Abstract
After 4-months of alpha interferon (IFN-α), a 64-year old woman with chronic hepatitis C developed a cough and dyspnea and showed diffuse infiltrative opacities on her chest X-ray. Her symptoms persisted after stopping the IFN-α therapy. Pulmonary function testing revealed a reduced forced vital capacity. High-resolution computed tomography of the lung showed peripheral and peribronchovascular ground glass attenuation and consolidation associated with reticulation. Bronchoalveolar lavage was performed for further evaluation and showed a lymphocyte level of 8.2%, an uncommon finding in IFN-α-induced interstitial pneumonitis. We performed a lung biopsy to diagnose her disease and it suggested interstitial pneumonitis. This was considered to be due to the immunomodulatory effects of INF-α. Although rare, any sign of significant pulmonary involvement should be evaluated.
Go to : 
References
1. Hoofnagle JH, Seeff LB. Peginterferon and ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:2444–2451.

3. Rehermann B, Nascimbeni M. Immunology of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005; 5:215–229.

4. Bowen DG, Walker CM. Adaptive immune responses in acute and chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Nature. 2005; 436:946–952.

5. Strader DB, Wright T, Thomas DL, Seeff LB. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2004; 39:1147–1171.

7. Davis GL, Balart LA, Schiff ER, et al. Treatment of chronic hepatitis C with recombinant interferon alfa. A multicenter randomized, controlled trial. Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group. N Engl J Med. 1989; 321:1501–1506.
8. Onoda K, Takai K, Sanada M, Aoki S, Watanabe T. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia induced by alpha-interferon therapy in a case of IgG-kappa type multiple myeloma. Rinsho Ketsueki. 1992; 33:844–846.
9. Schilling PJ, Kurzrock R, Kantarjian H, Gutterman JU, Talpaz M. Development of systemic lupus erythematosus after interferon therapy for chronic myelogenous leukemia. Cancer. 1991; 68:1536–1537.

10. Schattner A. Interferons and autoimmunity. Am J Med Sci. 1988; 295:532–544.
11. Quesada JR, Talpaz M, Rios A, Kurzrock R, Gutterman JU. Clinical toxicity of interferons in cancer patients: a review. J Clin Oncol. 1986; 4:234–243.

12. Hizawa N, Kojima J, Kojima T, et al. A patient with chronic hepatitis C who simultaneously developed interstitial pneumonia, hemolytic anemia and cholestatic liver dysfunction after al-pha-interferon administration. Intern Med. 1994; 33:337–341. July 2011.

13. Kumar KS, Russo MW, Borczuk AC, et al. Significant pulmonary toxicity associated with interferon and ribavirin therapy for hepatitis C. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002; 97:2432–2440.
14. Silva MO, Reddy KR, Jeffers LJ, Hill M, Schiff ER. Interferon-in-duced chronic active hepatitis? Gastroenterology. 1991; 101:840–842.

15. Okanoue T, Sakamoto S, Itoh Y, et al. Side effects of high-dose interferon therapy for chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 1996; 25:283–291.

16. Dumoulin FL, Leifeld L, Sauerbruch T, Spengler U. Autoimmunity induced by interferon-alpha therapy for chronic viral hepatitis. Biomed Pharmacother. 1999; 53:242–254.
17. Wolf Y, Haddad R, Jossipov J, Werbin N. Alpha-interferon induced severe pneumonitis. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 1997; 35:113–114.

18. Bini EJ, Weinshel EH. Severe exacerbation of asthma: a new side effect of interferon-alpha in patients with asthma and chronic hepatitis C. Mayo Clin Proc. 1999; 74:367–370.
Go to : 
 | Fig. 1.(A, B) CT on admission showing peripheral and peribronchovascular ground glass attenuation and consolidations. (C, D) Repeated CT scan performed after discontinuation of interferon. Bilateral lung parenchymal lesions show improvement. |
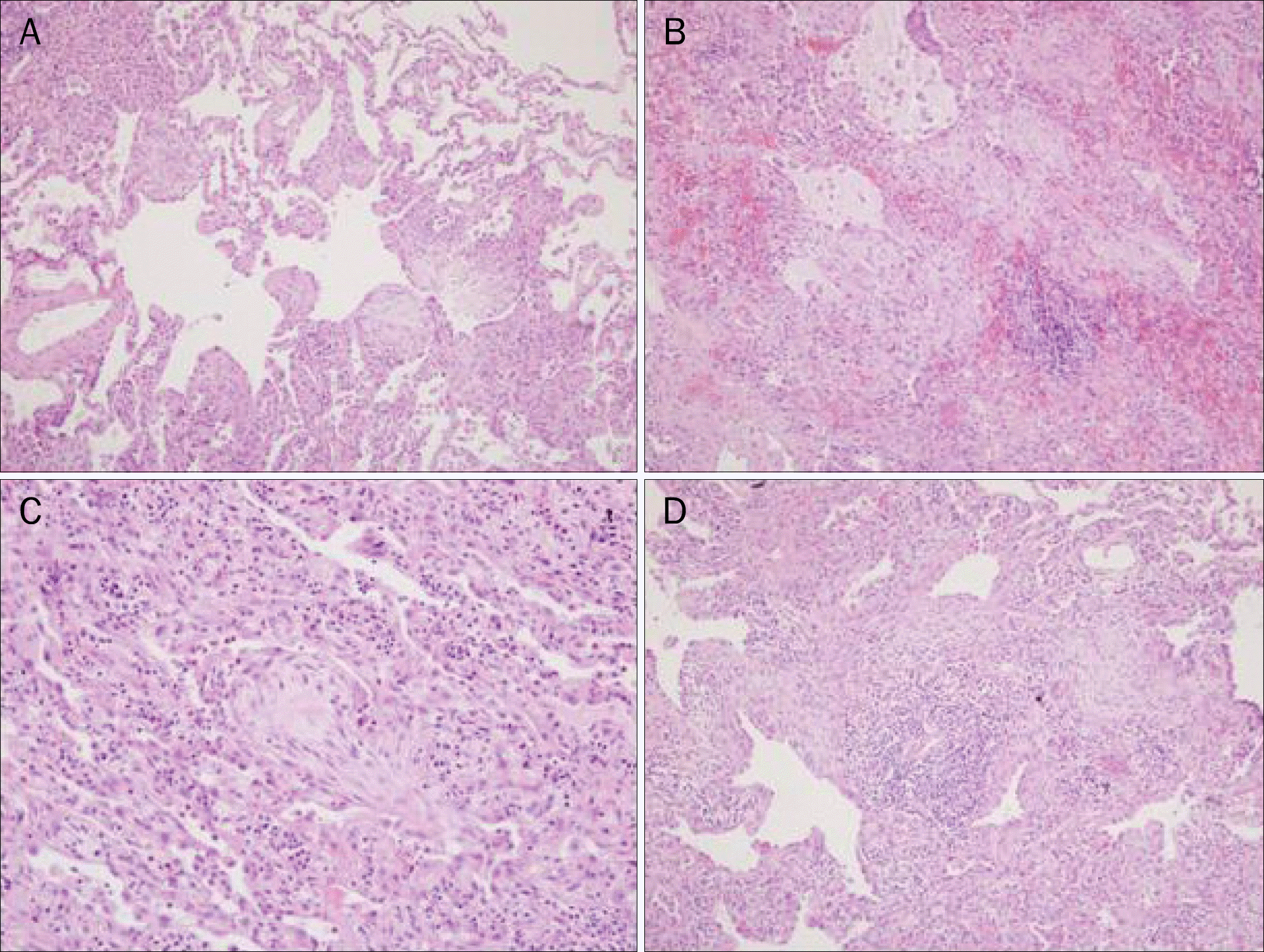 | Fig. 2.(A) Patchy areas of organizing pneumonia showing polypoid plugs of loose connective tissue (H&E, ×40). (B) Polypoid plugs of organizing pneumonia and acute alveolar hemorrhage (H&E, ×40). (C) An organizing intraluminal plug with chronic inflammatory infiltrate (H&E, ×100).(D) Chronic interstitial pneumonia pattern with interstitial fibrosis and inflammation (H&E, ×40). |
Table 1.
The Cases of Interferon-induced Pulmonary Complications
| No. | FEV1 (L) (% Predicted) | FVC (L) (% Predicted) | FEV1/FVC (% Predicted) | DLCO (ML/min/mmHg) (% Predicted) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1: On admission | 93 | 75 | 88 | 45 |
| 2: After 1 mo | 100 | 85 | 84 | 46 |
| 3: After 2 mo | 110 | 95 | 83 | 58 |
Table 2.
Pulmonary Function Tests




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download