Abstract
Aloe is one of the leading products used in phytomedicine. Several cases of aloe-induced toxic hepatitis have been reported in recent years. However, its toxicology has not yet been systematically described in the literature. A 21-year-old female patient was admitted to our hospital with acute hepatitis after taking an aloe vera preparation for four weeks. Her history, clinical manifestation, laboratory findings, and histological findings all led to the diagnosis of aloe vera-induced toxic hepatitis. We report herein on a case of acute toxic hepatitis induced by aloe vera.
Go to : 
References
1. Kelly JP, Kaufman DW, Kelley K, Rosenberg L, Anderson TE, Mitchell AA. Recent trends in use of herbal and other natural products. Arch Intern Med. 2005; 165:281–286.

2. Korea Food and Drug Administration. 2012 Food and drug statistical yearbook. Vol. 14. Cheongwon: Korea Food and Drug Administration;2012. p. 56–57.
3. Bénichou C. Criteria of drug-induced liver disorders. Report of an international consensus meeting. J Hepatol. 1990; 11:272–276.
4. Lee BM, Park KK. Beneficial and adverse effects of chemopreventive agents. Mutat Res. 2003; 523–524:265–278.

5. Jang DD, Cho JC, Choi KS, Kil KS, Han IS. Studies of the effectiveness and toxicity of aloe vera gel. Rep Natl Inst Saf Res. 1994; 7:225–233.
6. Kwack SJ, Kim KB, Lee BM. Estimation of tolerable upper intake level (UL) of active aloe. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2009; 72:1455–1462.

7. Rabe C, Musch A, Schirmacher P, Kruis W, Hoffmann R. Acute hepatitis induced by an Aloe vera preparation: a case report. World J Gastroenterol. 2005; 11:303–304.

8. Yang HN, Kim DJ, Kim YM, et al. Aloe-induced toxic hepatitis. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:492–495.

9. Bottenberg MM, Wall GC, Harvey RL, Habib S. Oral aloe vera-induced hepatitis. Ann Pharmacother. 2007; 41:1740–1743.

10. Curciarello J, De Ortúzar S, Borzi S, Bosia D. Severe acute hepatitis associated with intake of Aloe vera tea. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008; 31:436–438.
11. Kanat O, Ozet A, Ataergin S. Aloe vera-induced acute toxic hepatitis in a healthy young man. Eur J Intern Med. 2006; 17:589.

12. Rauff B, Idrees M, Shah SA, et al. Hepatitis associated aplastic anemia: a review. Virol J. 2011; 8:87.

13. Brugnara C. Use of reticulocyte cellular indices in the diagnosis and treatment of hematological disorders. Int J Clin Lab Res. 1998; 28:1–11.

14. Royer DJ, George JN, Terrell DR. Thrombocytopenia as an adverse effect of complementary and alternative medicines, herbal remedies, nutritional supplements, foods, and beverages. Eur J Haematol. 2010; 84:421–429.

15. Kang DY. Pathologic features of toxic and drug induced liver injury. Korean J Hepatol. 2004; 10(Suppl 1):19–29.
Go to : 
 | Fig. 1.The container bottle and gel of the aloe vera preparation that the patient had taken. |
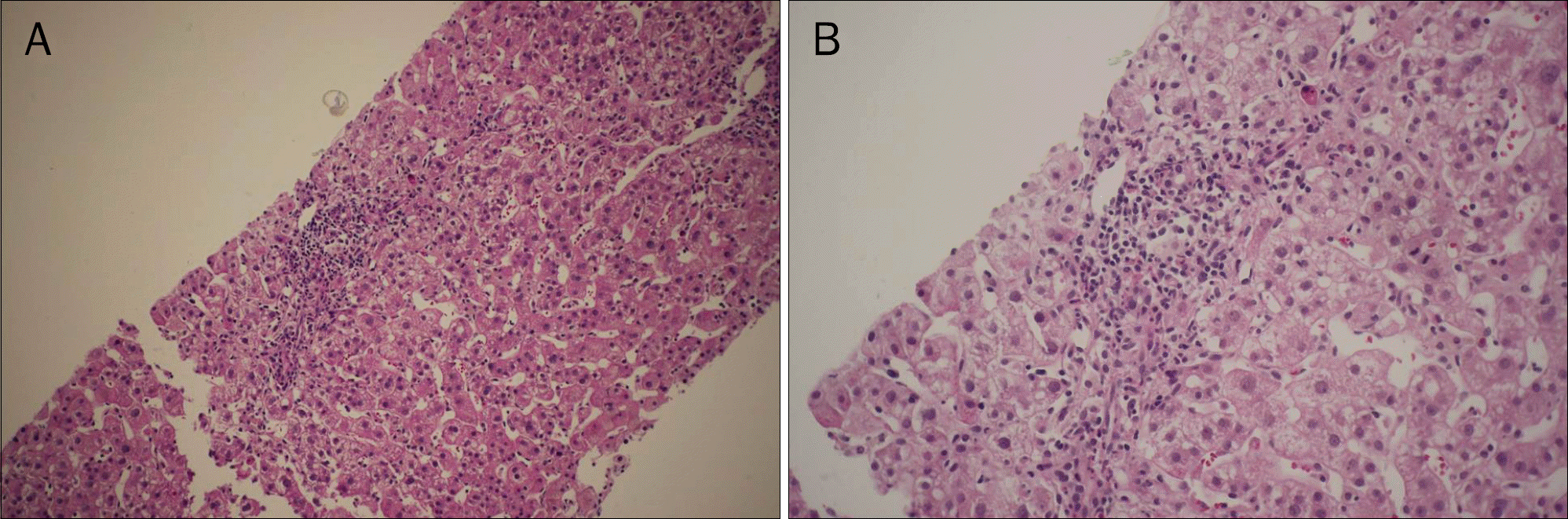 | Fig. 2.(A) Microphotograph of a gun biopsy specimen of the liver (H&E, ×200). (B) Higher magnification showed mixed infiltration of inflammatory cells at the portal and lobular spaces with neutrophils, lymphocytes, and eosinophils (H&E, ×400). |
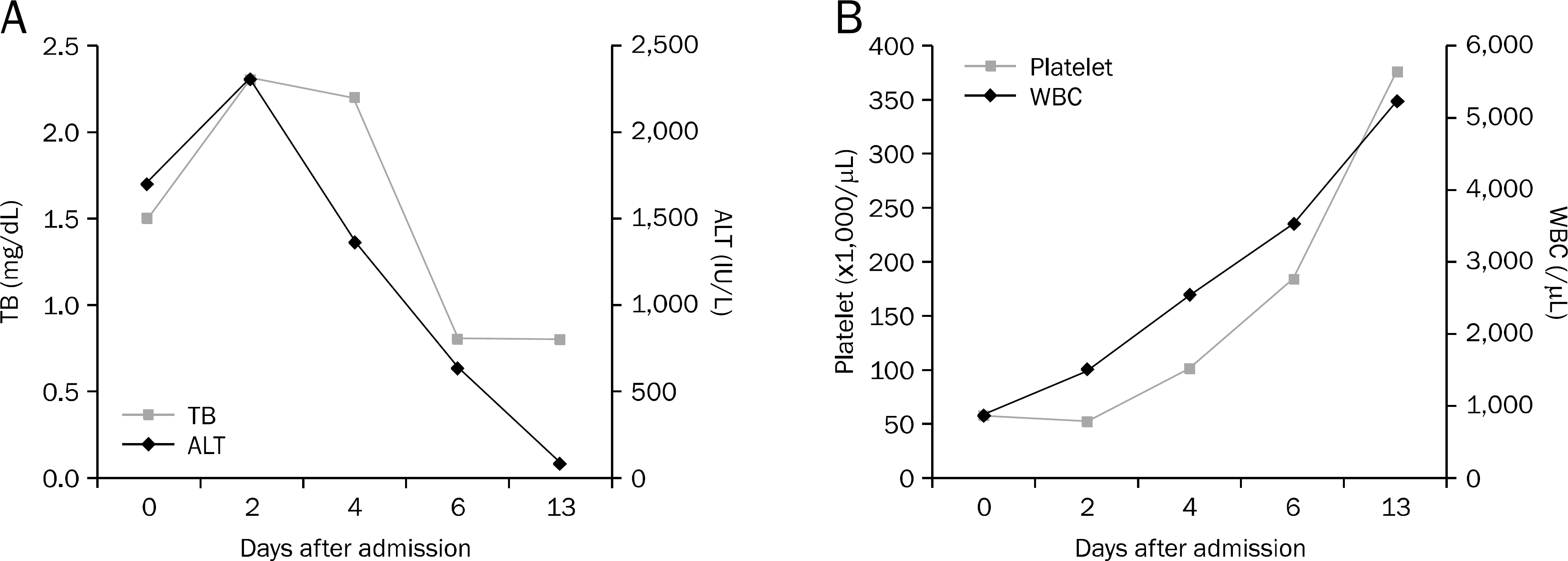 | Fig. 3.(A) Upon discontinuation of the intake of aloe vera, the liver enzymes returned to their normal level. (B) Upon discontinuation of the intake of aloe vera, the white blood cell and platelet counts returned to their normal levels. TB, total bilirubin; WBC, white blood cell. |
Table 1.
Patient Characteristics of Previously Reported Aloe-induced Toxic Hepatitis
| Patient (No) | Sex | Age (yr) | Medication duration (wk) | ALT (IU/L) | ALP (IU/L) | TB (mg/dL) | Type of liver injury | Re-challenge | Causality assessment a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | F | 57 | 4 | 1,480 | 256 | 8.90 | Hepatocellular | ND | Probable |
| 28 | F | 57 | 24 | 565 | 309 | 1.07 | Hepatocellular | ND | Probable |
| 38 | F | 62 | 12 | 1,564 | 211 | 14.64 | Hepatocellular | Positive | Definite |
| 48 | F | 55 | 20 | 641 | 291 | 0.48 | Hepatocellular | ND | Probable |
| 59 | F | 73 | 260 | 1,451 | 535 | 10.70 | Hepatocellular | ND | Probable |
| 610 | M | 26 | 156 | 799 | 200 | 8 | Hepatocellular | ND | Probable |
| 711 | M | 24 | 3 | 2,550 | 400 | 9.00 | Hepatocellular | ND | Probable |
| Current case | F | 21 | 4 | 1,703 | 709 | 1.5 | Hepatocellular | ND | Definite |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download