References
2. Relles D, Baek J, Witkiewicz A, Yeo CJ. Periampullary and duodenal neoplasms in neurofibromatosis type 1: two cases and an updated 20-year review of the literature yielding 76 cases. J Gastrointest Surg. 2010; 14:1052–1061.

4. Basile U, Cavallaro G, Polistena A, et al. Gastrointestinal and retroperitoneal manifestations of type 1 neurofibromatosis. J Gastrointest Surg. 2010; 14:186–194.

5. Kim ET, Namgung H, Shin HD, et al. Oncologic manifestations of neurofibromatosis type 1 in Korea. J Korean Surg Soc. 2012; 82:205–210.

6. Gottfried ON, Viskochil DH, Couldwell WT. Neurofibromatosis Type 1 and tumorigenesis: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Neurosurg Focus. 2010; 28:E8.

7. Andersson J, Sihto H, Meis-Kindblom JM, Joensuu H, Nupponen N, Kindblom LG. NF1-associated gastrointestinal stromal tumors have unique clinical, phenotypic, and genotypic characteristics. Am J Surg Pathol. 2005; 29:1170–1176.

8. Miettinen M, Lasota J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors-defi-nition, clinical, histological, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic features and differential diagnosis. Virchows Arch. 2001; 438:1–12.
9. Miettinen M, Fetsch JF, Sobin LH, Lasota J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors in patients with neurofibromatosis 1: a clinicopathologic and molecular genetic study of 45 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006; 30:90–96.
10. Choi W, Hong SD, Kim HN, et al. Two cases of neuroendocrine carcinoma and GIST in a patient with neurofibromatosis type 1. Korean J Med. 2011; 81:786–791.
11. Seo SO, Oh HJ, Kim KH, et al. A case of duodenal GIST accompanied with neurofibromatosis-1, presenting with gastrointestinal bleeding. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 35:254–257.
Fig. 1.
Initial esophagogastroduod-enoscopy. Mass-like lesions with overlying normal mucosa and central ulceration are seen in the 2nd and 3rd portion of the duodenum.
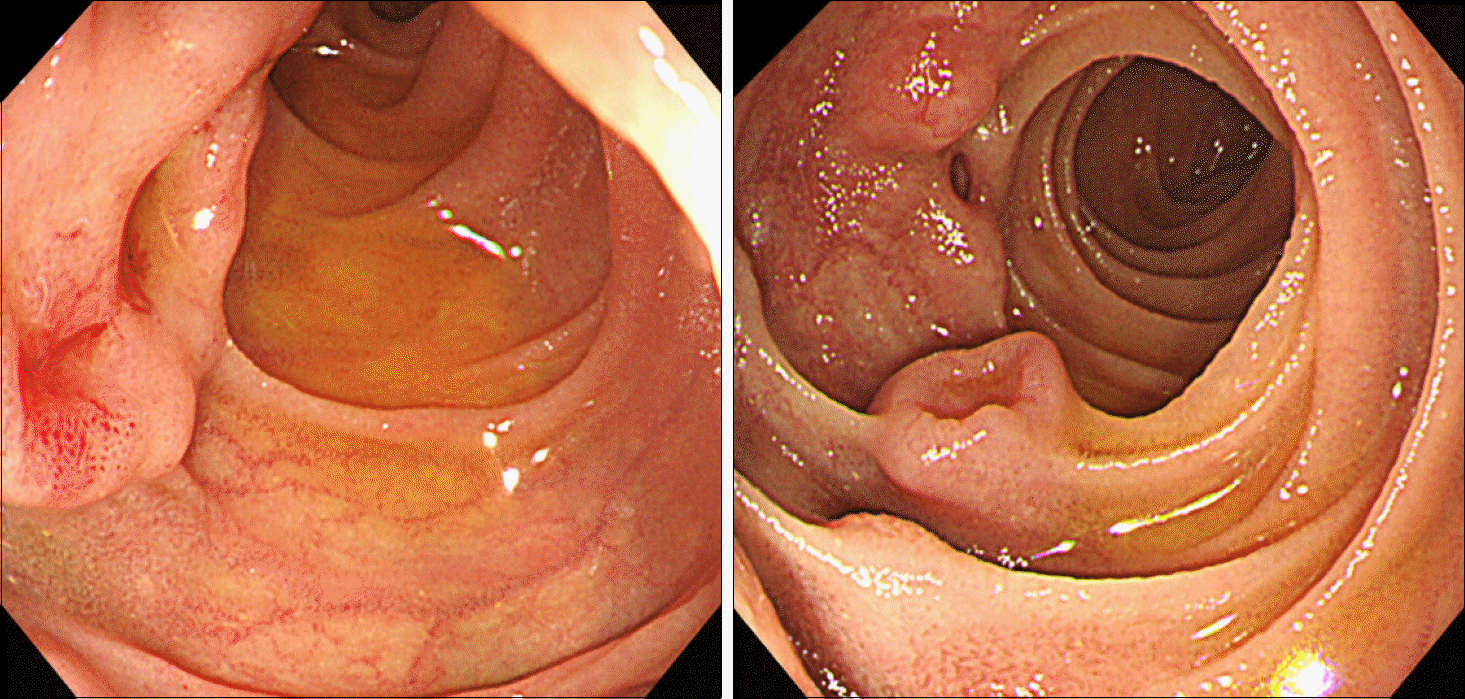
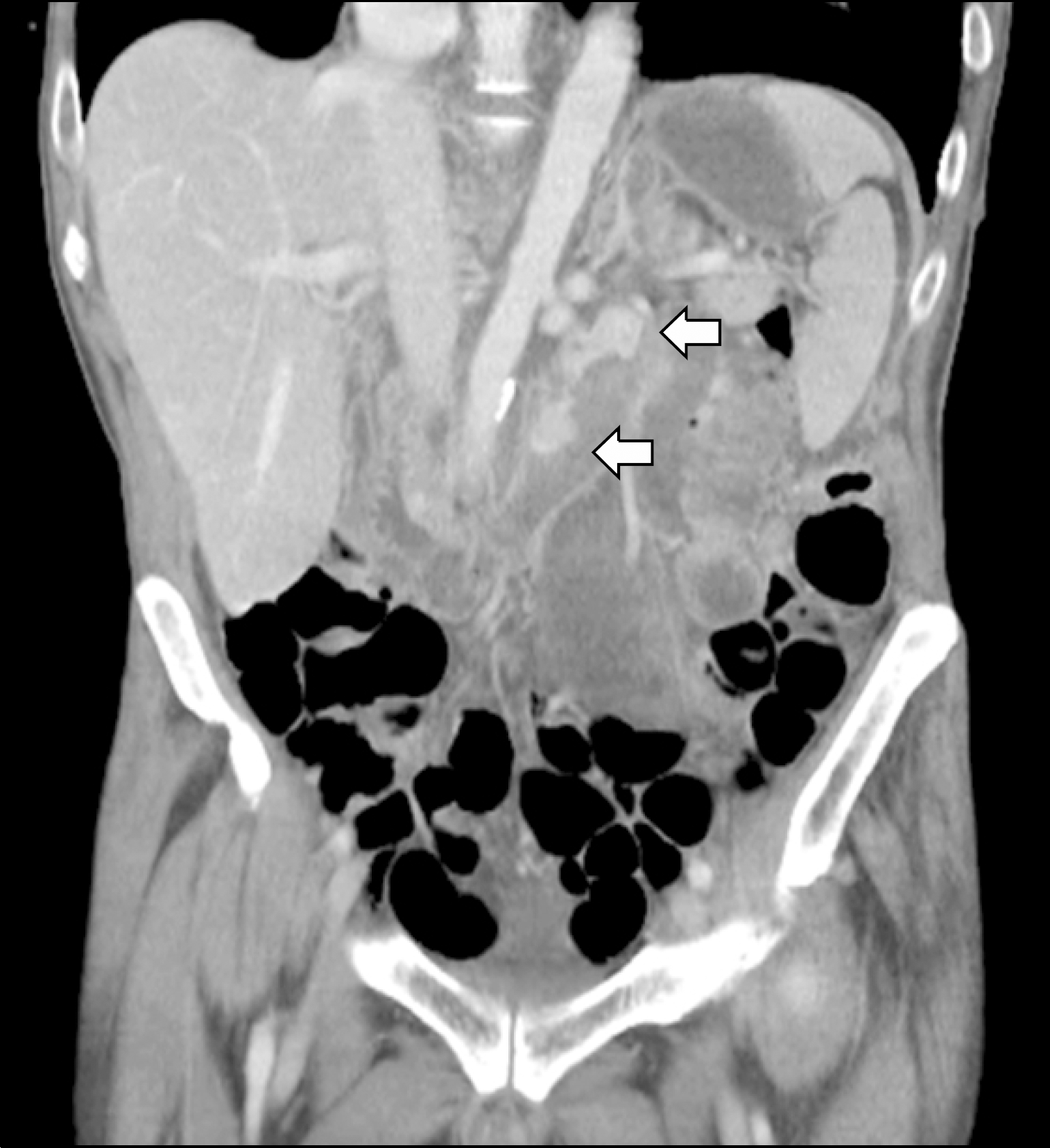
Fig. 2.
Abdominal computed tomography. Two well-enhancing lesions (arrows) are observed in the third portion of the duodenum.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download