Abstract
Background/Aims
Narrow band imaging (NBI) endoscopy can be used for gross differentiation between the types of colonic polyps. This study was conducted as a retrospective study for estimation of the interobserver and intraobserver agreement of the pit pattern of the mucosal surface and the accuracy of histology prediction.
Methods
A total of 159 patients underwent complete colonoscopy and 219 polyps examined by NBI endoscopy without magnification were assessed. Interobserver and intraobserver agreement were calculated by investigators in each group for determination of the surface pattern and prediction of histology based on the modified Kudo's classification using intraclass correlation coefficient.
Results
Interobserver agreement for the surface pit pattern and prediction of polyp type was 0.84 and 0.73 in experienced endoscopists, and 0.86 and 0.62 in trainees, respectively. Intra-observer agreement for the surface pit patterns and prediction of polyp type was 0.81, 0.83, 0.85, 0.83, 0.56, 0.84, 0.51, 0.83, and 0.71; and 0.71, 0.70, 0.82, 0.54, 0.72, 0.37, 0.51, 0.34, and 0.30, respectively. The diagnostic accuracy for prediction of polyp type was 69.4% for experienced endoscopists and 72.9% for trainees.
Conclusions
NBI endoscopy without magnification showed fairly good inter and intraobserver agreement for the pit pattern of the mucosal surface and the accuracy of histology prediction; however, it had some limitation for differentiation of colon polyp histologic type. Training and experience with NBI is needed for improvement of accuracy.
Go to : 
References
1. Huang Q, Fukami N, Kashida H, et al. Interobserver and intraobserver consistency in the endoscopic assessment of colonic pit patterns. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 60:520–526.

2. Muto M, Horimatsu T, Ezoe Y, et al. Narrow-band imaging of the gastrointestinal tract. J Gastroenterol. 2009; 44:13–25.

3. Larghi A, Lecca PG, Costamagna G. High-resolution narrow band imaging endoscopy. Gut. 2008; 57:976–986.

4. Su MY, Hsu CM, Ho YP, Chen PC, Lin CJ, Chiu CT. Comparative study of conventional colonoscopy, chromoendoscopy, and nar-row-band imaging systems in differential diagnosis of neoplastic and nonneoplastic colonic polyps. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:2711–2716.

5. Machida H, Sano Y, Hamamoto Y, et al. Narrow-band imaging in the diagnosis of colorectal mucosal lesions: a pilot study. Endoscopy. 2004; 36:1094–1098.

6. East JE, Suzuki N, Saunders BP. Comparison of magnified pit pattern interpretation with narrow band imaging versus chromoendoscopy for diminutive colonic polyps: a pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:310–316.

7. Rastogi A, Pondugula K, Bansal A, et al. Recognition of surface mucosal and vascular patterns of colon polyps by using nar-row-band imaging: interobserver and intraobserver agreement and prediction of polyp histology. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69:716–722.

8. Tischendorf JJ, Wasmuth HE, Koch A, Hecker H, Trautwein C, Winograd R. Value of magnifying chromoendoscopy and narrow band imaging (NBI) in classifying colorectal polyps: a prospective controlled study. Endoscopy. 2007; 39:1092–1096.

9. Kudo S, Hirota S, Nakajima T, et al. Colorectal tumours and pit pattern. J Clin Pathol. 1994; 47:880–885.

10. Kudo S, Tamura S, Nakajima T, Yamano H, Kusaka H, Watanabe H. Diagnosis of colorectal tumorous lesions by magnifying endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996; 44:8–14.

11. Singh R, Owen V, Shonde A, Kaye P, Hawkey C, Ragunath K. White light endoscopy, narrow band imaging and chromoendoscopy with magnification in diagnosing colorectal neoplasia. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 1:45–50.

12. Singh R, Nordeen N, Mei SL, Kaffes A, Tam W, Saito Y. West meets East: preliminary results of narrow band imaging with optical magnification in the diagnosis of colorectal lesions: a multicenter Australian study using the modified Sano's classification. Dig Endosc. 2011; 23(Suppl 1):126–130.

13. Wada Y, Kashida H, Kudo SE, Misawa M, Ikehara N, Hamatani S. Diagnostic accuracy of pit pattern and vascular pattern analyses in colorectal lesions. Dig Endosc. 2010; 22:192–199.

14. Wada Y, Kudo SE, Kashida H, et al. Diagnosis of colorectal lesions with the magnifying narrow-band imaging system. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 70:522–531.

15. East JE, Suzuki N, Bassett P, et al. Narrow band imaging with magnification for the characterization of small and diminutive colonic polyps: pit pattern and vascular pattern intensity. Endoscopy. 2008; 40:811–817.

16. Rastogi A, Bansal A, Wani S, et al. Narrow-band imaging colonoscopy–a pilot feasibility study for the detection of polyps and correlation of surface patterns with polyp histologic diagnosis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 67:280–286.
17. Uraoka T, Saito Y, Matsuda T, et al. Detectability of colorectal neoplastic lesions using a narrow-band imaging system: a pilot study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008; 23:1810–1815.

18. Mayinger B, Oezturk Y, Stolte M, et al. Evaluation of sensitivity and inter- and intraobserver variability in the detection of intestinal metaplasia and dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus with enhanced magnification endoscopy. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2006; 41:349–356.

19. Endo T, Awakawa T, Takahashi H, et al. Classification of Barrett's epithelium by magnifying endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 55:641–647.

20. Matsumoto T, Kudo T, Jo Y, Esaki M, Yao T, Iida M. Magnifying colonoscopy with narrow band imaging system for the diagnosis of dysplasia in ulcerative colitis: a pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:957–965.
21. Yao K, Anagnostopoulos GK, Jawhari AU, Kaye PV, Hawkey CJ, Ragunath K. Optical microangiography: high-definition magnification colonoscopy with narrow band imaging (NBI) for visualizing mucosal capillaries and red blood cells in the large intestine. Gut Liver. 2008; 2:14–18.

22. Sakamoto T, Saito Y, Nakajima T, Matsuda T. Comparison of magnifying chromoendoscopy and narrow-band imaging in estimation of early colorectal cancer invasion depth: a pilot study. Dig Endosc. 2011; 23:118–123.

23. Zhou QJ, Yang JM, Fei BY, Xu QS, Wu WQ, Ruan HJ. Narrow-band imaging endoscopy with and without magnification in diagnosis of colorectal neoplasia. World J Gastroenterol. 2011; 17:666–670.

24. Higashi R, Uraoka T, Kato J, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of nar-row-band imaging and pit pattern analysis significantly improved for less-experienced endoscopists after an expanded training program. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 72:127–135.

25. Ignjatovic A, Thomas-Gibson S, East JE, et al. Development and validation of a training module on the use of narrow-band imaging in differentiation of small adenomas from hyperplastic colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 73:128–133.

26. Rogart JN, Jain D, Siddiqui UD, et al. Narrow-band imaging without high magnification to differentiate polyps during real-time colonoscopy: improvement with experience. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 68:1136–1145.

Go to : 
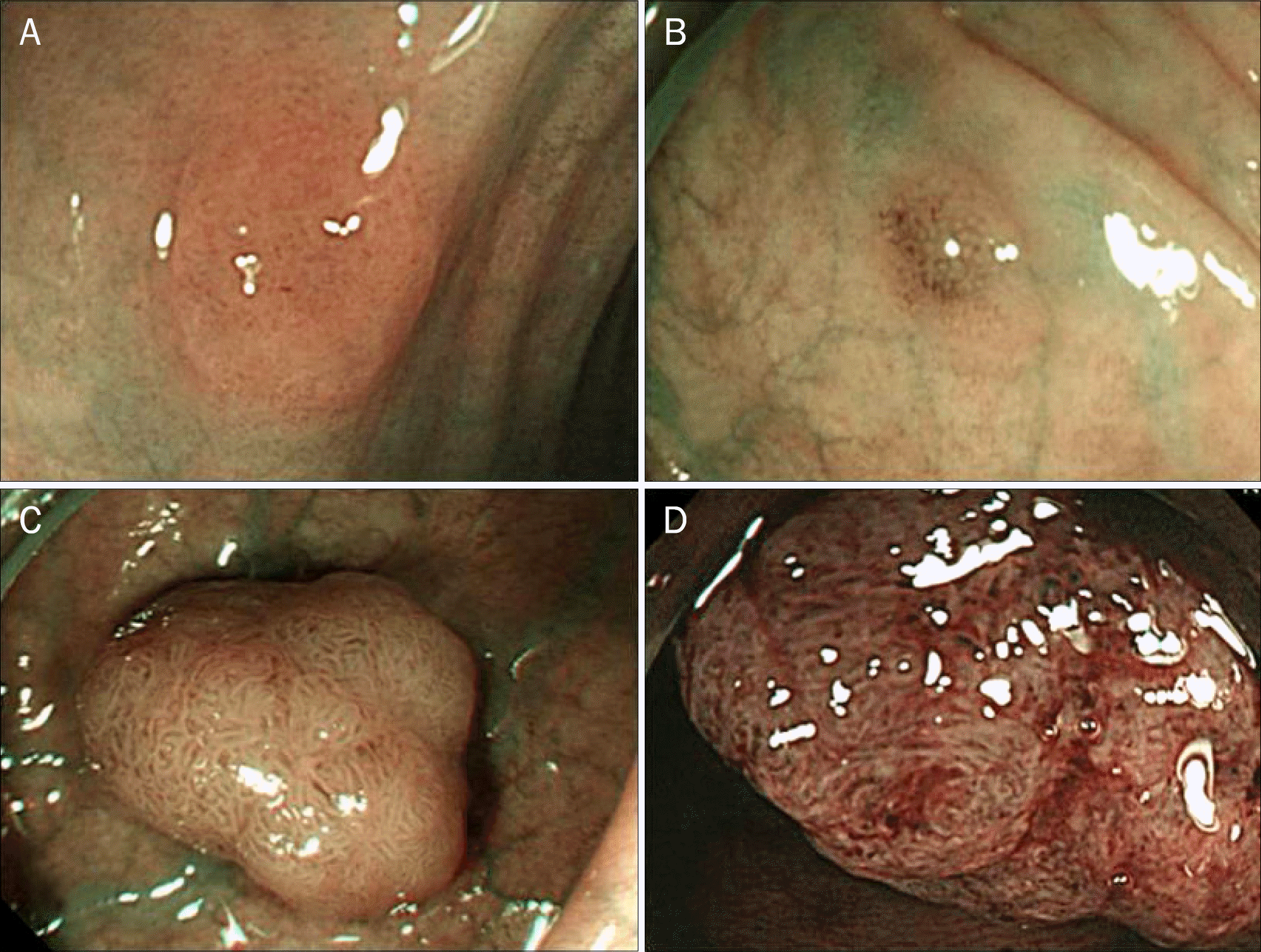 | Fig. 1.Polyp pattern on narrow banding imaging (whitish color). (A) Circular pattern with dots. (B) Round-oval pattern. (C) Tubulogyrus pattern.(D) Irregular pattern. |
Table 1.
Polyp Patterns by Narrow Banding Imaging Colonoscopy7
| Type 2 | Type 3 | Type 4 | Type 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pattern type | Circular pattern with dots | Round/oval | Tubulogyrus | Irregular/ sparse |
| Histology | Hyperplasia | Adenoma | Adenoma | Adenocar cinoma |
Table 2.
Characteristics of Colon Polyps Assessed by Narrow Band Imaging
| Investigator | Size (mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <5 | 6–10 | >11 | Total | |
| Hyperplasia | 3 | 3 | 1 | 7 |
| Adenoma (serrated adenoma) | 50 (1) | 111 (6) | 46 (1) | 205 (8) |
| Carcinoma | 0 | 0 | 7 | 7 |
| Total | 53 | 114 | 54 | 219 |
Table 3.
Interobserver Agreement for Pit Pattern and Differentiation of Polyp Type
| Investigator | Intraclass correlation coefficient | |
|---|---|---|
| Pit pattern | Polyp histologic type | |
| Experienced (n=3) | 0.84 | 0.73 |
| Trainees (n=6) | 0.86 | 0.62 |
Table 4.
Intra-observer Agreement for Pit Pattern and Differentiation of Polyp Type
| Investigator | Intraclass correlation coefficient | |
|---|---|---|
| Pit pattern | Polyp histologic type | |
| E1 | 0.81 | 0.71 |
| E2 | 0.83 | 0.70 |
| E3 | 0.85 | 0.82 |
| T1 | 0.83 | 0.54 |
| T2 | 0.56 | 0.72 |
| T3 | 0.84 | 0.37 |
| T4 | 0.51 | 0.51 |
| T5 | 0.83 | 0.34 |
| T6 | 0.71 | 0.30 |
Table 5.
Diagnostic Accuracy for Differentiation of Polyp Type Based on Pit Pattern
Table 6.
Diagnostic Accuracy for Differentiation of Polyp Type according to Size




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download