References
1. Katsura M, Mototake H, Takara H, Matsushima K. Management of spontaneous isolated dissection of the superior mesenteric artery: case report and literature review. World J Emerg Surg. 2011; 6:16.

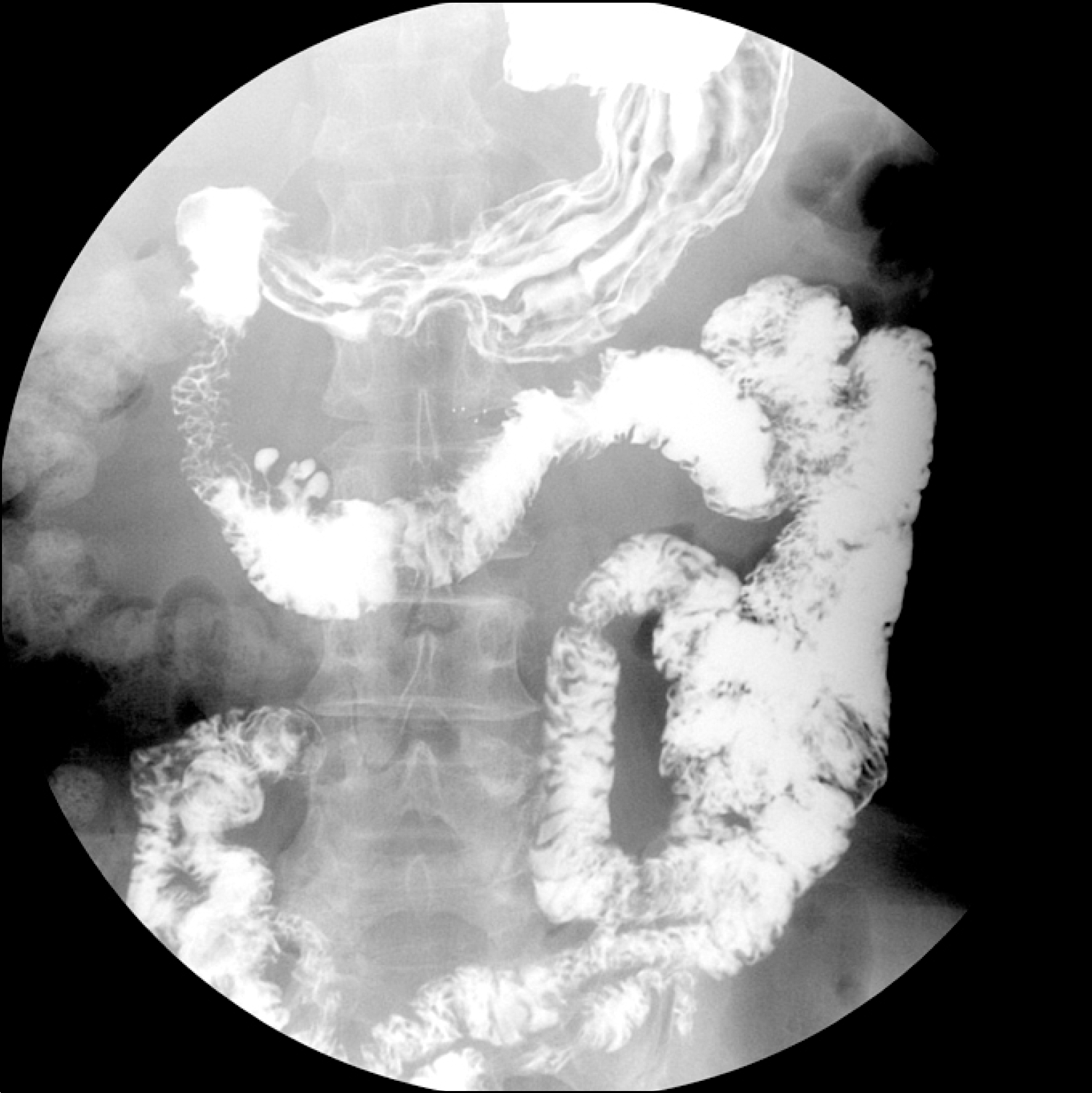
Fig. 1.
Abdominal CT scan reveals marked distension of stomach and duodenum (A, B), and narrowing of proximal jejunum (C). (D) An 8×6 mm-sized thrombus is seen within the proximal superior mesenteric artery.

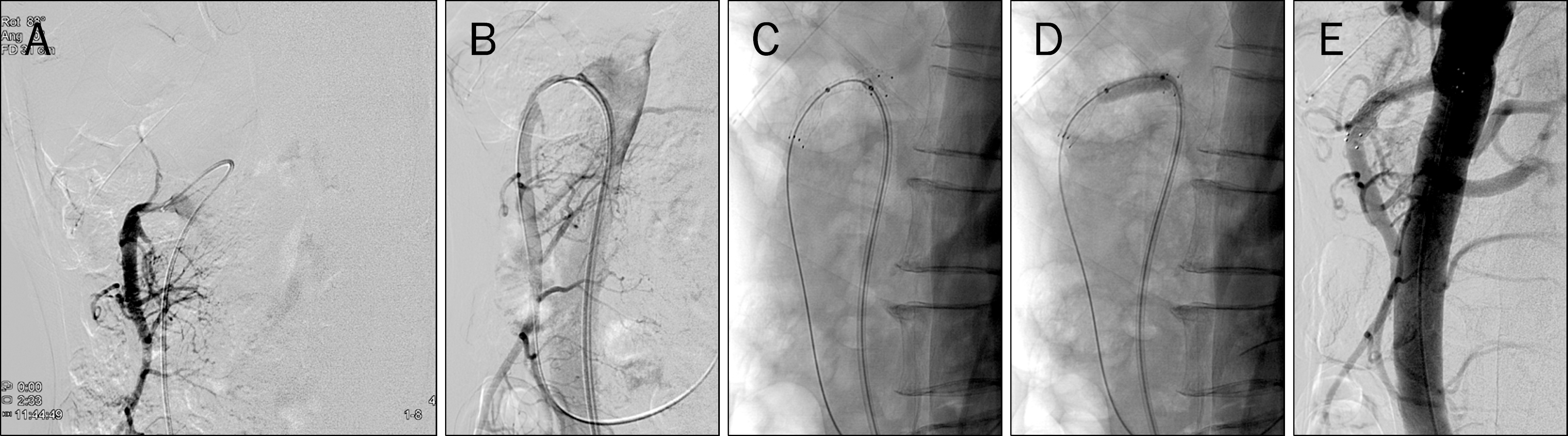
Fig. 2.
(A) Angiography shows moderate and eccentric stenosis of the proximal superior mesenteric artery. (B) An 8 Fr guiding catheter was inserted into arterial sheath over the 0.035 Fr guidewire and its tip was placed within the proximal portion of the superior mesenteric artery.(C, D) The stenotic site was dilated and an 8×40 mm self expandable stent (Zilver; Cook Medical, Bloomington, IN, USA) was inserted which was expanded wtih 6×20 mm balloon (Foxcross; Abbott Vascular, Abbott Park, IL, USA). (E) Follow-up renal arteriography reveals well positioned stent with patent superior mesenteric artery lumen.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download