Abstract
Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is one of the most effective therapies for unresectable hepatocelluar carcinoma or metastatic hypervascular tumors. Abscess occurring in the other organs beside the liver after TACE is a complication that often occurs, sometimes potentially fatal. We report a case of spinal epidural abscess occurred after liver abscess complicated by TACE in a patient with metastatic neuroendocrine tumors to the liver. A 67-year-old female underwent TACE first for the metastatic lesions to liver, with a history of pancreatoduodenectomy for the primary pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. Four days after TACE, sudden high fever occurred, and liver abscess was found on abdominal CT. Two days later, back pain and radiating pain to the right leg occurred, and lumbar spine MRI showed spinal epidural abscess. After intravenous antibiotics for 8 weeks and partial laminectomy, the patient recovered and was discharged without complications.
Go to : 
References
1. Robert TJ. Chapter 350: endocrine tumors of the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas. Charles W, Fauci A, editors. Harrison's principles of internal medicine: self-assessment and board review. Volume 2. 18th ed.New York: McGraw-Hill;2012. p. 3060–3061.
2. Llovet JM, Bruix J. Systematic review of randomized trials for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Chemoembolization improves survival. Hepatology. 2003; 37:429–442.

3. Paik YH, Chon CY, Cho JY, et al. Risk factors of acute hepatic failure associated with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Med. 2005; 69:622–630.
4. Ho AS, Picus J, Darcy MD, et al. Longterm outcome after chemoembolization and embolization of hepatic metastatic lesions from neuroendocrine tumors. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007; 188:1201–1207.

5. Xia J, Ren Z, Ye S, et al. Study of severe and rare complications of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) for liver cancer. Eur J Radiol. 2006; 59:407–412.

6. Choi BI, Kim CY, Lee HS, et al. A study on complications of chemoembolization of hepatic neoplasms. J Korean Radiol Soc. 1994; 31:839–845.

7. Han SY. Single topic symposium: Liver abscess. Korean J Hepatol. 2006; 12(Suppl 1):5–17.
8. Gates J, Hartnell GG, Stuart KE, Clouse ME. Chemoembolization of hepatic neoplasms: safety, complications, and when to worry. Radiographics. 1999; 19:399–414.

9. Kim W, Clark TW, Baum RA, Soulen MC. Risk factors for liver abscess formation after hepatic chemoembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001; 12:965–968.

10. Gyu J, KIM JW, Kim SJ, et al. A case of necrotizing liver abscess and bile duct necrosis following hepatic arterial chemoembolization in hepatocelluar carcinoma. Korean J Hepatol. 1999; 5:348–352.
11. Reihsaus E, Waldbaur H, Seeling W. Spinal epidural abscess: a metaanalysis of 915 patients. Neurosurg Rev. 2000; 23:175–204.

12. Huang CR, Lu CH, Chuang YC, et al. Clinical characteristics and therapeutic outcome of Gram-negative bacterial spinal epidural abscess in adults. J Clin Neurosci. 2011; 18:213–217.

13. Hsieh MJ, Lu TC, Ma MH, Wang HP, Chen SC. Unrecognized cervical spinal epidural abscess associated with metastatic Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia and liver abscess in non-diabetic patients. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009; 65:65–68.

14. Kuramochi G, Takei SI, Sato M, Isokawa O, Takemae T, Takahashi A. Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess associated with septic spinal epidural abscess. Hepatol Res. 2005; 31:48–52.
15. Cho TH, Kang SH, Park JY, Kwon TH, Chung YG, Lee HK. Brain abscess after hepatic artery chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: case report. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 1998; 27:511–515.
16. Woo SG, Jung SW, Kim BS, et al. A case of hepatopleural fistula complicated by transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma with liver abscess. Korean J Med. 2002; 62:278–284.
Go to : 
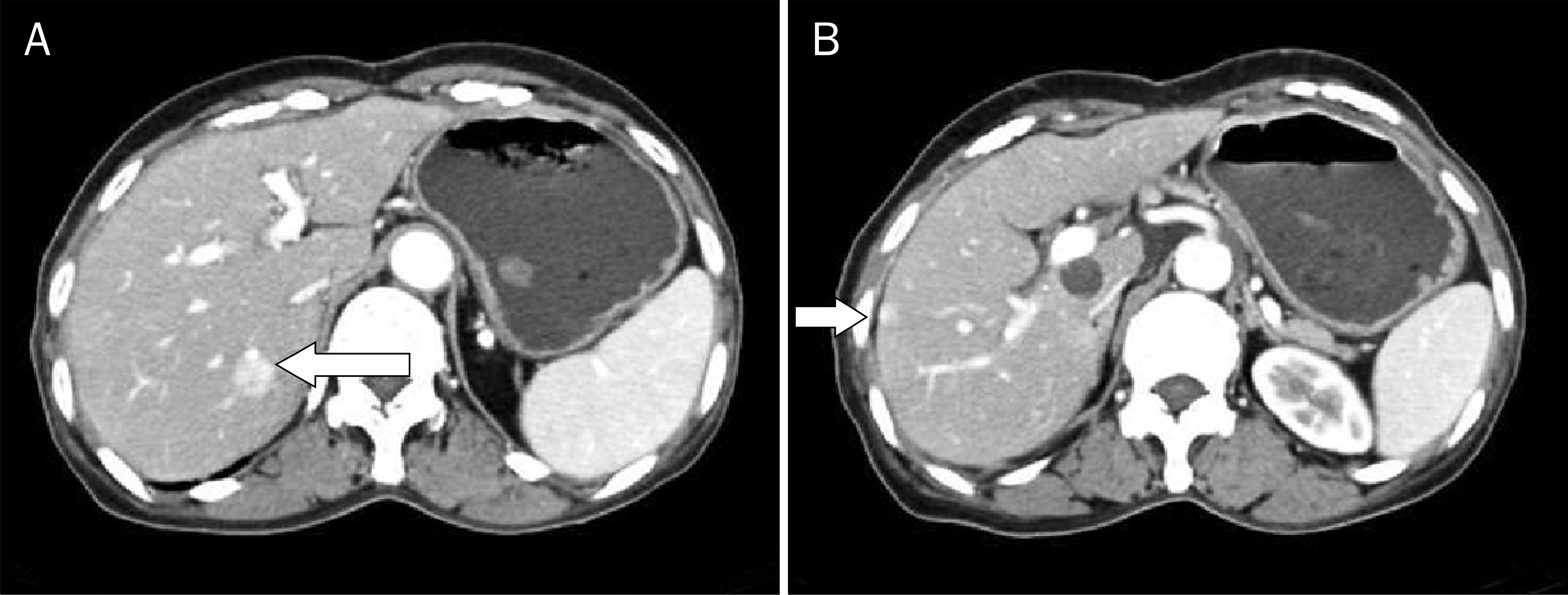
 | Fig. 1.A mass (6.3×5.1 cm; arrow) with multifocal low attenuation areas was seen in the head of the pancreas at first visit. |
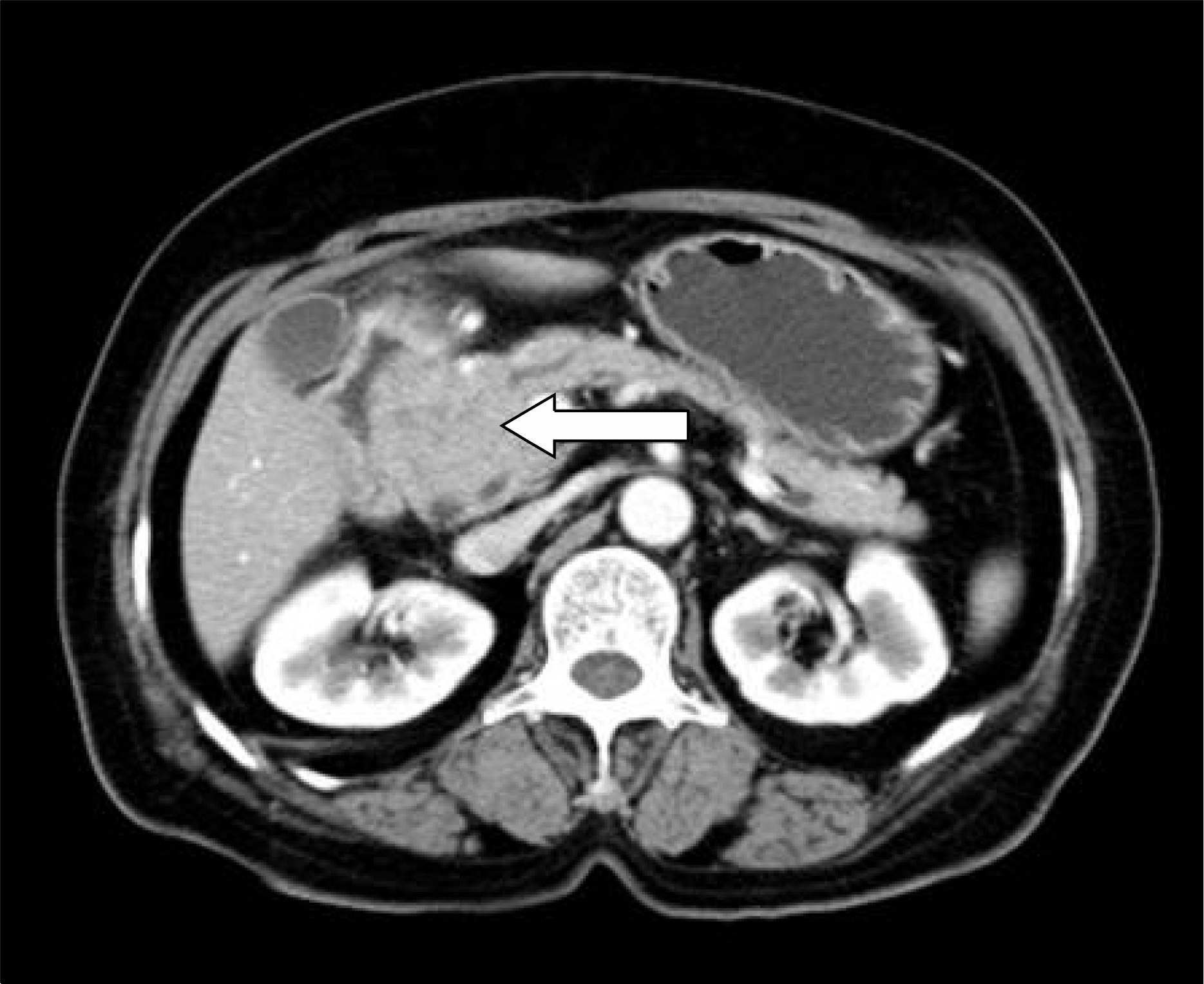
 | Fig. 2.Contrast-enhanced CT revealed hepatic metastatic lesions in the right lobe of the liver (arrow). |
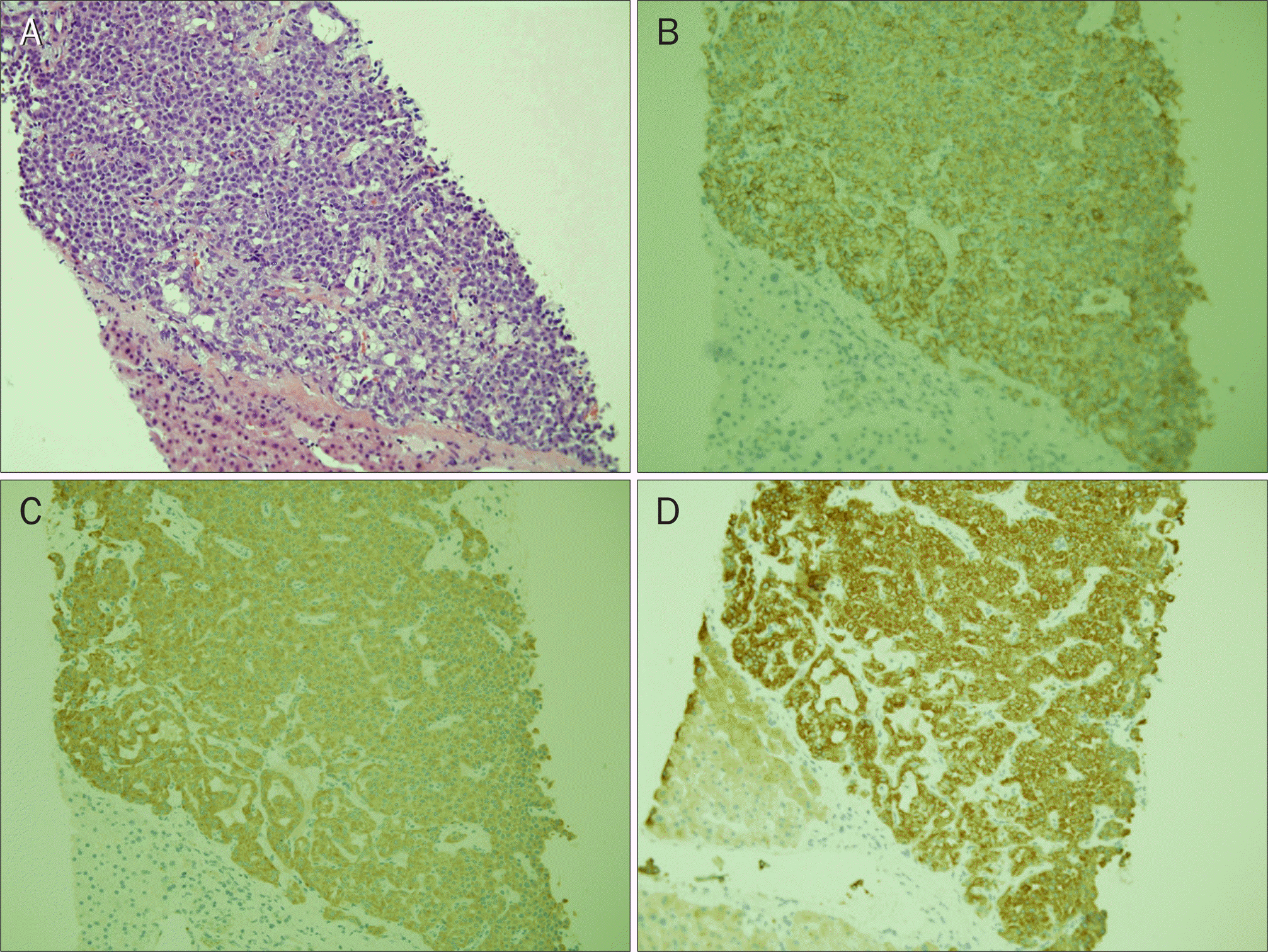 | Fig. 3.Liver biopsy showed (A) infiltration of round tumor cells which have uniform nuclei and monotonous in size (H&E, ×40). Tumor cell nests were strongly stained for CD 56 (B, ×200), synaptophysin (C, ×200), and pancytokeratin (D, ×200). |
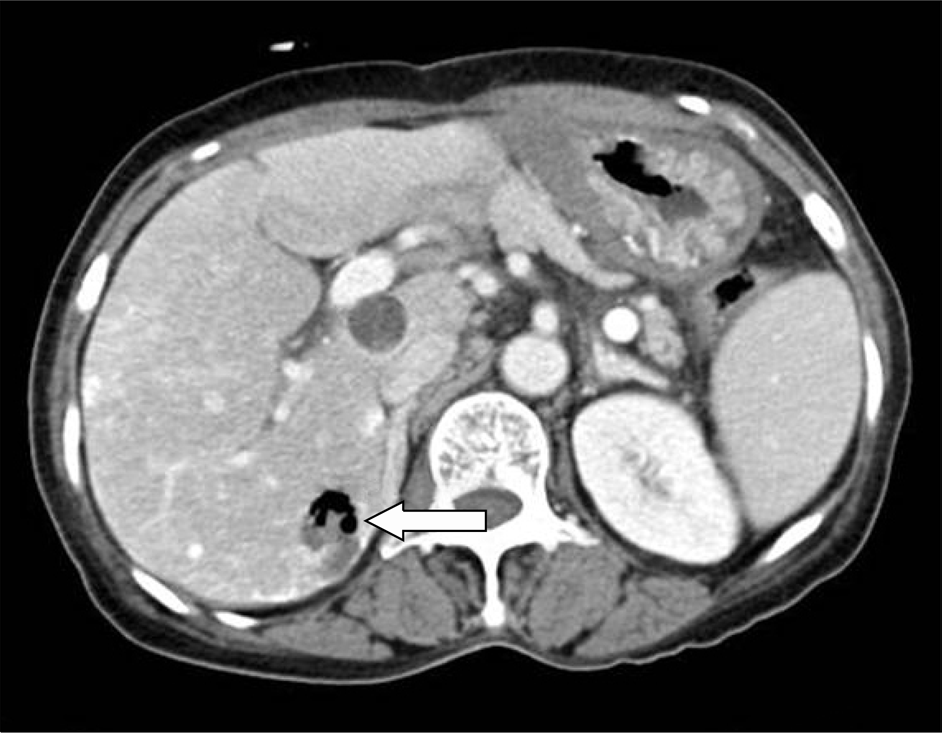 | Fig. 4.At 4 days after the transarterial chemoembolization, contrast-enhanced CT revealed a round-shaped necrotic lesion with abscess formation and air bubble (arrow). |
 | Fig. 5.(A, B) Spinal epidural abscess with spinal cord compression was seen at the L3/4 on a sagittal and axial contrast enhanced fat-sat T1 weighted MRI view (arrow). (C, D) Eight weeks after the treatment of antibiotics and operation, spinal epidural abscess was nearly subsided and spinal cord compression was improved on a sagittal and axial contrast enhanced fat-sat T1 weighted MRI view (arrow). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download