References
1. Opitz JM, Schultka R, Göbbel L. Meckel on developmental pathology. Am J Med Genet A. 2006; 140:115–128.

2. Petras RE. Nonneoplstic intestinal disease. Sternberg SS, Mills SE, Carter D, editors. Sternberg's diagnostic surgical pathology. 4th ed.Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2004. p. 1475–1542.
3. Sawin RS. Appendix and Meckel's diverticulum. Oldham KT, editor. Principles and practice of pediatric surgery. Vol. 2. 2nd ed.Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2005. p. 1269–1282.
4. Ymaguchi M, Takeuchi S, Awazu S. Meckel's diverticulum. Investigation of 600 patients in Japanese literature. Am J Surg. 1978; 136:247–249.
5. Rossi P, Gourtsoyiannis N, Bezzi M, et al. Meckel's diverticulum: imaging diagnosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996; 166:567–573.

6. Artigas V, Calabuig R, Badia F, Rius X, Allende L, Jover J. Meckel's diverticulum: value of ectopic tissue. Am J Surg. 1986; 151:631–634.

Fig. 1.
Erect abdominal radiograph shows multiple dilated loops predominantly on the left side of the abdomen.
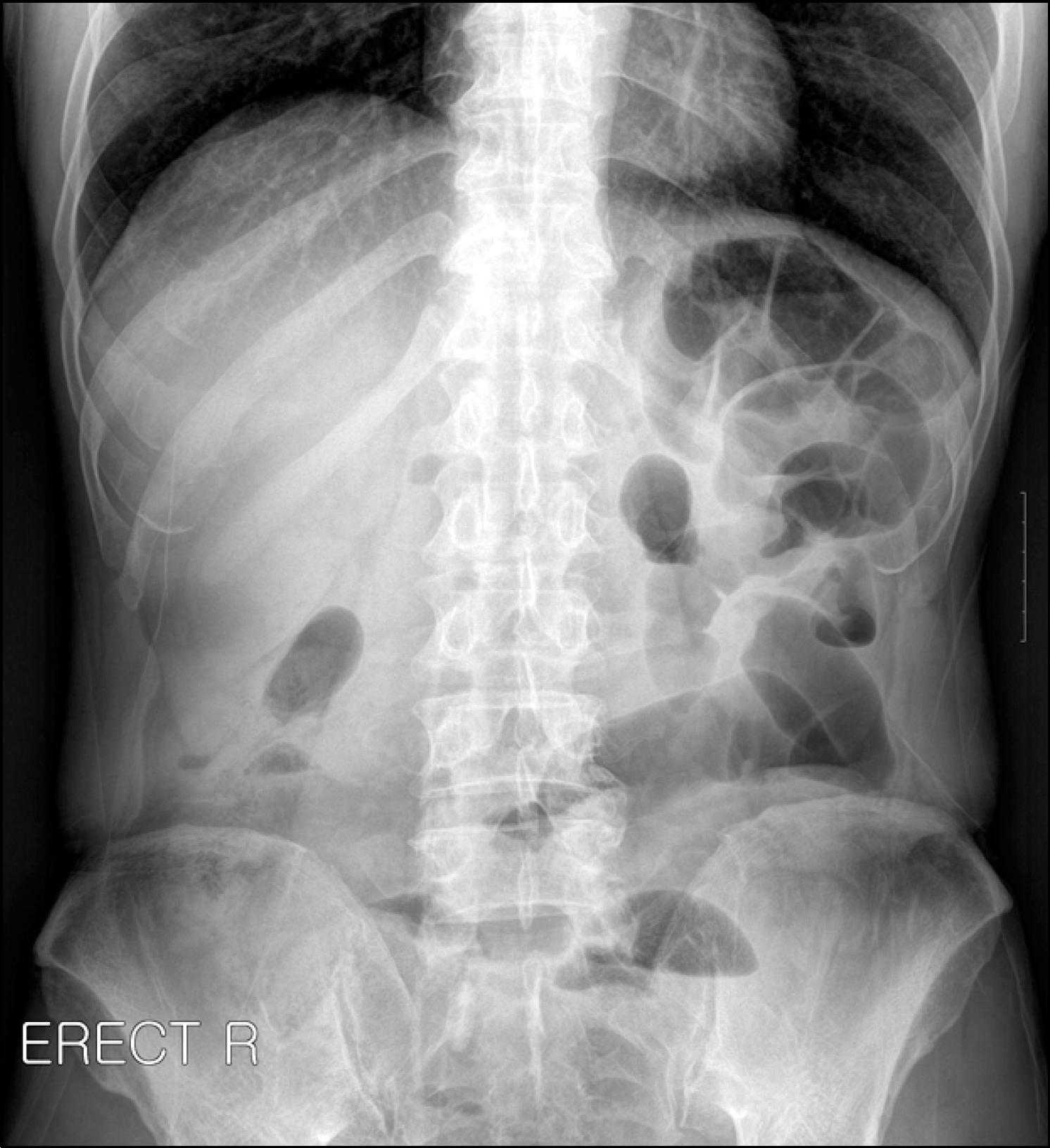
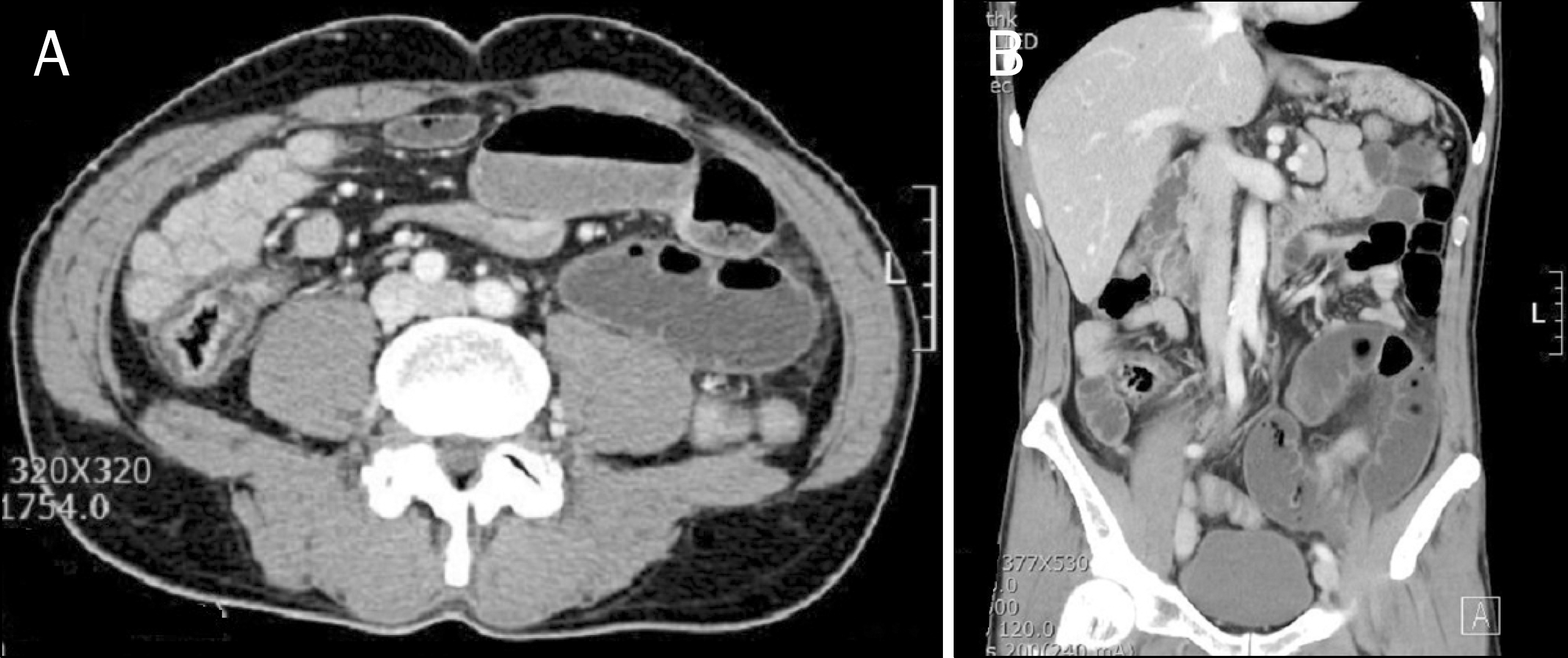
Fig. 2.
Preoperative abdominal CT scan findings. (A) Axial CT image shows fluid distended small bowel in the left lower quadrant. (B) This fluid distended small bowel loop is seen as a reverse C-shaped loop on coronal CT image.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download