Abstract
Colonic diffuse ganglioneuromatosis is a benign neoplastic condition characterized by disseminated, intramural, or transmural proliferation of neural elements involving the enteric plexuses, sometimes associated with von Recklinghausen's disease and other multiple tumor syndromes. Colonic diffuse ganglioneuromatosis is usually large, ranging from 1 to 17 cm, and thus can distort the surrounding tissue architecture as well as infiltrate the adjacent bowel wall. However, colonic diffuse ganglioneuromatosis is an exceptional finding in adults and only individual cases are reported in the literature. Herein, we report two unusual cases of adult patients with colonic diffuse transmural ganglioneuromatosis presenting as a large subepithelial tumor.
Go to : 
References
1. Shekitka KM, Sobin LH. Ganglioneuromas of the gastrointestinal tract. Relation to Von Recklinghausen disease and other multiple tumor syndromes. Am J Surg Pathol. 1994; 18:250–257.
2. Chambonnière ML, Porcheron J, Scoazec JY, Audigier JC, Mosnier JF. Intestinal ganglioneuromatosis diagnosed in adult patients. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2003; 27:219–224.
3. Mateş I, Iosif C, Dinu D, Constantinoiu S. Solitary ganglioneuromatosis of the descending colon, presenting as giant retroperitoneal tumour. Chirurgia (Bucur). 2013; 108:584–588.
4. Jung YW, Jang BI, Chang KA, Kim KO, Kim MJ. The solitary polypoid ganglioneuroma of the ascending colon. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 41:390–393.
5. Bang BW, Jeong S, Kim CH, et al. A case of polypoid ganglioneuroma of the colon. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 36:48–51.
6. Kim SH, Choi CH, Paik YH, Kim WH, Kim H. Isolated polypoid ganglioneuroma in the rectum. Korean J Pathol. 2001; 35:344–346.
7. Park JY, Kang YN, Park KS, Choe M. Solitary polypoid ganglioneuroma of the cecum. J Korean Soc Coloproctol. 2009; 25:264–267.

8. Miettinen M, Fletcher CDM, Kindblom LG, Tsui WMS. Mesechimal tumors of the colon and rectum. Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruman RH, Theise ND, editors. WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. 4th ed.Lion: IARC;2010. p. 140–141.
9. DeSchryver-Kecskemeti K, Clouse RE, Goldstein MN, Gersell D, O'Neal L. Intestinal ganglioneuromatosis. A manifestation of overproduction of nerve growth factor? N Engl J Med. 1983; 308:635–639.
10. Srinivasan R, Mayle JE. Polypoid ganglioneuroma of colon. Dig Dis Sci. 1998; 43:908–909.
11. Carney JA, Go VL, Sizemore GW, Hayles AB. Alimentary-tract ganglioneuromatosis. A major component of the syndrome of multiple endocrine neoplasia, type 2b. N Engl J Med. 1976; 295:1287–1291.
12. Hochberg FH, Dasilva AB, Galdabini J, Richardson EP Jr. Gastrointestinal involvement in von Recklinghausen's neurofibromatosis. Neurology. 1974; 24:1144–1151.

13. DiLiberti JH, Weleber RG, Budden S. Ruvalcaba-Myhre-Smith syndrome: a case with probable autosomal-dominant inheritance and additional manifestations. Am J Med Genet. 1983; 15:491–495.

14. Urschel JD, Berendt RC, Anselmo JE. Surgical treatment of colonic ganglioneuromatosis in neurofibromatosis. Can J Surg. 1991; 34:271–276.
Go to : 
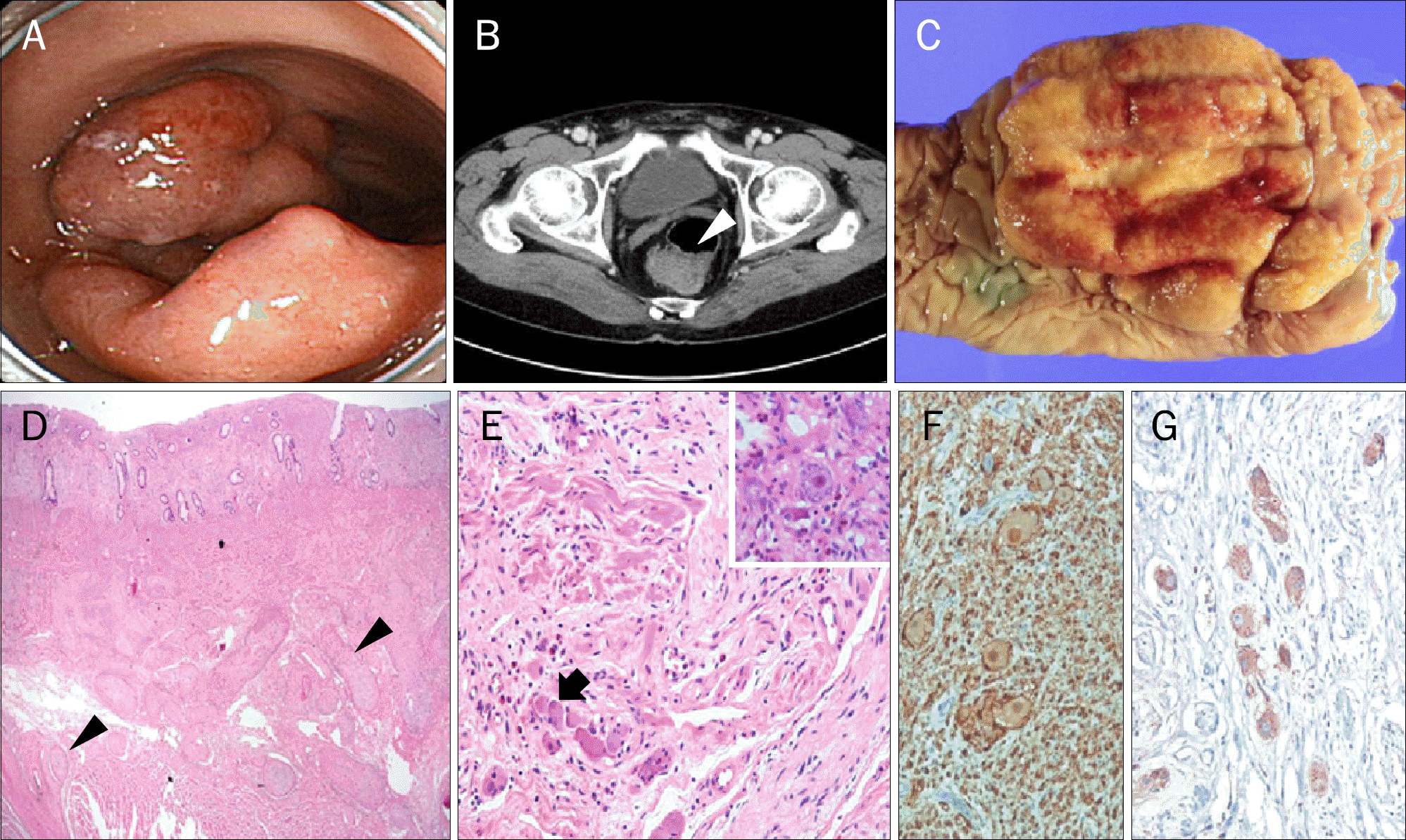 | Fig. 1.Rectal diffuse ganglioneuromatosis. (A) Colonoscopy shows an 8 cm sized subepithelial tumor in the rectum that occupies half of the lumen. (B) CT scan shows subtle enhancement at the left-side wall in the rectosigmoid junction (white arrowhead). (C) The huge polypoid mass and adjacent mucosa reveal yellowish granular surface after overnight fixation in 10% neutral formalin. (D) The thickened mucosa is noted. The submucosa and muscle layer show proliferation of haphazardly arranged, large nerve plexuses (arrowheads) (H&E, ×40). (E) The thickened mucosa shows ganglion cell clusters (arrow) with nerve fibers (H&E, ×100; inset: ×400). (F) Immunohistochemical staining for S-100 protein highlights the abnormal nerve fibers and ganglion cells in the mucosa of colon (S-100, ×400). (G) The immunoreactivity for chromogranin reveals ganglion cell proliferation in the mucosa of colon (chromagranin, ×400). |
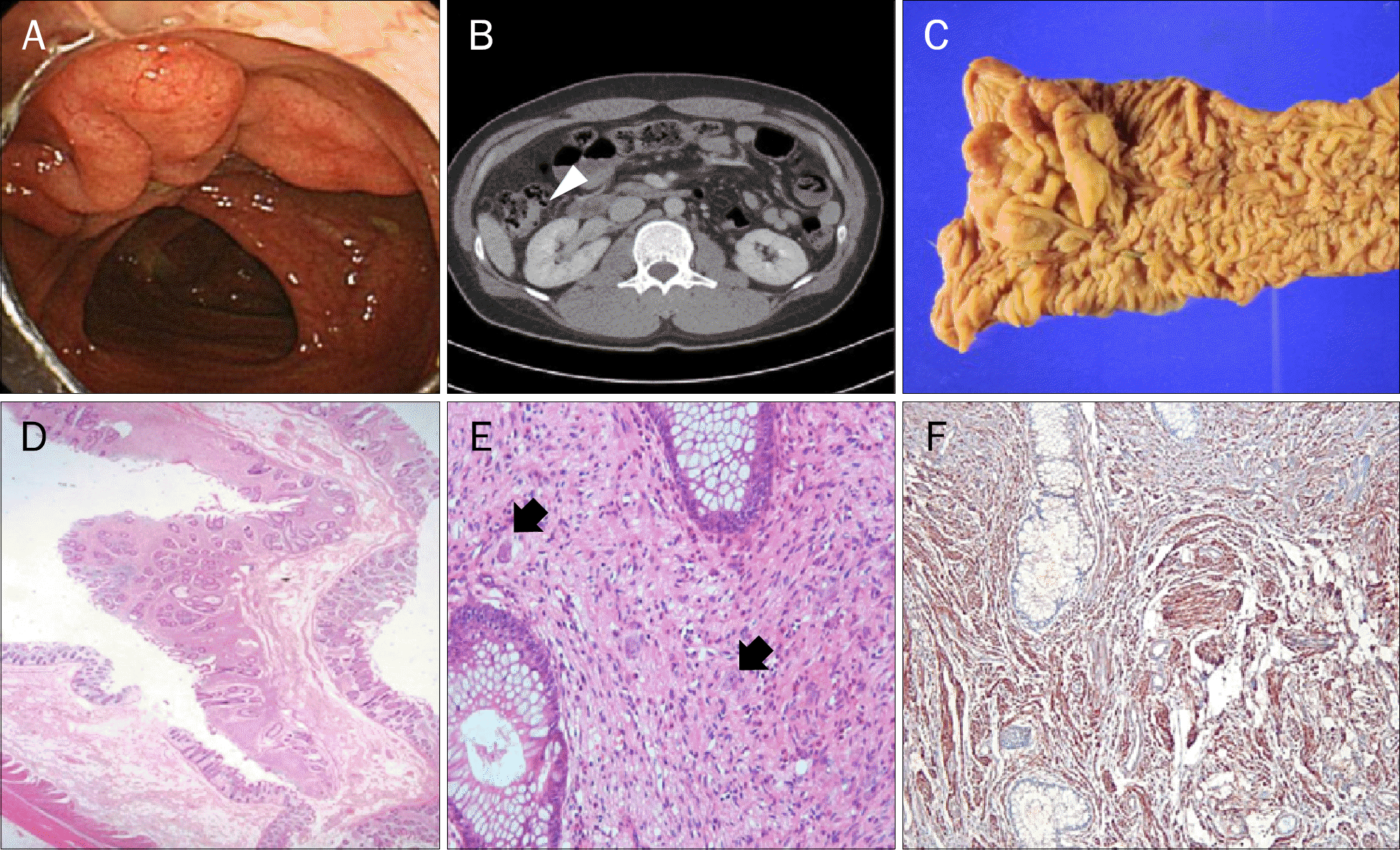 | Fig. 2.Diffuse ganglioneuromatosis of ascending colon. (A) Colonoscopy shows a 5 cm sized laterally spreading tumor in the ascending colon that has intact overlying mucosa. (B) CT scan shows an approximately 5 cm sized eccentric haustral fold thickening in the distal ascending colon (white arrowhead). (C) The surgical specimen shows a polypoid mass with finger-like projections. (D) The finger-like projection of the lesion consists of mucosal thickening and submucosal proliferations of thick nerve bundles (H&E, ×40). (E) The mucosa shows a uniform appearance of scattered ganglion cells (arrows) mixed with bland, spindle-shaped cells with Schwannian features (H&E, ×100). (F) Immunohistochemical staining shows strong positivity for S-100 protein in the mucosa of colon, consistent with the proliferation of ganglion and Schwann cells (S-100, ×40). |
Table 1.
Summary of Colonic Ganglioneuroma reported in Korea




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download