Abstract
Background/Aims
Adequate screening colonoscopy in the general population decreases the mortality associated with colorectal cancer through detection and removal of adenomatous polyps. Prolonged colonoscopic withdrawal times (>6 min) are reportedly beneficial for adenoma detection rates (ADRs). However, the quality of the endoscopist compared with colonoscopic withdrawal times is not known. The aims of this study were to investigate the difference in ADRs between trainees and experienced examiners.
Methods
A total of 967 consecutive patients who underwent screening colonoscopy in a single University hospital from June 2010 to November 2011 were enrolled in this prospective observational study. Colonoscopy was performed by four experienced staff and seven gastroenterology fellows.
Results
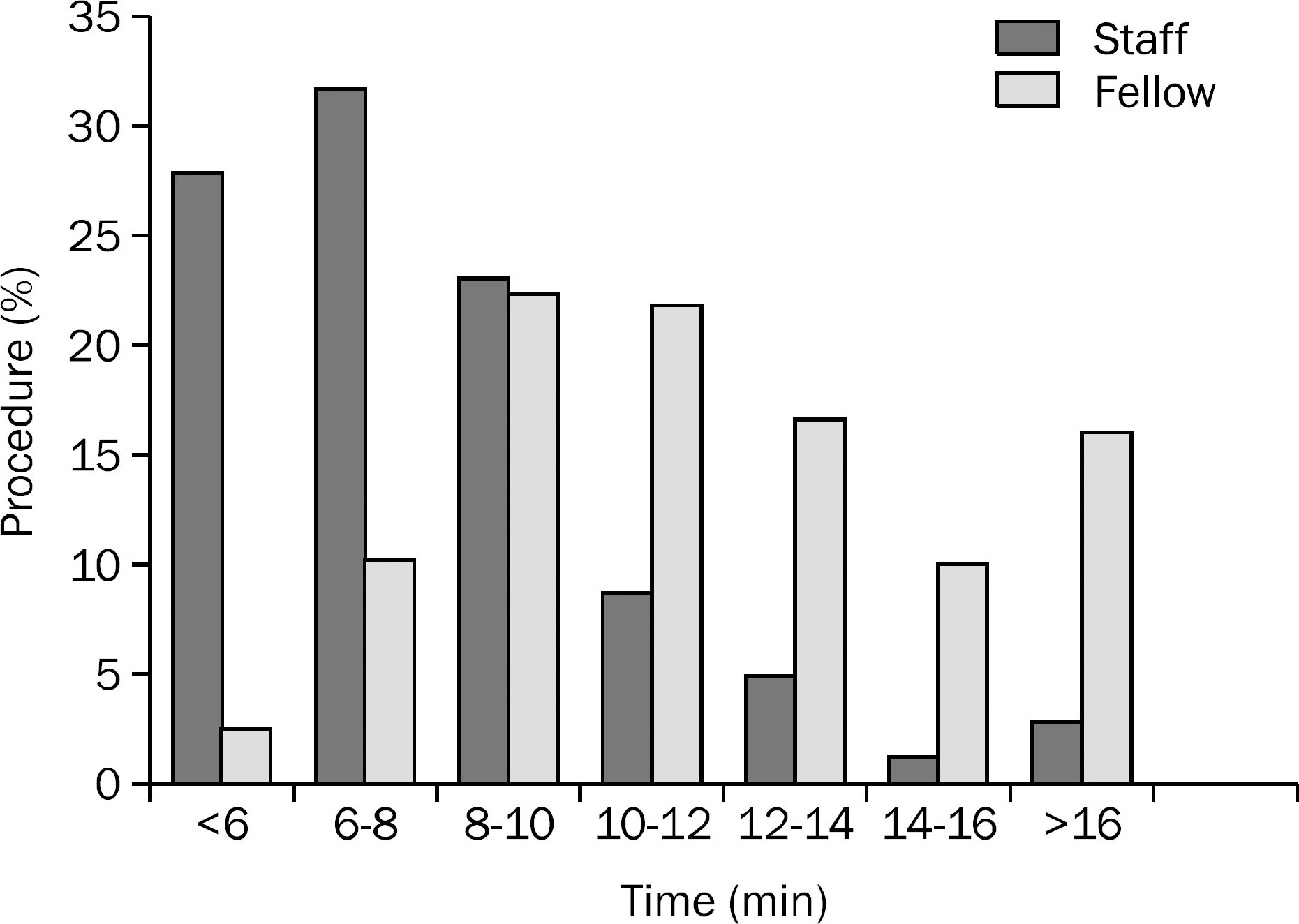
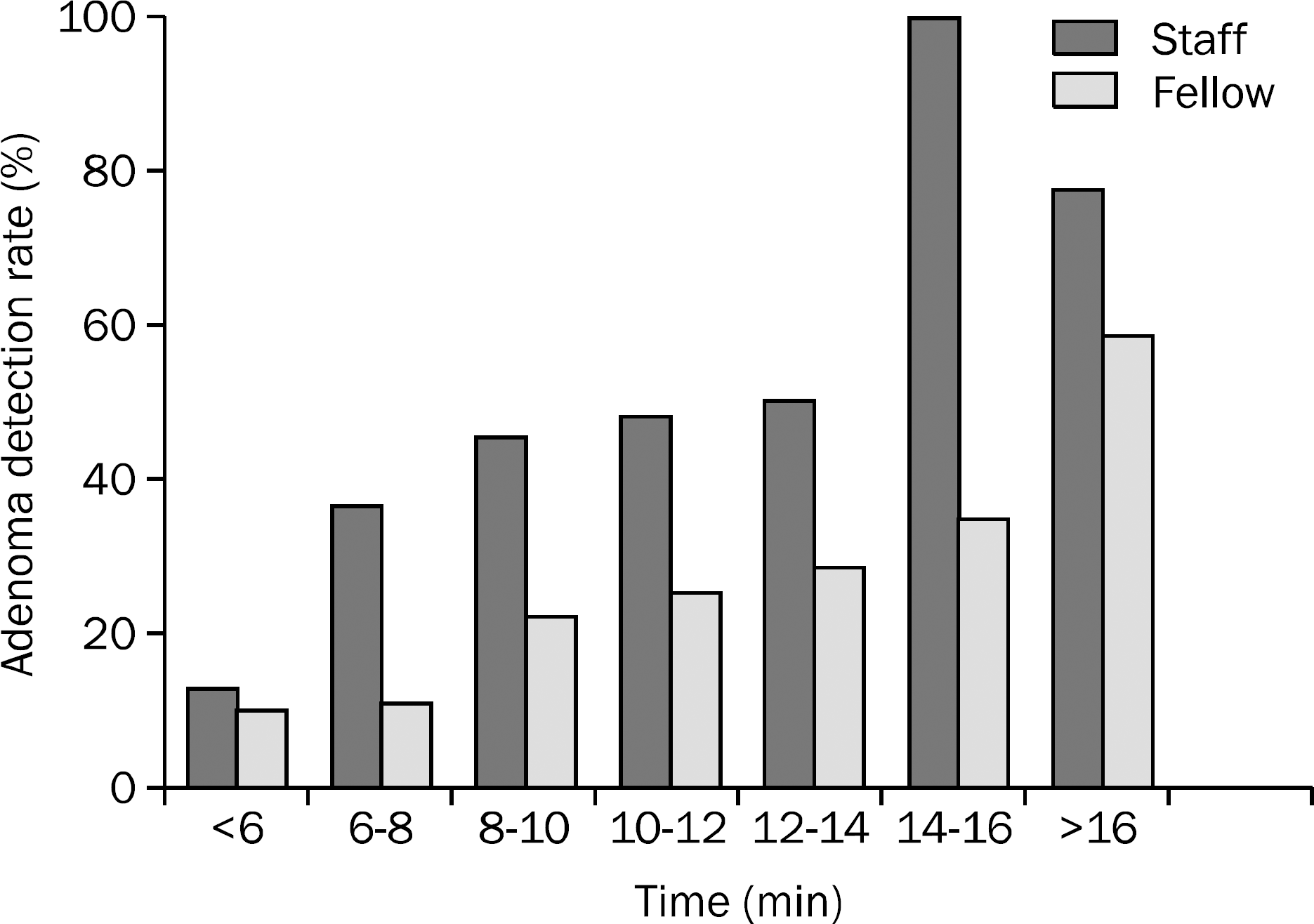
Seven gastroenterology fellows performed 633 colonoscopies and four experienced staff performed 334 colonoscopies. The overall detection rates of colorectal adenoma were 31.5% with ADRs of fellows and staff of 29.4% and 35.6%, respectively (p=0.047). Fellows also showed lower advanced ADRs (5.7% vs. 9.9%, p=0.016), and fellows had longer mean withdrawal times than staff (12.4±4.9 min vs. 8.2±4.1 min, p<0.001). Multivariate analysis showed significantly increased ADRs and advanced ADRs for staff compared with fellows (adjusted OR 2.41, 95% CI 1.70-3.43; adjusted OR 2.55, 95% CI 1.47-4.45, respectively).
References
1. Jung KW, Won YJ, Kong HJ, Oh CM, Lee DH, Lee JS. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2011. Cancer Res Treat. 2014; 46:109–123.

2. Lee BI, Hong SP, Kim SE, et al. Korean Guidelines for colorectal cancer screening and polyp detection. Intest Res. 2012; 10:67–88.

3. van Rijn JC, Reitsma JB, Stoker J, Bossuyt PM, van Deventer SJ, Dekker E. Polyp miss rate determined by tandem colonoscopy: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:343–350.

4. Rex DK, Bond JH, Winawer S, et al. U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Quality in the technical performance of colonoscopy and the continuous quality improvement process for colonoscopy: recommendations of the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002; 97:1296–1308.

5. Rex DK. Maximizing detection of adenomas and cancers during colonoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:2866–2877.

6. Froehlich F, Wietlisbach V, Gonvers JJ, Burnand B, Vader JP. Impact of colonic cleansing on quality and diagnostic yield of colonoscopy: the European panel of appropriateness of gastrointestinal Endoscopy European multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 61:378–384.

7. Barclay RL, Vicari JJ, Doughty AS, Johanson JF, Greenlaw RL. Colonoscopic withdrawal times and adenoma detection during screening colonoscopy. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:2533–2541.

8. Chen SC, Rex DK. Endoscopist can be more powerful than age and male gender in predicting adenoma detection at colonoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; 102:856–861.

9. Jiang M, Sewitch MJ, Barkun AN, Joseph L, Hilsden RJ. Endoscopist specialty is associated with colonoscopy quality. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013; 13:78.

10. Rex DK. Colonoscopic withdrawal technique is associated with adenoma miss rates. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000; 51:33–36.

11. Peters SL, Hasan AG, Jacobson NB, Austin GL. Level of fellowship training increases adenoma detection rates. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 8:439–442.

12. Lieberman DA, Rex DK, Winawer SJ, Giardiello FM, Johnson DA, Levin TR. United States Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Guidelines for colonoscopy surveillance after screening and polypectomy: a consensus update by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2012; 143:844–857.

13. Lee RH, Tang RS, Muthusamy VR, et al. Quality of colonoscopy withdrawal technique and variability in adenoma detection rates (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 74:128–134.

14. Rex DK, Hewett DG, Raghavendra M, Chalasani N. The impact of videorecording on the quality of colonoscopy performance: a pilot study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010; 105:2312–2317.

15. Citarda F, Tomaselli G, Capocaccia R, Barcherini S, Crespi M. Italian Multicentre Study Group. Efficacy in standard clinical practice of colonoscopic polypectomy in reducing colorectal cancer incidence. Gut. 2001; 48:812–815.

16. Wallace MB. Improving colorectal adenoma detection: technology or technique? Gastroenterology. 2007; 132:1221–1223.

17. Overholt BF, Brooks-Belli L, Grace M, et al. Benchmark Colonoscopy Group. Withdrawal times and associated factors in colonoscopy: a quality assurance multicenter assessment. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010; 44:e80–e86.
18. Simmons DT, Harewood GC, Baron TH, et al. Impact of endoscopist withdrawal speed on polyp yield: implications for optimal colonoscopy withdrawal time. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006; 24:965–971.

19. Millan MS, Gross P, Manilich E, Church JM. Adenoma detection rate: the real indicator of quality in colonoscopy. Dis Colon Rectum. 2008; 51:1217–1220.

20. Leyden JE, Doherty GA, Hanley A, et al. Quality of colonoscopy performance among gastroenterology and surgical trainees: a need for common training standards for all trainees? Endoscopy. 2011; 43:935–940.

21. Lieberman DA, Weiss DG, Harford WV, et al. Five-year colon surveillance after screening colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2007; 133:1077–1085.

22. IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Tobacco smoke and involuntary smoking. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum. 2004; 83:1–1438.
23. Rex DK, Lehman GA, Ulbright TM, et al. Colonic neoplasia in asymptomatic persons with negative fecal occult blood tests: influence of age, gender, and family history. Am J Gastroenterol. 1993; 88:825–831.
Fig. 1.
Study enrollment. Listed exclusions include prior colonoscopy, poor bowel preparation, history of inflam matory bowel disease (IBD), occurrence of complication, history of prior colonic resection, and inability to reach the cecum.
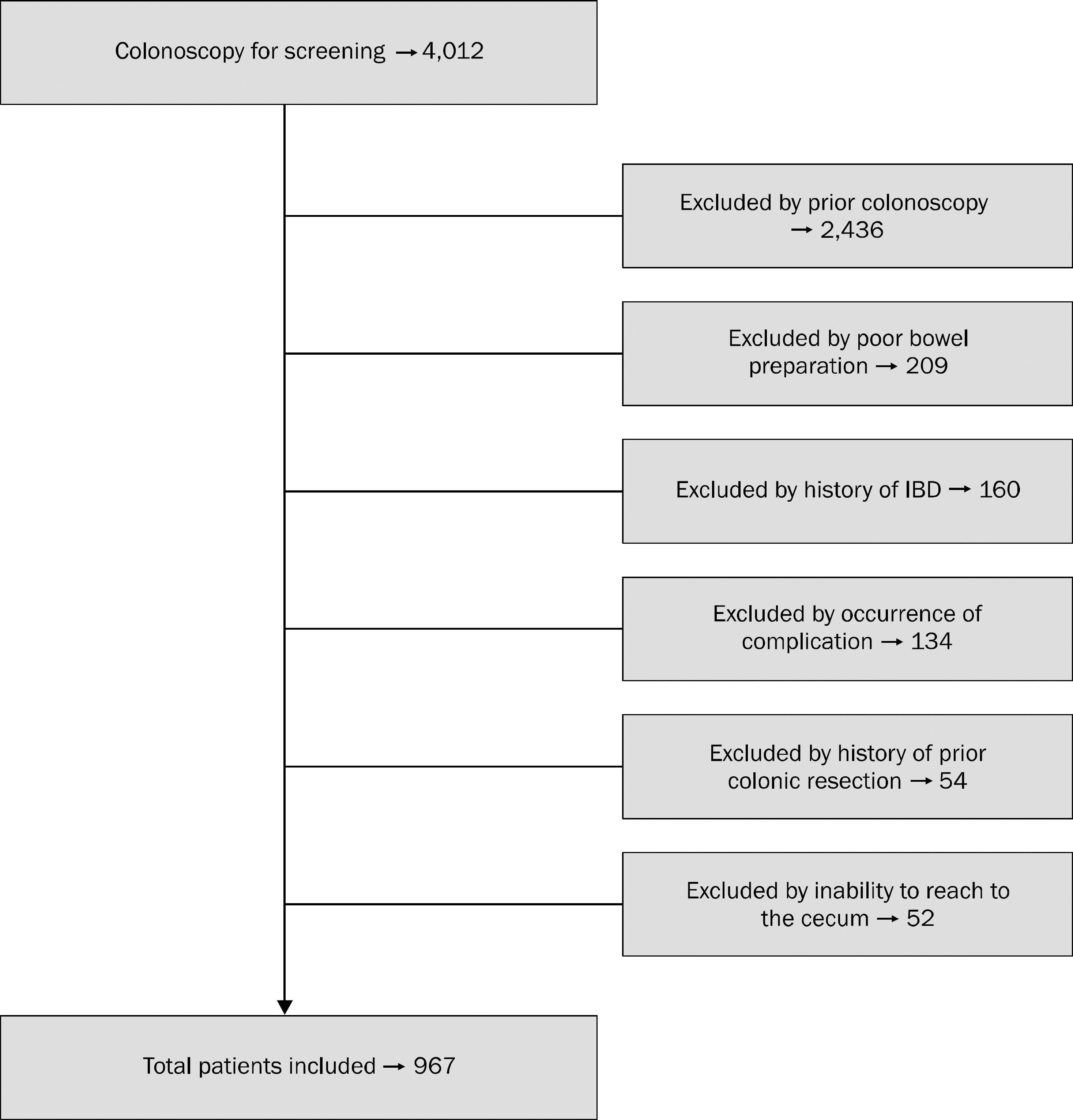
Table 1.
Variables Influencing Adenoma Detection
Table 2.
Results of a Logistic Regression Model Predicting Adenoma Detection and Advanced Adenoma Detection
Table 3.
Comparison of Study Factors by Staff vs. Fellows




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download