Abstract
Mucinous gastric carcinoma (MGC) is an unusual histologic subtype, and early detection of MGC is very rare. Early-stage MGC appears as an elevated lesion resembling a submucosal tumor (SMT) due to abundant mucin pools in the submucosa or mucosa. We report a rare case of SMT-like early-stage MGC. Tumor type was predicted preoperatively based on characteristic endoscopic findings, in which an SMT-like mass was observed at the gastric fundus. The tumor was covered by nearly normal mucosa, but with an opening allowing for the passage of copious mucus discharge. A total gastrectomy with Roux-en-Y esophagojejunostomy was subsequently performed. Histopathology of the tumor revealed early-stage (lamina propria) mucinous adenocarcinoma.
Go to : 
References
1. Kawamura H, Kondo Y, Osawa S, et al. A clinicopathologic study of mucinous adenocarcinoma of the stomach. Gastric Cancer. 2001; 4:83–86.

2. Fang WL, Wu CW, Lo SS, et al. Mucin-producing gastric cancer: clinicopathological difference between signet ring cell carcinoma and mucinous carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 2009; 56:1227–1231.
3. Adachi Y, Mori M, Kido A, Shimono R, Maehara Y, Sugimachi K. A clinicopathologic study of mucinous gastric carcinoma. Cancer. 1992; 69:866–871.

4. Wu CY, Yeh HZ, Shih RT, Chen GH. A clinicopathologic study of mucinous gastric carcinoma including multivariate analysis. Cancer. 1998; 83:1312–1318.

5. Yasuda K, Shiraishi N, Inomata M, Shiroshita H, Ishikawa K, Kitano S. Clinicopathologic characteristics of early-stage mucinous gastric carcinoma. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2004; 38:507–511.

Go to : 
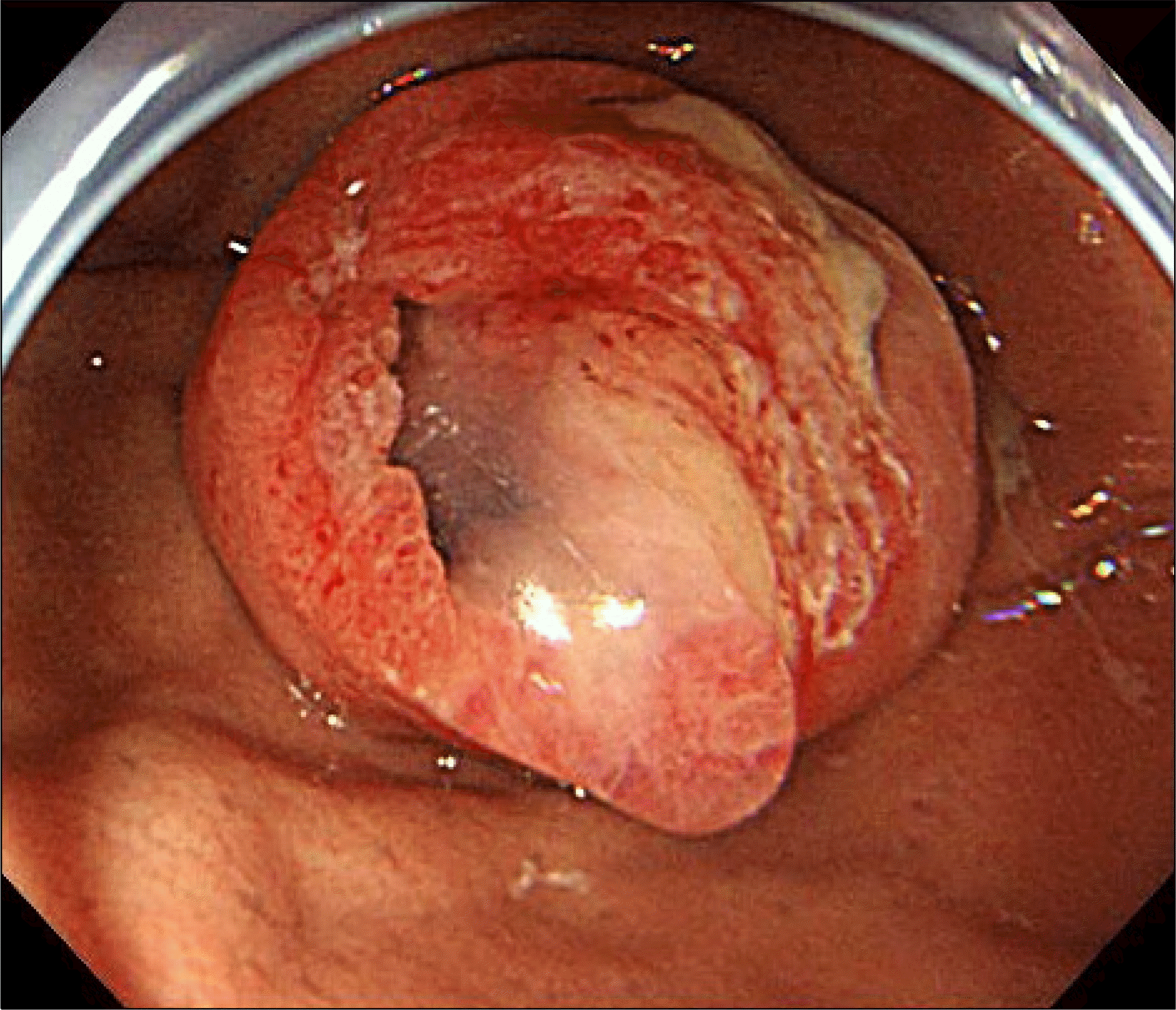 | Fig. 1.Esophagogastroduodenoscopy showed a submucosal tumor-like mass at the gastric fundus. The mass was covered by nearly normal mucosa, with an opening allowing for the passage of copious mucus discharge. |
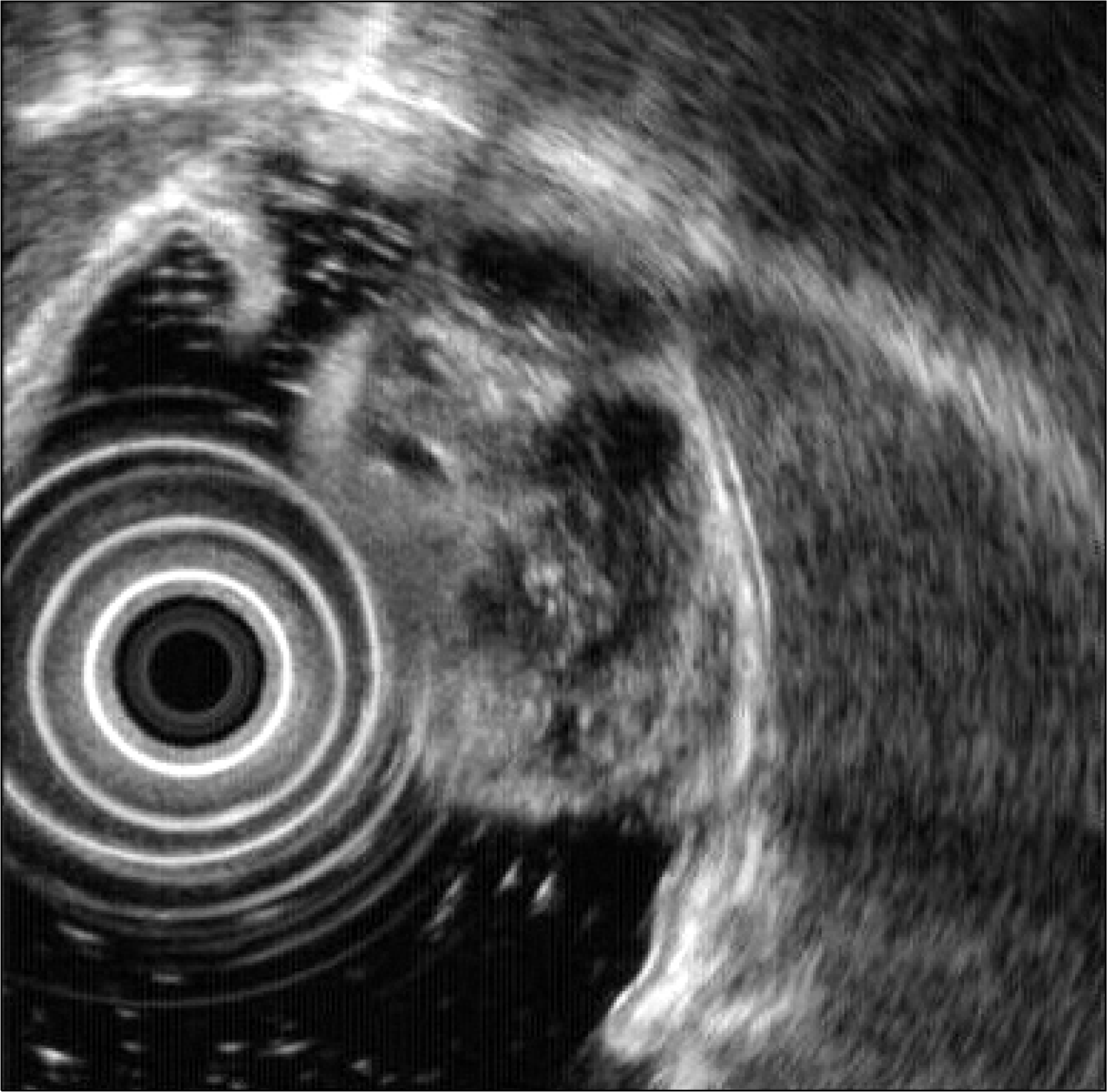 | Fig. 2.Radial endoscopic ultrasound findings. A 26×23 mm round, elevated, heterogenous and hyperechoic mass with multiple anechoic cystic spaces was observed. The lesion did not invade into the submucosal layer. |
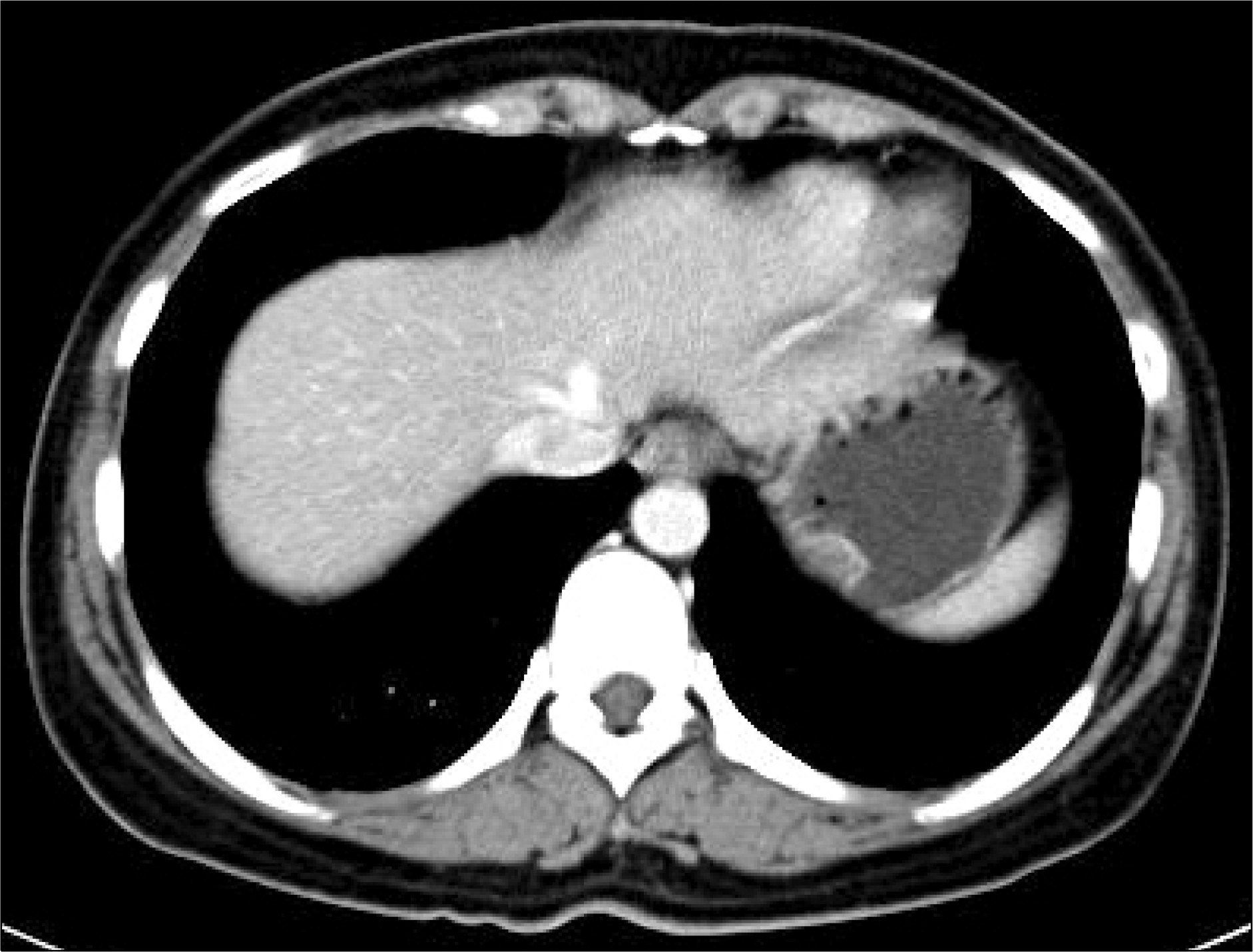 | Fig. 3.Contrast-enhanced abdominal CT scan revealed a 25×23 mm polypoid intraluminal mass with heterogenous enhancement and partial mucosal irregularity at the gastric fundus. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download