Abstract
Background/Aims
This study compared the clinical outcomes between endoscopic and radiologic placement of self-expandable metal stent (SEMS) in patients with malignant colorectal obstruction.
Methods
In total, 111 patients were retrospectively enrolled in this study between January 2003 and June 2011 at Seoul National University Boramae Hospital. Technical and clinical success rates, complication rates, and stent patency were compared between using an endoscopic (n=73) or radiologic (n=38) method during the SEMS placement procedure.
Results
The technical success rate was higher in the endoscopic method than in the radiologic method (100% [73/73] vs. 92.1% [35/38], respectively; p=0.038). In addition, in 3 of the remaining 35 patients in the radiologic-method group, adjuvant endoscopic assistance was required. In the six patients (including the three aforementioned patients), the causes of technical failure were the inability to pass the guidewire into an obstructive lesion due to a tortuous, curved angulation of the sigmoid or descending colon (n=4), and a difficult approach to a lesion located at the descending or transverse colon (n=2). The clinical success rate, complication rate, and stent patency did not differ significantly between the two methods (p=0.424, 0.303, and 0.423, respectively).
Conclusions
When the colorectal obstruction had a tortuous, curved angulation of the colon or was located at or proximal to the descending colon, the endoscopic method of SEMS placement appears to be more useful than the radiologic method. However, once SEMS placement was technically successful, the clinical success rate, complication rate, and stent patency did not differ with the method of insertion.
Go to : 
References
1. Baron TH. Colonic stenting: technique, technology, and outcomes for malignant and benign disease. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2005; 15:757–771.

2. Vitale MA, Villotti G, d'Alba L, Frontespezi S, Iacopini F, Iacopini G. Preoperative colonoscopy after self-expandable metallic stent placement in patients with acute neoplastic colon obstruction. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 63:814–819.

3. Mucci-Hennekinne S, Kervegant AG, Regenet N, et al. Management of acute malignant large-bowel obstruction with self-ex-panding metal stent. Surg Endosc. 2007; 21:1101–1103.

4. Sebastian S, Johnston S, Geoghegan T, Torreggiani W, Buckley M. Pooled analysis of the efficacy and safety of self-expanding metal stenting in malignant colorectal obstruction. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004; 99:2051–2057.

5. Small AJ, Coelho-Prabhu N, Baron TH. Endoscopic placement of self-expandable metal stents for malignant colonic obstruction: long-term outcomes and complication factors. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:560–572.

6. Jung MK, Park SY, Jeon SW, et al. Factors associated with the long-term outcome of a self-expandable colon stent used for palliation of malignant colorectal obstruction. Surg Endosc. 2010; 24:525–530.

7. Repici A, Adler DG, Gibbs CM, Malesci A, Preatoni P, Baron TH. Stenting of the proximal colon in patients with malignant large bowel obstruction: techniques and outcomes. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:940–944.

8. Kim H, Kim SH, Choi SY, et al. Fluoroscopically guided placement of self-expandable metallic stents and stent-grafts in the treatment of acute malignant colorectal obstruction. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2008; 19:1709–1716.

9. Khot UP, Lang AW, Murali K, Parker MC. Systematic review of the efficacy and safety of colorectal stents. Br J Surg. 2002; 89:1096–1102.

10. Watt AM, Faragher IG, Griffin TT, Rieger NA, Maddern GJ. Self-ex-panding metallic stents for relieving malignant colorectal obstruction: a systematic review. Ann Surg. 2007; 246:24–30.
11. Fan YB, Cheng YS, Chen NW, et al. Clinical application of self-ex-panding metallic stent in the management of acute left-sided colorectal malignant obstruction. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:755–759.

12. Baron TH, Rey JF, Spinelli P. Expandable metal stent placement for malignant colorectal obstruction. Endoscopy. 2002; 34:823–830.

13. Harris GJ, Senagore AJ, Lavery IC, Fazio VW. The management of neoplastic colorectal obstruction with colonic endolumenal stenting devices. Am J Surg. 2001; 181:499–506.

14. Baron TH, Dean PA, Yates MR 3rd, Canon C, Koehler RE. Expandable metal stents for the treatment of colonic obstruction: techniques and outcomes. Gastrointest Endosc. 1998; 47:277–286.

15. Turégano-fuentes F, Echenagusia-belda A, Simó-muerza G, et al. Transanal self-expanding metal stents as an alternative to palliative colostomy in selected patients with malignant obstruction of the left colon. Br J Surg. 1998; 85:232–235.

16. Wallis F, Campbell KL, Eremin O, Hussey JK. Self-expanding metal stents in the management of colorectal carcinoma–a preliminary report. Clin Radiol. 1998; 53:251–254.
17. Song HY, Shin JH, Lim JO, Kim TH, Lee GH, Lee SK. Use of a newly designed multifunctional coil catheter for stent placement in the upper gastrointestinal tract. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2004; 15:369–373.

18. Shin JH, He X, Lee JH, et al. Newly designed multifunctional coil catheter for gastrointestinal intervention: feasibility determined by experimental study in dogs. Invest Radiol. 2003; 38:796–801.
19. Kim TH, Song HY, Shin JH, et al. Usefulness of multifunctional gastrointestinal coil catheter for colorectal stent placement. Eur Radiol. 2008; 18:2530–2534.

20. Chang IS, Park SW, Hwang DY, et al. The efficacy of the coaxial technique using a 6-Fr introducer sheath in stent placement for treating the obstructions proximal to the descending colon. Korean J Radiol. 2011; 12:107–112.

21. Baraza W, Lee F, Brown S, Hurlstone DP. Combination endo-radiological colorectal stenting: a prospective 5-year clinical evaluation. Colorectal Dis. 2008; 10:901–906.

Go to : 
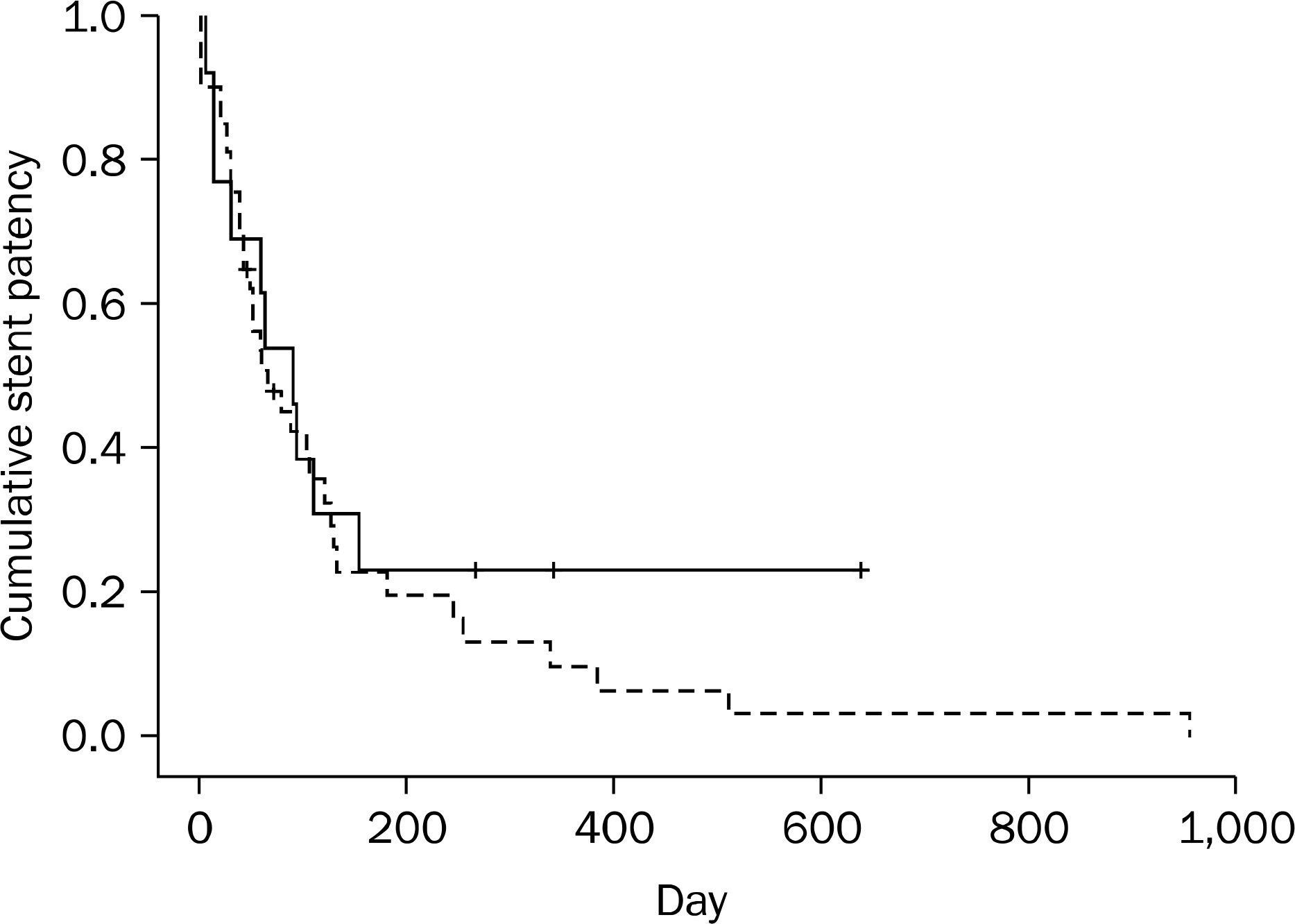 | Fig. 1.Cumulative rates for stent patency duration between the endoscopic (dotted line) and radiologic (solid line) methods (p=0.423). |
Table 1.
Baseline Characteristics of the Patients with Malignant Colorectal Obstruction according to the Method of Stent Placement
| Characteristic | Endoscopic method (n=73) | Radiologic method (n=38) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male/female) | 38/35 (52.1/47.9) | 23/15 (60.5/39.5) | 0.395 |
| Age (yr) | 67.0±13.0 (33–91) | 67.2±11.4 (38–85) | 0.929 |
| Locations of obstruction | 0.260 a | ||
| Left colon | 66 (90.4) | 37 (97.4) | |
| Rectum | 15 (20.5) | 9 (23.7) | |
| Sigmoid | 43 (58.9) | 26 (68.4) | |
| Descending | 8 (11.0) | 2 (5.3) | |
| Right colon | 7 (9.6) | 1 (2.7) | |
| Transverse | 5 (6.8) | 1 (2.6) | |
| Ascending | 2 (2.7) | 0 | |
| Stages | 0.748 | ||
| No metastasis | 38 (52.1) | 21 (55.3) | |
| Metastasis | 35 (47.9) | 17 (44.7) | |
| Carcinomatosis | 0.427 | ||
| Absent | 62 (84.9) | 30 (78.9) | |
| Present | 11 (15.1) | 8 (21.1) | |
| Etiology | 1.000 b | ||
| Intrinsic | 68 (93.2) | 36 (94.7) | |
| Extrinsic | 5 (6.8) | 2 (5.3) | |
| Gastric | 3 (60.0) | 2 (100.0) | |
| Gynecologic | 2 (40.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Purposes of stenting | 0.054 | ||
| Palliative | 39 (53.4) | 13 (34.2) | |
| Preoperative | 34 (46.6) | 25 (65.8) | |
| Length of obstruction (mm) | 39.4±14.1 | 44.2±17.3 | 0.125 |
| Types of inserted stent | 0.086 | ||
| Uncovered | 59 (80.8) | 23 (65.7) | |
| Covered | 14 (19.2) | 12 (34.3) | |
| Diameter of stent (mm) | 23.2±1.6 | 23.3±2.7 | 0.916 |
| Length of stent (mm) | 103.0±28.4 | 102.3±21.6 | 0.894 |
| No. of inserted stents at presentation | 0.658 | ||
| One | 70 (95.9) | 33 (94.3) | |
| Two | 3 (4.1) | 2 (5.7) | |
| Total procedure time (min) Palliative chemotherapy c | 25±15 n=39 | 31±15 n=13 | 0.066 0.733 |
| Yes | 12 (30.8) | 3 (23.1) | |
| No | 27 (69.2) | 10 (76.9) |
Table 2.
Technical and Clinical Success Rates, and Causes of Te chnical and Clinical Failures
| Endoscopic method | Radiologic method | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technical success | 73 (100) | 35 (92.1) | 0.038 |
| Causes of technical failure | |||
| Inability to pass guidewire | 0 (0.0) | 2 (5.3) | 0.115 |
| Approach difficulties | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.6) | 0.342 |
| Clinical success | 67 (91.8) | 34 (97.1) a | 0.424 |
| Causes of clinical failure | |||
| Incomplete expansion | 2 (2.7) | 1 (2.9) | 1.000 |
| Additional obstruction | 1 (1.4) | 0 (0.0) | 1.000 |
| Perforation | 2 (2.7) | 0 (0.0) | 1.000 |
| Migration | 1 (1.4) | 0 (0.0) | 1.000 |
Table 3.
Complications in the Patients Who Received Stent Placement for the Purpose of Palliation (n=50)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download