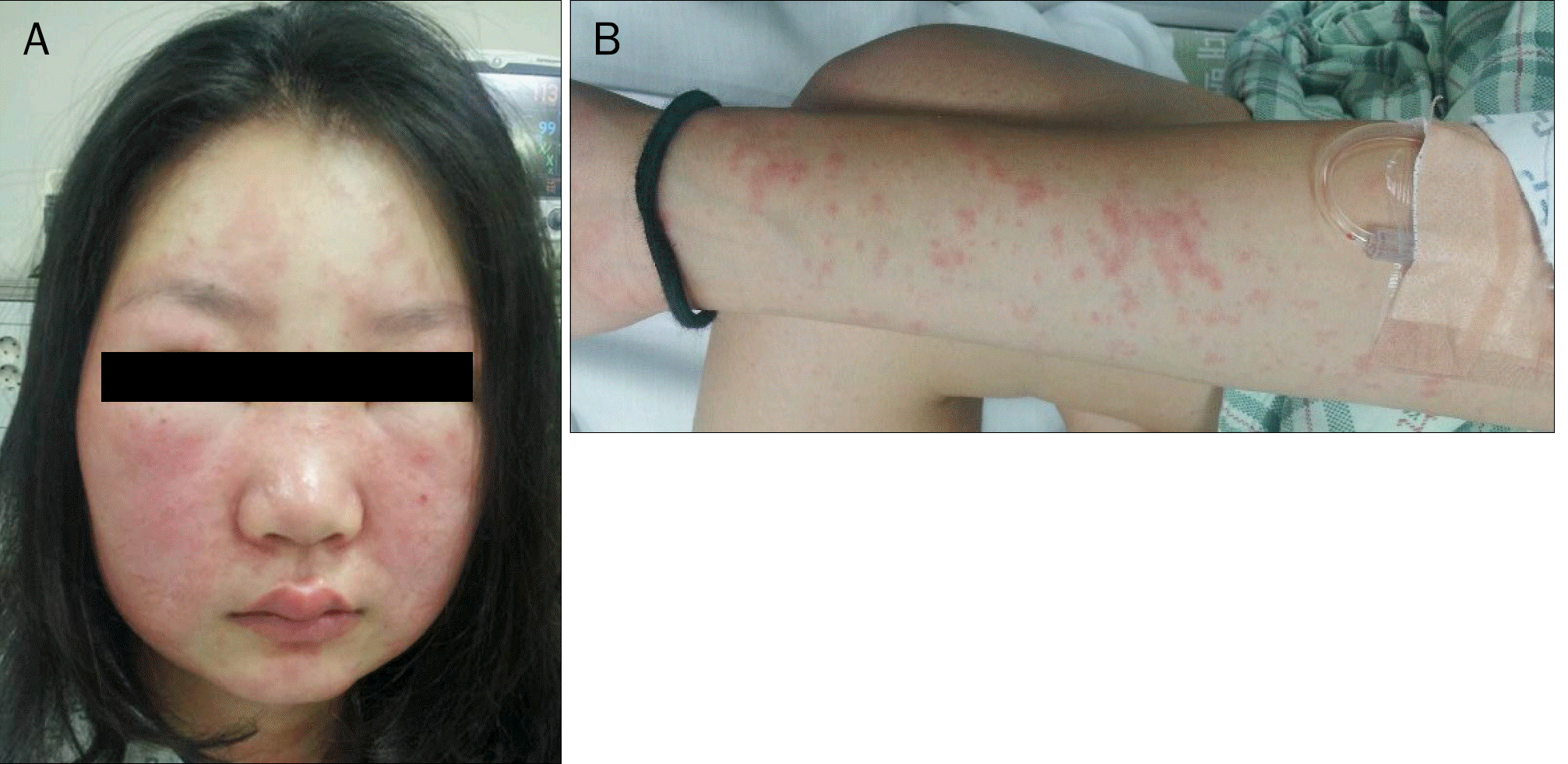 | Fig. 1.The patient developed an erythematous facial edema (A) and generalized maculopapular skin rash (B). |
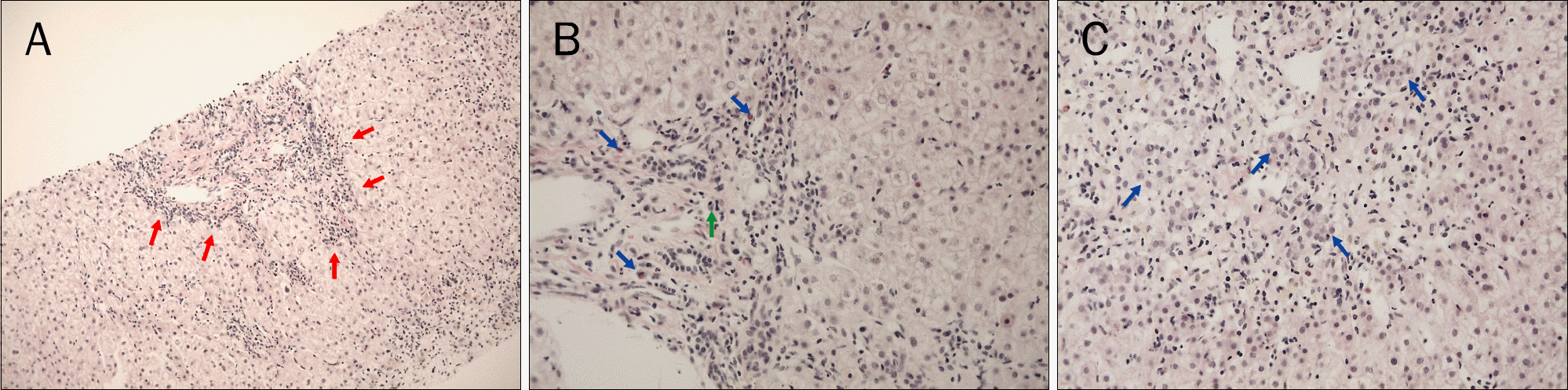 | Fig. 2.Liver biopsy showed interface hepatitis (red arrows) (H&E, ×100; A), and lympho-dominant infiltration with eosinophil (blue arrows) and plasma cell (green arrow) in portal tract (H&E, ×200; B). (C) Some lobular hepatocytes showed the rosette formation (blue arrows) (H&E, ×200). |
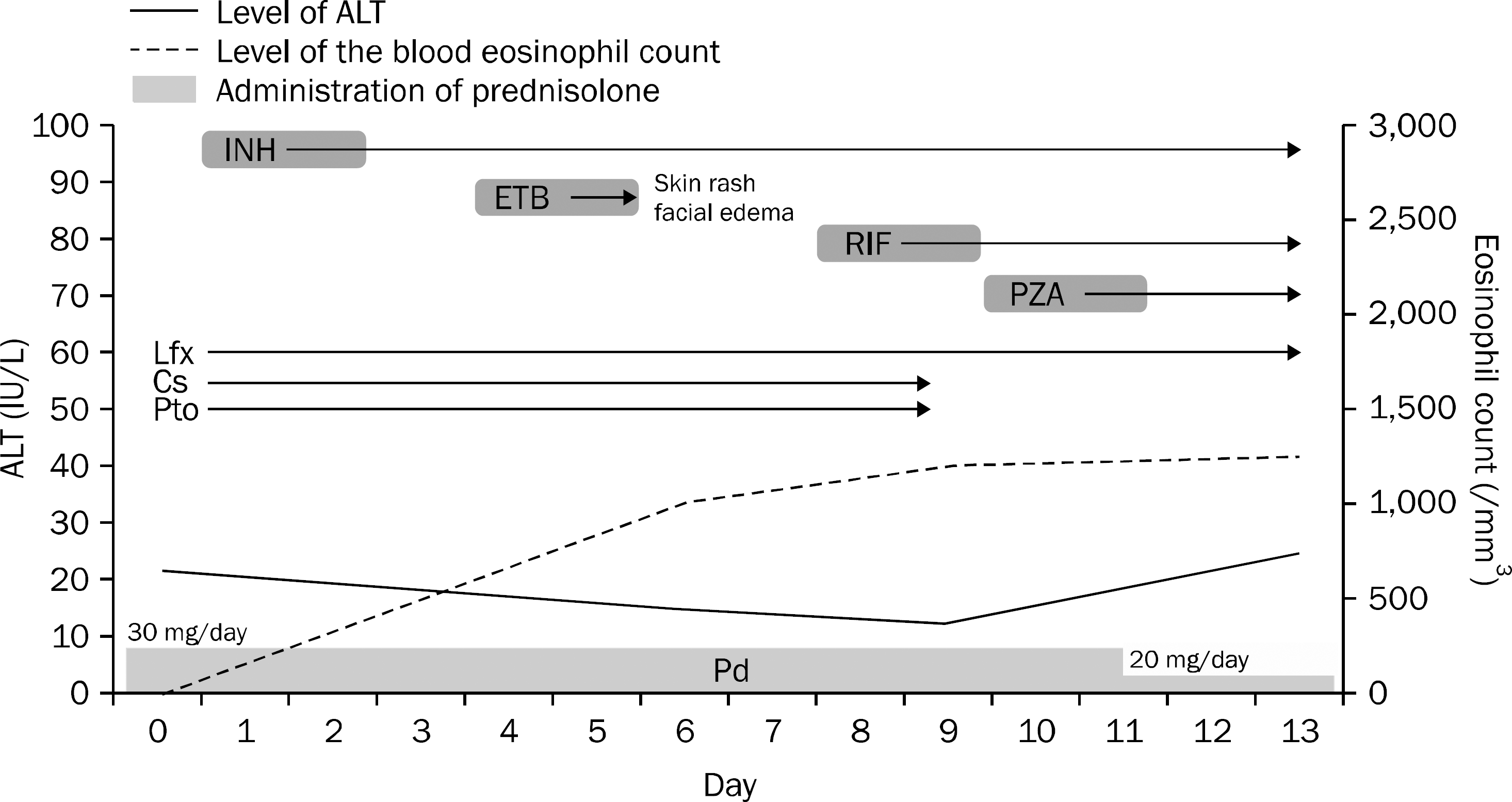 | Fig. 3.The treatment flow during the desensitization for the primary anti-tuberculosis drugs. INH, isoniazid; ETB, ethambutol; RIF, rifampin; PZA, pyrazinamide; Lfx, levofloxacin; Cs, cycloserine; Pto, prothionamide; Pd, prednisolone. |
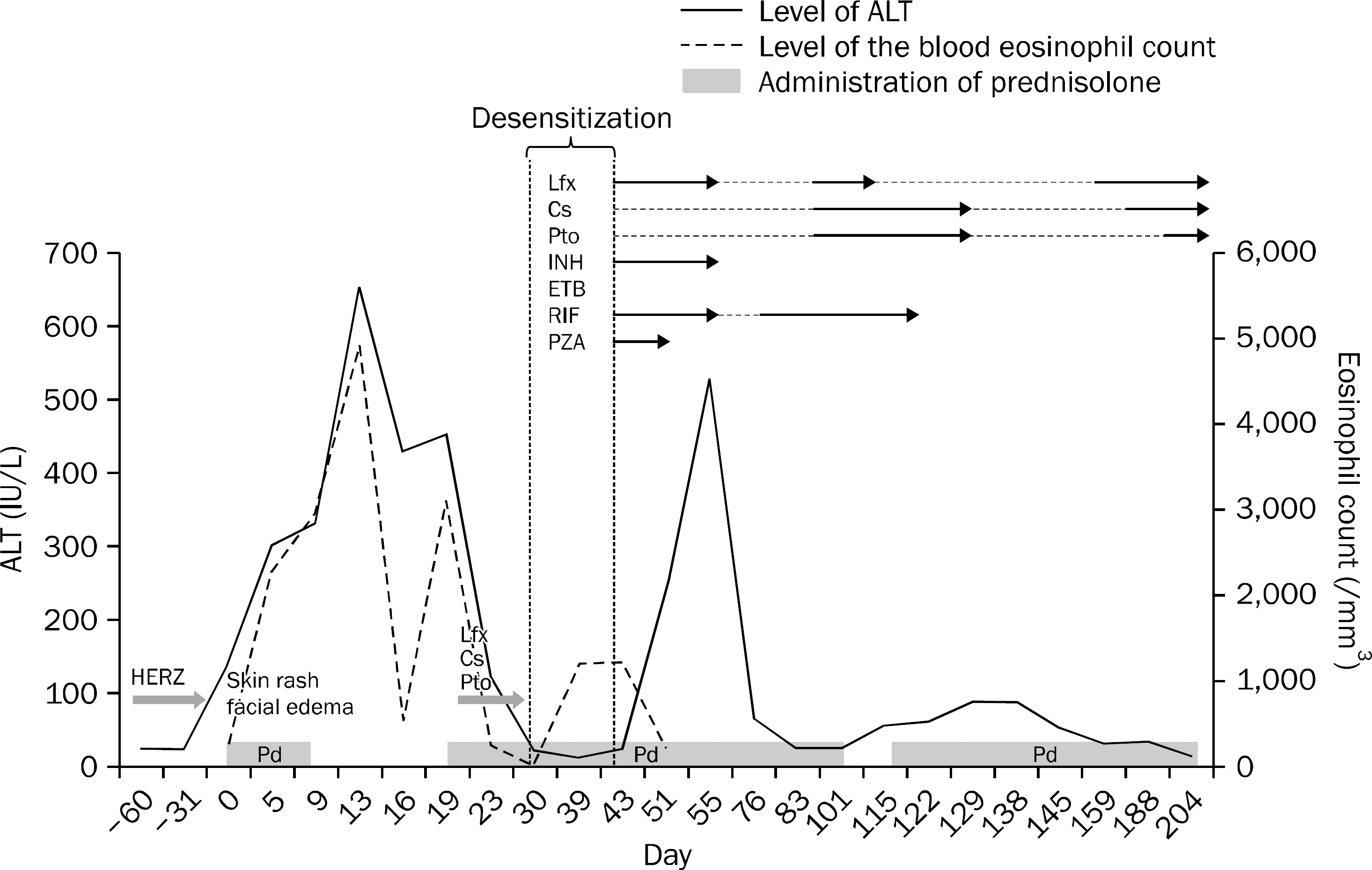 | Fig. 4.The level of alanine aminotransferase according to the anti-tuberculosis medications and prednisolone administration. Lfx, levofloxacin; Cs, cycloserine; Pto, prothionamide; INH, isoniazid; ETB, ethambutol; RIF, rifampin; PZA, pyrazinamide; HERZ, isoniazid, ethambutol, rifiampin, pyrazinamide; Pd, prednisolone. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download