Abstract
Wernicke's encephalopathy (WE) caused by thiamine deficiency is an acute neurological disorder. Clinically, the classic triad of WE consists of ophthalmoplegia, ataxia, and mental status changes. Thiamine deficiency is known to occur commonly in chronic alcoholic patients. Sometimes, it can occur in patients after gastrointestinal surgery and in those with malabsorption. In addition, patients undergoing renal dialysis, suffering from hyperemesis gravidarum, receiving total parenteral nutrition (TPN), and being treated with chemotherapeutic agents are also prone to develop thiamine deficiency. Herein, we report two cases of WE that developed following simultaneous 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) chemotherapy and TPN in colon cancer patients which was successfully treated with thiamine administration.
Go to : 
References
2. Cho IJ, Chang HJ, Lee KE, et al. A case of Wernicke's encephalopathy following fluorouracil-based chemotherapy. J Korean Med Sci. 2009; 24:747–750.

3. Jung ES, Kwon O, Lee SH, et al. Wernicke's encephalopathy in advanced gastric cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 2010; 42:77–81.

4. Thomson AD, Cook CC, Touquet R, Henry JA. Royal College of Physicians, London. The Royal College of Physicians report on alcohol: guidelines for managing Wernicke's encephalopathy in the accident and Emergency Department. Alcohol Alcohol. 2002; 37:513–521.

5. Sechi G, Serra A. Wernicke's encephalopathy: new clinical set-tings and recent advances in diagnosis and management. Lancet Neurol. 2007; 6:442–455.

6. Kweon YM, Kim JE, Kwon OD, Do JK, Lee DK. Two cases of wernicke encephalopathy with focal cerebral cortical involvement and convulsive seizure. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2004; 22:539–544.
7. Kim MH, Baek JM, Sung GY, et al. Wernicke's encephalopathy following gastrectomy in patients with gastric cancer. J Korean Surg Soc. 2006; 70:218–222.
8. Park JC, Park SY, Kim DW. Wernicke-Korsakoff encephalopathy following cancer treatment in a patient with schizophrenia. Korean J Med. 2009; 77:S1289–S1292.
9. Lee H, Lee EH, Lee SC, Park HP. A case of Wernicke's encephalopathy in a postoperative patient with parenteral nutrition and tem-porary oral feeding: a case report. Korean J Crit Care Med. 2010; 25:186–189.
10. Jung YH, Yu HA, Youn GJ, Lee JI, Woo IS, Han CW. Case of atypical Wernicke's encephalopathy in a GB cancer patient. Korean J Med. 2013; 84:602–607.

11. Harper CG, Giles M, Finlay-Jones R. Clinical signs in the Wernicke-Korsakoff complex: a retrospective analysis of 131 cases diagnosed at necropsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986; 49:341–345.

12. Pagnan L, Berlot G, Pozzi-Mucelli RS. Magnetic resonance imaging in a case of Wernicke's encephalopathy. Eur Radiol. 1998; 8:977–980.

13. Heier MS, Fosså SD. Wernicke-Korsakoff-like syndrome in patients with colorectal carcinoma treated with high-dose doxi-fluridine (5'-dFUrd). Acta Neurol Scand. 1986; 73:449–457.

14. Scheiner JM, Araujo MM, DeRitter E. Thiamine destruction by so-dium bisulfite in infusion solutions. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1981; 38:1911–1913.

15. Yeh KH, Cheng AL. High-dose 5-fluorouracil infusional therapy is associated with hyperammonaemia, lactic acidosis and encephalopathy. Br J Cancer. 1997; 75:464–465.

16. Kondo K, Fujiwara M, Murase M, et al. Severe acute metabolic acidosis and Wernicke's encephalopathy following chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin: case report and review of the literature. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1996; 26:234–236.

17. Pirzada NA, Ali II, Dafer RM. Fluorouracil-induced neurotoxicity. Ann Pharmacother. 2000; 34:35–38.

18. Davies SB, Joshua FF, Zagami AS. Wernicke's encephalopathy in a nonalcoholic patient with a normal blood thiamine level. Med J Aust. 2011; 194:483–484.

Go to : 
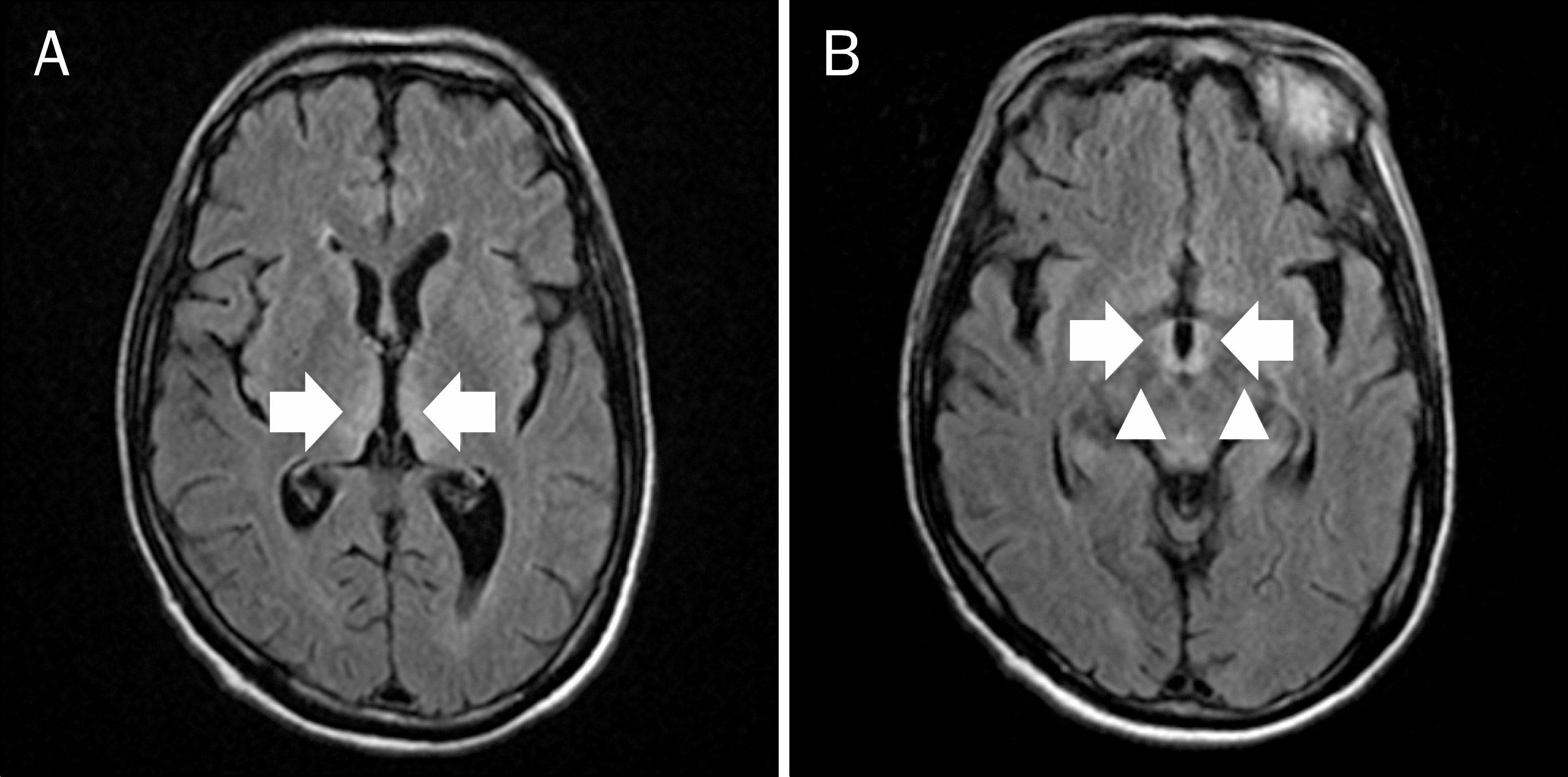 | Fig. 1.Brain magnetic resonance images. T2 weighted images and fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) images show (A) high signal intensity in both medial thalamus and (B) high signal intensity in mamillary body (arrows) and dorsal midbrain (arrow-heads). |
 | Fig. 2.Brain magnetic resonance images. T2 weighted images and fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) images show (A) high signal intensity in anterior precentral gyrus, (B) high signal intensity in both medial thalamus, (C) high signal intensity in the walls of the third ventricle (arrow-heads), periaqueductal gray matter, and dorsal midbrain (arrows), and (D) high signal intensity in mamillary body. |
Table 1.
Summary of the Reported Cases of Wernicke's Encephalopathy in Gastrointestinal Tract Cancer Patients in Korea




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download