Article: Induction of Colonic Regulatory T Cells by Indigenous Clostridium Species ([Related article:] Science 2011;331:337-341)
See the article "".
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
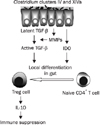
Summary of the induction of regulatory T (Treg) cells through the interaction between indigenous Clostridium species (clusters IV and XIVa) and intestinal epithelial cells (IECs). After weaning, Clostridium species containing clusters IV and XIVa become prominent in the colon, where they form a thick layer on the IECs. Clostridium species enhance the production of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) from IECs to convert transforming growth factor (TGF)-β from the latent to the active form. In addition, Clostridium clusters IV and XIVa promote the production of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) from IECs. Naive CD4+ T cells stimulated with the active form of TGF-β and IDO are differentiated into Treg cells that produce interleukin (IL)-10, leading to suppression of inflammatory responses in the gut (modified from Fig. 2 in the article of Kunisawa and Kiyono [Cell Host Microbe 2011;9:83-84]).
References
1. Atarashi K, Tanoue T, Shima T, et al. Induction of colonic regulatory T cells by indigenous Clostridium species. Science. 2011. 331:337–341.
2. Kim JM. Inflammatory bowel diseases and enteric microbiota. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2010. 55:4–18.
3. Kang JS. Journal walk regarding the expanding role of microbiota in our gut. J Bacteriol Virol. 2011. 41:63–64.
4. Cerf-Bensussan N, Gaboriau-Routhiau V. The immune system and the gut microbiota: friends or foes? Nat Rev Immunol. 2010. 10:735–744.
5. Gaboriau-Routhiau V, Rakotobe S, Lécuyer E, et al. The key role of segmented filamentous bacteria in the coordinated maturation of gut helper T cell responses. Immunity. 2009. 31:677–689.
6. Ivanov II, Atarashi K, Manel N, et al. Induction of intestinal Th17 cells by segmented filamentous bacteria. Cell. 2009. 139:485–498.
7. Hall JA, Bouladoux N, Sun CM, et al. Commensal DNA limits regulatory T cell conversion and is a natural adjuvant of intestinal immune responses. Immunity. 2008. 29:637–649.
8. Di Giacinto C, Marinaro M, Sanchez M, Strober W, Boirivant M. Probiotics ameliorate recurrent Th1-mediated murine colitis by inducing IL-10 and IL-10-dependent TGF-beta-bearing regulatory cells. J Immunol. 2005. 174:3237–3246.
9. Round JL, Mazmanian SK. Inducible Foxp3+ regulatory T-cell development by a commensal bacterium of the intestinal microbiota. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. 107:12204–12209.
10. Frank DN, St Amand AL, Feldman RA, Boedeker EC, Harpaz N, Pace NR. Molecular-phylogenetic characterization of microbial community imbalances in human inflammatory bowel diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. 104:13780–13785.
11. Momose Y, Maruyama A, Iwasaki T, Miyamoto Y, Itoh K. 16S rRNA gene sequence-based analysis of clostridia related to conversion of germfree mice to the normal state. J Appl Microbiol. 2009. 107:2088–2097.
12. Kwon HK, Lee CG, So JS, et al. Generation of regulatory dendritic cells and CD4+Foxp3+ T cells by probiotics administration suppresses immune disorders. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. 107:2159–2164.
13. Chiba T, Seno H. Indigenous clostridium species regulate systemic immune responses by induction of colonic regulatory T cells. Gastroenterology. 2011. 141:1114–1116.
14. Barnes MJ, Powrie F. Regulatory T cells reinforce intestinal homeostasis. Immunity. 2009. 31:401–411.
15. Kim JM. Inflammatory bowel diseases and inflammasome. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2011. 58:300–310.
16. de Vries IJ, Castelli C, Huygens C, et al. Frequency of circulating Tregs with demethylated FOXP3 intron 1 in melanoma patients receiving tumor vaccines and potentially Treg-depleting agents. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. 17:841–848.
17. Rech AJ, Vonderheide RH. Clinical use of anti-CD25 antibody daclizumab to enhance immune responses to tumor antigen vaccination by targeting regulatory T cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009. 1174:99–106.
18. Hooper LV, Macpherson AJ. Immune adaptations that maintain homeostasis with the intestinal microbiota. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010. 10:159–169.
19. Sokol H, Seksik P, Furet JP, et al. Low counts of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in colitis microbiota. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009. 15:1183–1189.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download