Abstract
Background/Aims
ERCP using fluoroscopy should be practiced with an adequate radiation protection. However, the awareness of gastrointestinal endoscopists to radiation protection was considered insufficient. In Korea, a country with a rapid increase the number of ERCP procedures, there is no data about radiation protection practices for gastrointestinal endoscopists. The purpose of this study was to investigate current clinical practices and the awareness on radiation protection in ERCP performing physicians in Korea.
Methods
An anonymous questionnaire regarding radiation protection practices was mailed to 100 members of Korean Pancreatobiliary Association who was porforming ERCP. The questionnaire included ERCP volume of each endoscopist, use of protection devices such as apron, thyroid shield, lead glasses and any mobile shield for scattered radiation, and whether they monitored their own radiation exposure dosage.
Results
All respondents wore lead aprons during ERCP. While 52.5% of endoscopists answered that they always wear thyroid guards, 26.9% rarely or never wore it. Only 14% wore lead glasses during the procedure and 69% never wore it. The preparation rates of mobile shields or lead curtains were only 14% and 24%, respectively. Only 10% of endoscopists attached an X-ray badge and 66.7% never used it. Moreover, 75% of endoscopists responded that they did not monitor their own exposure dose to radiation during ERCP.
Go to : 
References
1. Hendee WR. Estimation of radiation risks. BEIR V and its significance for medicine. JAMA. 1992; 268:620–624.

3. Russell WL. Comments on mutagenesis risk estimation. Genetics. 1979; 92(1 Suppl):S187–S194.
6. Bush WH, Jones D, Brannen GE. Radiation dose to personnel during percutaneous renal calculus removal. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1985; 145:1261–1264.

7. McParland BJ, Nosil J, Burry B. A survey of the radiation exposures received by the staff at two cardiac catheterization laboratories. Br J Radiol. 1990; 63:885–888.

8. Ramsdale ML, Walker WJ, Horton PW. Extremity doses during interventional radiology. Clin Radiol. 1990; 41:34–36.

9. Campbell N, Sparrow K, Fortier M, Ponich T. Practical radiation safety and protection for the endoscopist during ERCP. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 55:552–557.

10. Naidu LS, Singhal S, Preece DE, Vohrah A, Loft DE. Radiation exposure to personnel performing endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Postgrad Med J. 2005; 81:660–662.

11. Chen MY, Van Swearingen FL, Mitchell R, Ott DJ. Radiation exposure during ERCP: effect of a protective shield. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996; 43:1–5.

12. Cohen RV, Aldred MA, Paes WS, et al. How safe is ERCP to the endoscopist? Surg Endosc. 1997; 11:615–617.

13. Niklason LT, Marx MV, Chan HP. Interventional radiologists: oc-cupational radiation doses and risks. Radiology. 1993; 187:729–733.

14. Campbell N, Sparrow K, Fortier M, Ponich T. Practical radiation safety and protection for the endoscopist during ERCP. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 55:552–557.

15. Merriam GR Jr, Focht EF. A clinical study of radiation cataracts and the relationship to dose. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1957; 77:759–785.
16. Kim YJ, Cho KB, Kim ES, et al. Efficacy of a self-designed protective lead shield in reduction of radiation exposure dose during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2011; 57:28–33.

17. Geise RA, O'Dea TJ. Radiation dose in interventional fluoroscopic procedures. Appl Radiat Isot. 1999; 50:173–184.

Go to : 
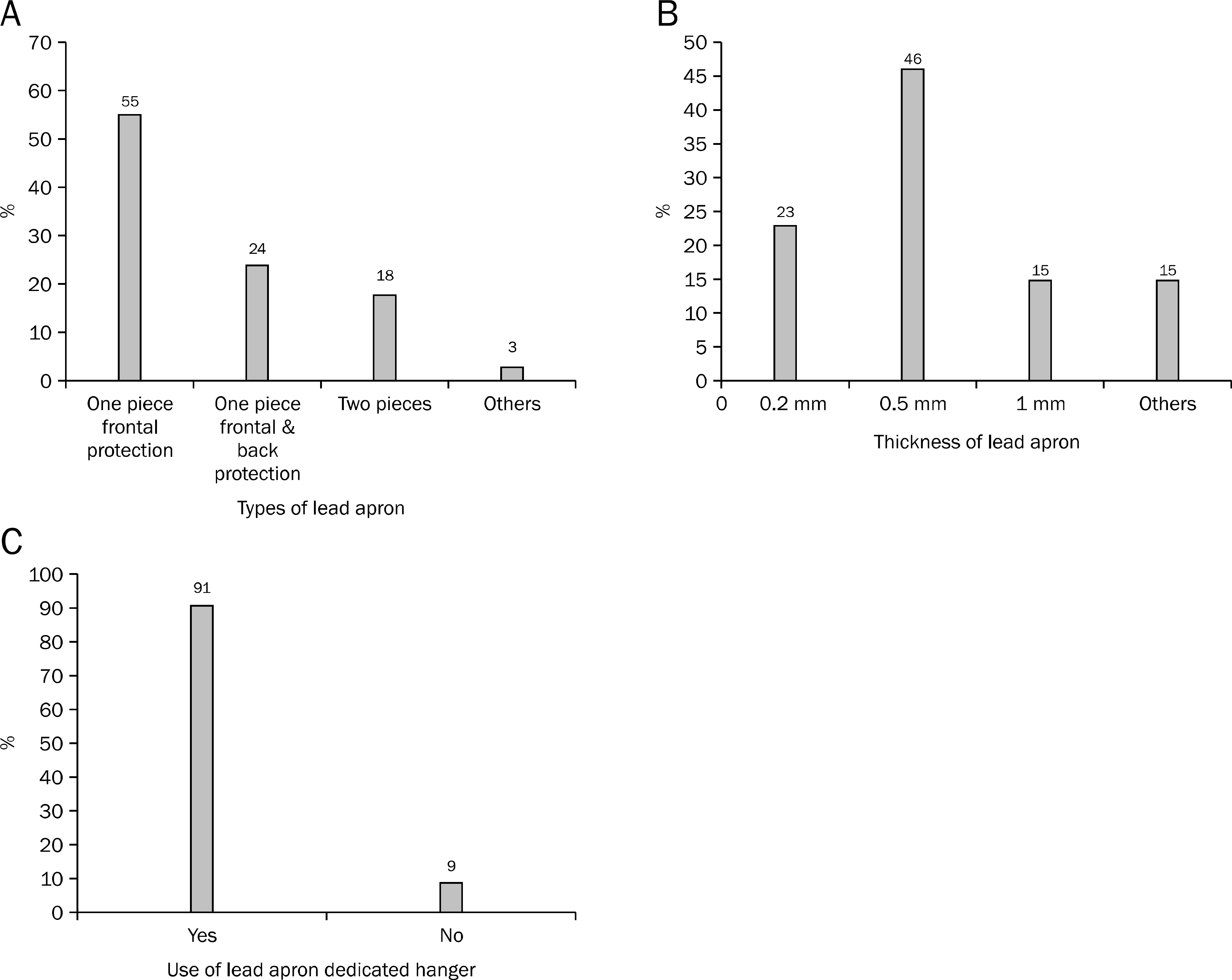 | Fig. 1.Use of lead aprons for ERCP endoscopists. (A) Lead apron types, (B) lead apron thickness, (C) lead apron dedicated hanger. |
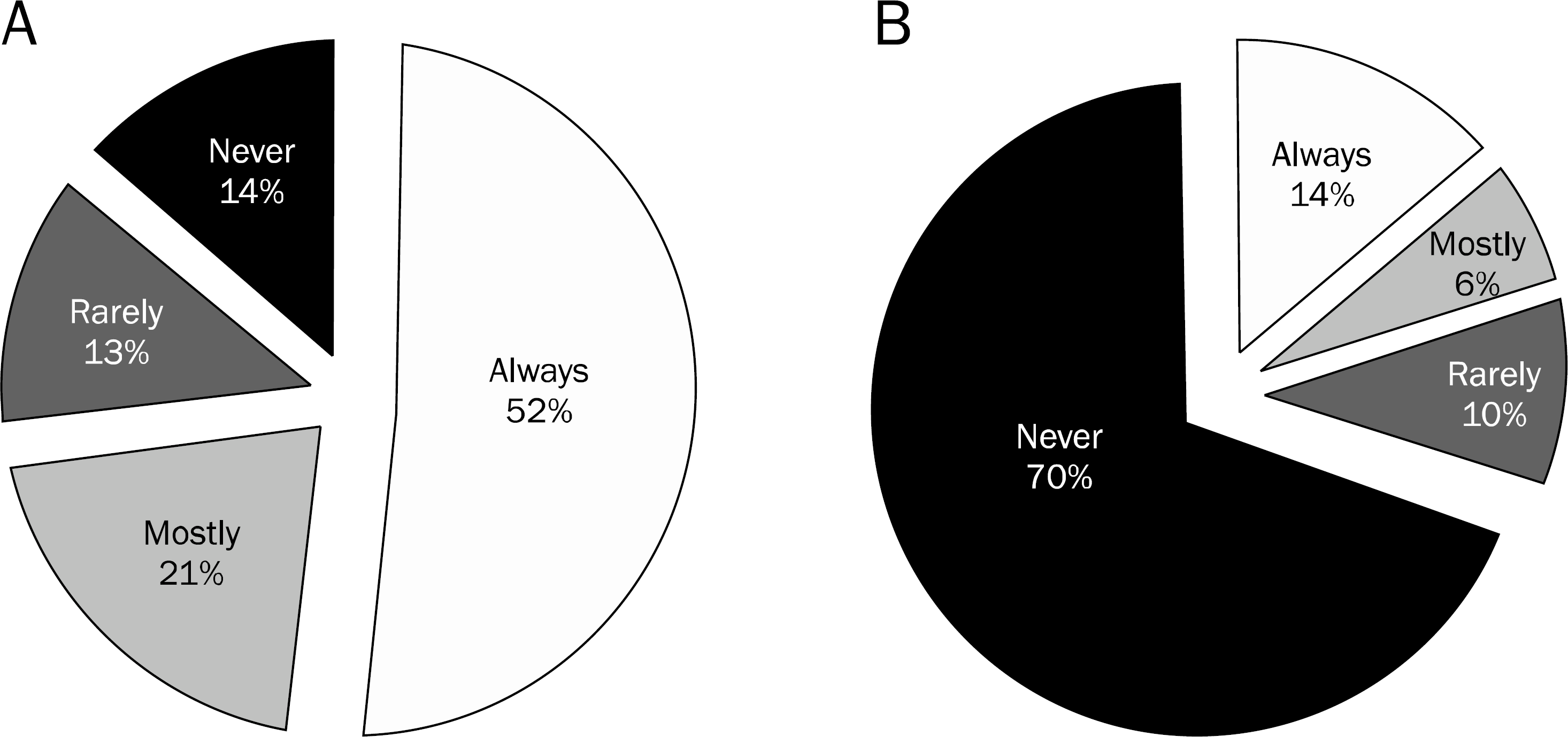 | Fig. 2.Thyroid and eye protection for ERCP endoscopists. (A) Wearing a thyroid guard, (B) wearing leaded glasses. |
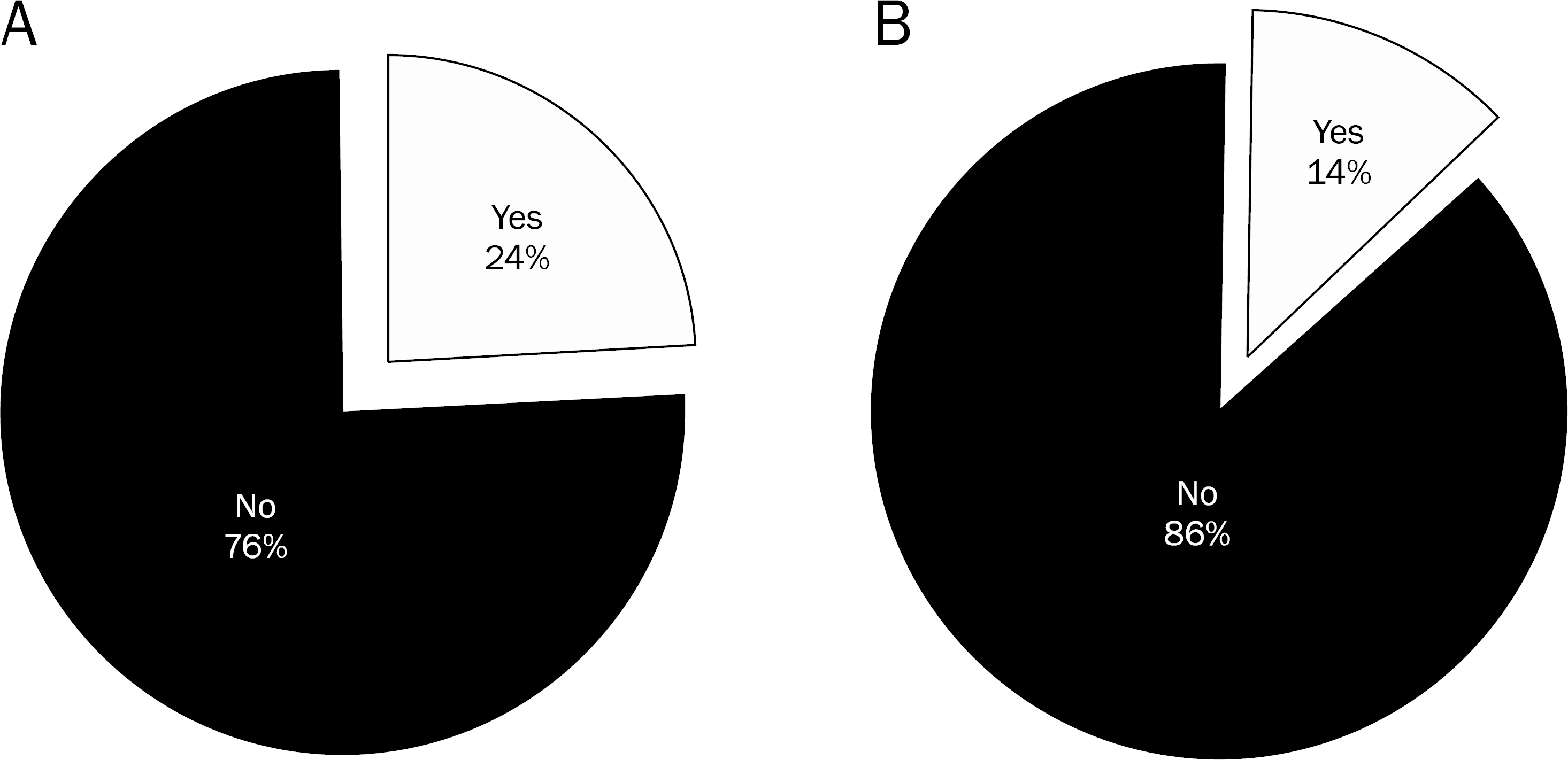 | Fig. 3.Use of equipment to protect scattered radiation for ERCP endoscopists. (A) Preparation and use of a mobile shield, (B) a lead curtain or table shield. |
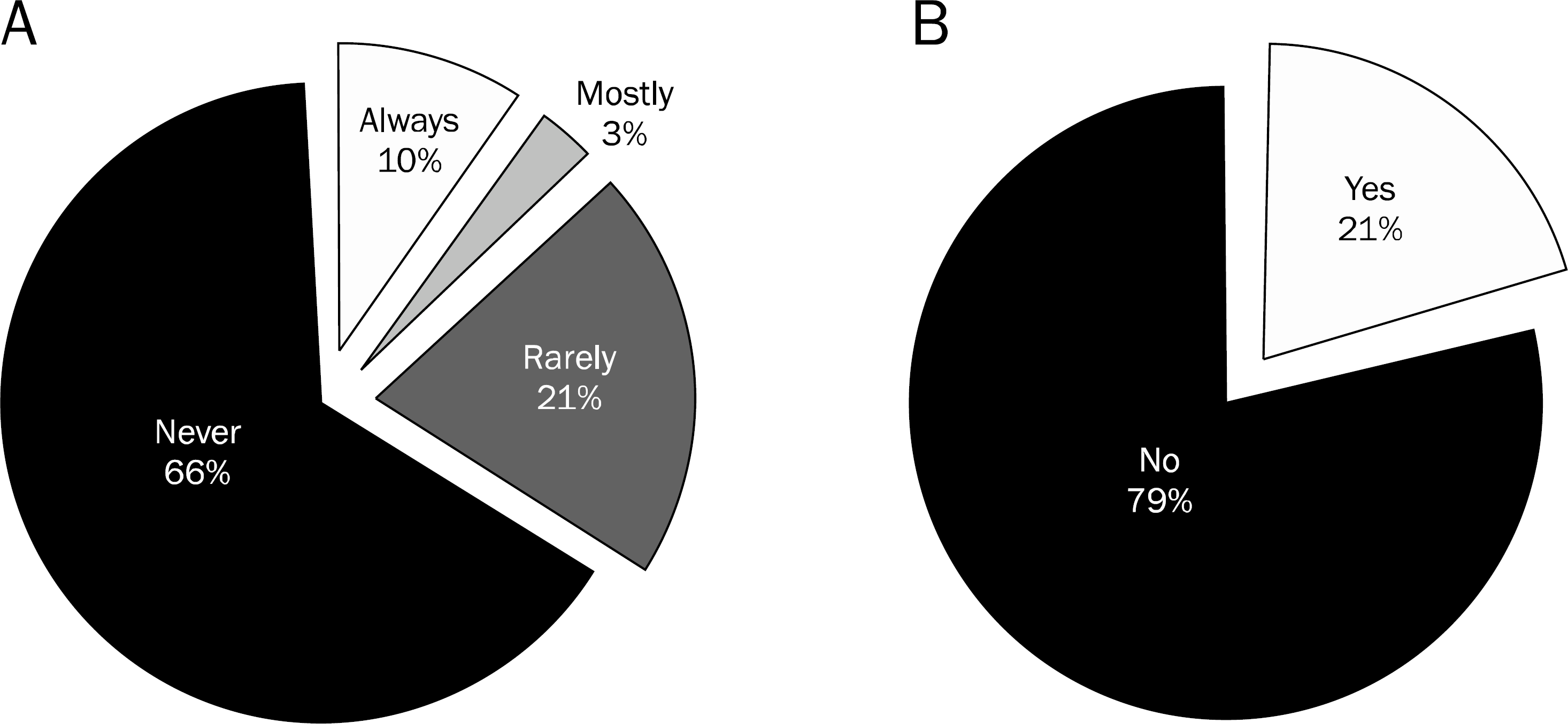 | Fig. 4.Monitoring of radiation dose for ERCP endoscopists. (A) Wearing a radiation dosimeter, (B) measuring radiation exposure doses. |
Table 1.
Anonymous Questionare Regarding Radiation Protection Practices during ERCP




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download