Abstract
IgG4-related systemic diseases are characterized by a diffuse or mass forming inflammatory reaction rich in lymphocytes and IgG4-positive plasma cells (lymphoplasmacytic infiltration), fibrosclerosis of variable organs and obliterative phlebitis. They usually involve various organs including the pancreas, bile duct, gallbladder, salivary gland, retroperitoneum, kidney, lung, and prostate. However, most of them are accompanied by autoimmune pancreatitis, and good response to steroid treatment is one of the hallmarks of this disease. We report a case of an 67-year-old man with IgG4 associated sclerosing cholangitis, who was diagnosed by endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and successfully treated with steroid therapy.
References
1. Divatia M, Kim SA, Ro JY. IgG4-related sclerosing disease, an emerging entity: a review of a multi-system disease. Yonsei Med J. 2012; 53:15–34.

2. Maillette de Buy Wenniger L, Rauws EA, Beuers U. What an endoscopist should know about immunoglobulin-G4-associated disease of the pancreas and biliary tree. Endoscopy. 2012; 44:66–73.

3. Kamisawa T, Okamoto A. IgG4-related sclerosing disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2008; 14:3948–3955.

4. Alderlieste YA, van den Elzen BD, Rauws EA, Beuers U. Immunoglobulin G4-associated cholangitis: one variant of immunoglobulin G4-related systemic disease. Digestion. 2009; 79:220–228.

5. Hyun JJ, Lee HS. Etiology, pathogenesis and natural course of chronic pancreatitis. Korean J Med. 2012; 83:1–17.

6. Montefusco PP, Geiss AC, Bronzo RL, Randall S, Kahn E, McKinley MJ. Sclerosing cholangitis, chronic pancreatitis, and Sjogren's syndrome: a syndrome complex. Am J Surg. 1984; 147:822–826.

7. Erkelens GW, Vleggaar FP, Lesterhuis W, van Buuren HR, van der Werf SD. Sclerosing pancreato-cholangitis responsive to steroid therapy. Lancet. 1999; 354:43–44.

8. Ghazale A, Chari ST, Smyrk TC, et al. Value of serum IgG4 in the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis and in distinguishing it from pancreatic cancer. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; 102:1646–1653.

9. Björnsson E, Chari ST, Smyrk TC, Lindor K. Immunoglobulin G4 associated cholangitis: description of an emerging clinical entity based on review of the literature. Hepatology. 2007; 45:1547–1554.

10. Ghazale A, Chari ST, Zhang L, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-associ-ated cholangitis: clinical profile and response to therapy. Gastroenterology. 2008; 134:706–715.

11. Jang JW, Kim MH, Kim TG, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-associated sclerosing cholangitis mimicking hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Korean J Pancreatobiliary. 2012; 17:44–46.
12. Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:732–738.

13. Vosskuhl K, Negm AA, Framke T, et al. Measurement of IgG4 in bile: a new approach for the diagnosis of IgG4-associated cholangiopathy. Endoscopy. 2012; 44:48–52.

14. Sepehr A, Mino-Kenudson M, Ogawa F, Brugge WR, Deshpande V, Lauwers GY. IgG4+ to IgG+ plasma cells ratio of ampulla can help differentiate autoimmune pancreatitis from other "mass forming" pancreatic lesions. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008; 32:1770–1779.

15. Sah RP, Chari ST, Pannala R, et al. Differences in clinical profile and relapse rate of type 1 versus type 2 autoimmune pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2010; 139:140–148.

16. Kamisawa T, Shimosegawa T, Okazaki K, et al. Standard steroid treatment for autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut. 2009; 58:1504–1507.

Fig. 1.
Abdominal CT findings. (A) Initial coronal CT scan showed diffusely enhancing ductal wall which was thickened from the intrahepatic duct to proximal common bile duct (arrow). (B) Follow up CT scan after 2 months of steroid treatment showed ductal wall thickening of the biliary tree improved (arrow). (C) The pancreas initially appeared swollen and somewhat enlarged in the axial scan of abdominal CT. (D) After steroid treatment, the size of the pancreas decreased compared to initial CT scan. However, there was no other evidence of pancreatitis.

Fig. 2.
EUS findings. Diffuse wall thickening of the common bile duct was noted on the EUS. The wall seemed to be hypoechoic, homogenous and smooth.
Fig. 3.
ERCP findings. (A) Initial ERCP cholangiogram demonstrated diffuse and relatively irregular stricture of the intrahepatic duct and common hepatic duct. (B) After 2 months of steroid treatment, narrowings of the common and intrahepatic bile duct were resolved.
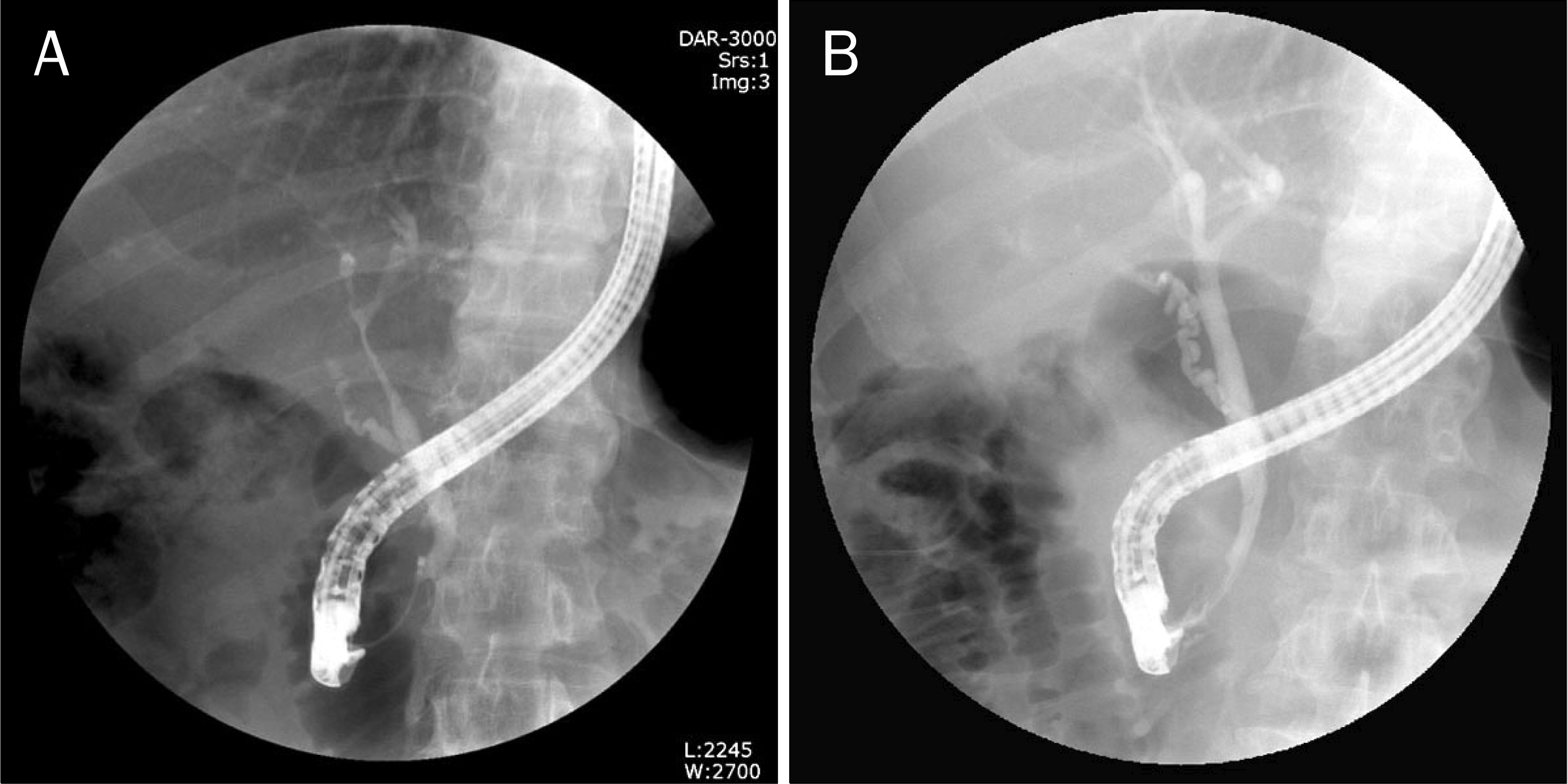
Fig. 4.
Pathologic findings. Photos of H&E stain and IgG4 immunohistochemical stain of bile ductal tissue which were retrieved during ERCP. (A) H&E stain showed diffusely infiltrated inflammatory cells and some plasma cells were observed among numerous lymphocytes (×400). (B) Before steroid treatment, plasma cells were strongly stained by IgG4 immunochemical stain (×400). (C) After 2 months of steroid treatment, lymphocytes and plasma cells were not seen (H&E, ×100). (D) IgG4 immunohistochemical stain was also negative (×100).





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download