Abstract
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) with adults, as a new disease emerging during the last decade, is a clinicopathologic disorder of the esophagus characterized by a dense esophageal eosinophilic infiltration and typical esophageal symptoms. As numerous studies about EoE had been reported during last several years, updated consensus of EoE was reported in July 2011. The conceptual definition of EoE is coming. EoE is defined as a chronic, immune/antigen-mediated esophageal disease characterized clinically by symptoms related to esophageal dysfunction and histologically by eosinophil-predominat inflammation. Other important addition is genotyping feature that implicates thymic stromal lymphopoietin genes or filagrrin as EoE susceptibility genes. The majority of patients has the concurrent allergic disease, especially food or aeroallergen sensitization. Main therapeutic options include topical steroids and dietary modification. Recent issues of EoE include a new concept for proton pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia that it should be excluded to diagnose EoE.
Figures and Tables
Table 1
Histologic Features of Eosinophilic Esophagitis

Quoted from the article of Liacouras et al.2 (J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011;128:3-20).
Table 2
Endoscopic Features of Eosinophilic Esophagitis

Modified from the article of Liacouras et al.2 (J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011;128:3-20. e26; quiz 21-22).
Table 3
Recommended Doses of Corticosteroids for Eosinophilic Esophagitis
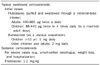
Quoted from the article of Liacouras et al.2 (J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011;128:3-20).
References
1. Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Collins MH, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults: a systematic review and consensus recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology. 2007. 133:1342–1363.
2. Liacouras CA, Furuta GT, Hirano I, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011. 128:3–20.
3. Prasad GA, Talley NJ, Romero Y, et al. Prevalence and predictive factors of eosinophilic esophagitis in patients presenting with dysphagia: a prospective study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007. 102:2627–2632.
4. Ronkainen J, Talley NJ, Aro P, et al. Prevalence of oesophageal eosinophils and eosinophilic oesophagitis in adults: the population-based Kalixanda study. Gut. 2007. 56:615–620.
5. Prasad GA, Alexander JA, Schleck CD, et al. Epidemiology of eosinophilic esophagitis over three decades in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009. 7:1055–1061.
6. Lee B, Park H, Yoon H, Kim HK, Kim HS. Three cases of eosinophilic esophagitis with dysphagia as a chief complaint. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2008. 36:145–149.
7. Park SB, Kim GH, Choi MK, et al. A case of eosinophilic esophagitis found incidentally during the evaluation of a gastric submucosal tumor. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2009. 39:212–216.
8. Kim NI, Jo Y, Ahn SB, et al. A case of eosinophilic esophagitis with food hypersensitivity. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2010. 16:315–318.
9. Yu YH, Jo YJ, Jung MY, et al. Prevalence of eosinophilic esophagitis with dysphagia and reflux related symptoms in Korean patients. Korean J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2009. 15:15–22.
10. Joo MK, Park JJ, Kim SH, et al. Prevalence and endoscopic features of eosinophilic esophagitis in patients with esophageal or upper gastrointestinal symptoms. J Dig Dis. 2012. 13:296–303.
11. Sperry SL, Woosley JT, Shaheen NJ, Dellon ES. Influence of race and gender on the presentation of eosinophilic esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012. 107:215–221.
12. Hurrell JM, Genta RM, Dellon ES. Prevalence of esophageal eosinophilia varies by climate zone in the United States. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012. 107:698–706.
13. Sorser SA, Barawi M, Hagglund K, Almojaned M, Lyons H. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adolescents: epidemiology, clinical presentation and seasonal variation. J Gastroenterol. 2012. [Epub ahead of print].
14. Almansa C, Krishna M, Buchner AM, et al. Seasonal distribution in newly diagnosed cases of eosinophilic esophagitis in adults. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009. 104:828–833.
15. Liacouras CA, Spergel JM, Ruchelli E, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: a 10-year experience in 381 children. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005. 3:1198–1206.
16. Kwon HJ, Yi DY, Ryoo E, Cho KH, Son DW, Tcha H. Prevalence and risk factors associated with esophagitis in children with abdominal pain. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008. 11:103–109.
17. Pasha SF, Dibaise JK, Kim HJ, et al. Patient characteristics, clinical, endoscopic, and histologic findings in adult eosinophilic esophagitis: a case series and systematic review of the medical literature. Dis Esophagus. 2007. 20:311–319.
18. Blanchard C, Wang N, Stringer KF, et al. Eotaxin-3 and a uniquely conserved gene-expression profile in eosinophilic esophagitis. J Clin Invest. 2006. 116:536–547.
19. Bhattacharya B, Carlsten J, Sabo E, et al. Increased expression of eotaxin-3 distinguishes between eosinophilic esophagitis and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Hum Pathol. 2007. 38:1744–1753.
20. Gupta SK, Fitzgerald JF, Kondratyuk T, HogenEsch H. Cytokine expression in normal and inflamed esophageal mucosa: a study into the pathogenesis of allergic eosinophilic esophagitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006. 42:22–26.
21. Zuo L, Fulkerson PC, Finkelman FD, et al. IL-13 induces esophageal remodeling and gene expression by an eosinophil-independent, IL-13R alpha 2-inhibited pathway. J Immunol. 2010. 185:660–669.
22. Abonia JP, Blanchard C, Butz BB, et al. Involvement of mast cells in eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. 126:140–149.
23. Sherrill JD, Gao PS, Stucke EM, et al. Variants of thymic stromal lymphopoietin and its receptor associate with eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. 126:160–165.
24. Blanchard C, Stucke EM, Rodriguez-jimenez B, et al. A striking local esophageal cytokine expression profile in eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011. 127:208–217.
25. Kahrilas PJ, Shaheen NJ, Vaezi MF, et al. American Gastroenterological Association Medical Position Statement on the management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology. 2008. 135:1383–1391.
26. Shah A, Kagalwalla AF, Gonsalves N, Melin-aldana H, Li BU, Hirano I. Histopathologic variability in children with eosinophilic esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009. 104:716–721.
27. Lee RG. Marked eosinophilia in esophageal mucosal biopsies. Am J Surg Pathol. 1985. 9:475–479.
28. Chehade M, Sampson HA, Morotti RA, Magid MS. Esophageal subepithelial fibrosis in children with eosinophilic esophagitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007. 45:319–328.
29. Gupta SK. Noninvasive markers of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2008. 18:157–167.
30. Talley NJ, Kephart GM, Mcgovern TW, Carpenter HA, Gleich GJ. Deposition of eosinophil granule major basic protein in eosinophilic gastroenteritis and celiac disease. Gastroenterology. 1992. 103:137–145.
31. Mueller S, Aigner T, Neureiter D, Stolte M. Eosinophil infiltration and degranulation in oesophageal mucosa from adult patients with eosinophilic oesophagitis: a retrospective and comparative study on pathological biopsy. J Clin Pathol. 2006. 59:1175–1180.
32. Kim CK, Callaway Z, Fletcher R, Koh YY. Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin in childhood asthma: correlation with disease severity. J Asthma. 2010. 47:568–573.
33. Konikoff MR, Blanchard C, Kirby C, et al. Potential of blood eosinophils, eosinophil-derived neurotoxin, and eotaxin-3 as biomarkers of eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006. 4:1328–1336.
34. Rao GS, Mitchell L, Ohnuki L, et al. Can eosinophil derived neurotoxin (EDN) act as a surrogate marker of disease activity in children with allergic eosinophilic esophagitis (AEE)? Gastrointest Endosc. 2004. 59:A103.
35. Kephart GM, Alexander JA, Arora AS, et al. Marked deposition of eosinophil-derived neurotoxin in adult patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010. 105:298–307.
36. Dellon ES, Chen X, Miller CR, et al. Tryptase staining of mast cells may differentiate eosinophilic esophagitis from gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011. 106:264–271.
37. Aceves SS, Chen D, Newbury RO, Dohil R, Bastian JF, Broide DH. Mast cells infiltrate the esophageal smooth muscle in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis, express TGF-β1, and increase esophageal smooth muscle contraction. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. 126:1198–1204.
38. Molina-infante J, Ferrando-lamana L, Ripoll C, et al. Esophageal eosinophilic infiltration responds to proton pump inhibition in most adults. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011. 9:110–117.
39. Fox VL, Nurko S, Teitelbaum JE, Badizadegan K, Furuta GT. High-resolution EUS in children with eosinophilic "allergic" esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003. 57:30–36.
40. Dalby K, Nielsen RG, Kruse-andersen S, Fenger C, Durup J, Husby S. Gastroesophageal reflux disease and eosinophilic esophagitis in infants and children. A study of esophageal pH, multiple intraluminal impedance and endoscopic ultrasound. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2010. 45:1029–1035.
41. Korsapati H, Babaei A, Bhargava V, Dohil R, Quin A, Mittal RK. Dysfunction of the longitudinal muscles of the oesophagus in eosinophilic oesophagitis. Gut. 2009. 58:1056–1062.
42. Kahrilas PJ, Ghosh SK, Pandolfino JE. Esophageal motility disorders in terms of pressure topography: the Chicago Classification. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2008. 42:627–635.
43. Dellon ES, Gibbs WB, Fritchie KJ, et al. Clinical, endoscopic, and histologic findings distinguish eosinophilic esophagitis from gastroesophageal reflux disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009. 7:1305–1313.
44. Chehade M, Sampson HA. Epidemiology and etiology of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2008. 18:33–44.
45. Straumann A, Conus S, Degen L, et al. Budesonide is effective in adolescent and adult patients with active eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2010. 139:1526–1537.
46. Roy-ghanta S, Larosa DF, Katzka DA. Atopic characteristics of adult patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008. 6:531–535.
47. Erwin EA, James HR, Gutekunst HM, Russo JM, Kelleher KJ, Platts-mills TA. Serum IgE measurement and detection of food allergy in pediatric patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010. 104:496–502.
48. Moawad FJ, Veerappan GR, Lake JM, et al. Correlation between eosinophilic oesophagitis and aeroallergens. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010. 31:509–515.
49. Wang FY, Gupta SK, Fitzgerald JF. Is there a seasonal variation in the incidence or intensity of allergic eosinophilic esophagitis in newly diagnosed children? J Clin Gastroenterol. 2007. 41:451–453.
50. Dellon ES, Sheikh A, Speck O, et al. Viscous topical is more effective than nebulized steroid therapy for patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2012. [Epub ahead of print].
51. Gonsalves N, Yang GY, Doerfler B, Ritz S, Ditto AM, Hirano I. Elimination diet effectively treats eosinophilic esophagitis in adults; food reintroduction identifies causative factors. Gastroenterology. 2012. 142:1451–1459.
52. Steiner SJ, Gupta SK, Croffie JM, Fitzgerald JF. Correlation between number of eosinophils and reflux index on same day esophageal biopsy and 24 hour esophageal pH monitoring. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004. 99:801–805.
53. Remedios M, Campbell C, Jones DM, Kerlin P. Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults: clinical, endoscopic, histologic findings, and response to treatment with fluticasone propionate. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006. 63:3–12.
54. Konikoff MR, Noel RJ, Blanchard C, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of fluticasone propionate for pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2006. 131:1381–1391.
55. Aceves SS, Newbury RO, Chen D, et al. Resolution of remodeling in eosinophilic esophagitis correlates with epithelial response to topical corticosteroids. Allergy. 2010. 65:109–116.
56. Attwood SE, Lewis CJ, Bronder CS, Morris CD, Armstrong GR, Whittam J. Eosinophilic oesophagitis: a novel treatment using Montelukast. Gut. 2003. 52:181–185.
57. Garrett JK, Jameson SC, Thomson B, et al. Anti-interleukin-5 (mepolizumab) therapy for hypereosinophilic syndromes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004. 113:115–119.
58. Stein ML, Collins MH, Villanueva JM, et al. Anti-IL-5 (mepolizumab) therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006. 118:1312–1319.
59. Straumann A, Conus S, Grzonka P, et al. Anti-interleukin-5 antibody treatment (mepolizumab) in active eosinophilic oesophagitis: a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. Gut. 2010. 59:21–30.
60. Schoepfer AM, Gonsalves N, Bussmann C, et al. Esophageal dilation in eosinophilic esophagitis: effectiveness, safety, and impact on the underlying inflammation. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010. 105:1062–1070.
61. Jung KW, Gundersen N, Kopacova J, et al. Occurrence of and risk factors for complications after endoscopic dilation in eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011. 73:15–21.
62. Straumann A, Spichtin HP, Grize L, Bucher KA, Beglinger C, Simon HU. Natural history of primary eosinophilic esophagitis: a follow-up of 30 adult patients for up to 11.5 years. Gastroenterology. 2003. 125:1660–1669.
63. Straumann A. The natural history and complications of eosinophilic esophagitis. Thorac Surg Clin. 2011. 21:575–587.
64. Francalanci P, De AP, Minnei F, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis and Barrett's esophagus: an occasional association or an overlap disease? Esophageal 'double trouble' in two children. Digestion. 2008. 77:16–19.
65. Mukkada V, Atkins D, Furuta GT. Uncertain association of Barrett's esophagus with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008. 6:832.
66. Carr S, Watson W. Eosinophilic esophagitis. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2011. 7:Suppl 1. S8.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download