Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignant neoplasms occuring worldwide. Although surgical resection still remains the treatment of choice for HCC, radiofrequency ablation (RFA) has emerged as reliable alternatives to resection. It is less invasive and can be repeated after short intervals for sequential ablation in case of multiple lesions. The most common complication of RFA is liver abscess, and bile duct injury such as bile duct stricture has been reported. This is a case report of a rare complication of abscesso-colonic fistula after RFA for HCC. The case was treated by percutaneous abscess drainage and antibiotics and occlusion of abscesso-colonic fistula with n-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate embolization.
Go to : 
References
1. Lau WY. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 2002; 47:389–399.
3. Lau WY. The history of liver surgery. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1997; 42:303–309.
4. Lau WY. A review on the operative techniques in liver resection. Chin Med J (Engl). 1997; 110:567–570.
6. Khan MR, Poon RT, Ng KK, et al. Comparison of percutaneous and surgical approaches for radiofrequency ablation of small and medium hepatocellular carcinoma. Arch Surg. 2007; 142:1136–1143.

7. Guglielmi A, Ruzzenente A, Valdegamberi A, et al. Radiofrequency ablation versus surgical resection for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis. J Gastrointest Surg. 2008; 12:192–198.

8. Lencioni R, Cioni D, Crocetti L, Bartolozzi C. Percutaneous ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: state-of-the-art. Liver Transpl. 2004; 10(2 Suppl 1):S91–97.

9. Lencioni R, Crocetti L. A critical appraisal of the literature on local ablative therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Liver Dis. 2005; 9:301–314.

10. Gillams AR, Lees WR. Radiofrequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases in 167 patients. Eur Radiol. 2004; 14:2261–2267.

11. Rhim H, Lim HK. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: pros and cons. Gut Liver. 2010; 4(Suppl 1):S113–S118.

12. Livraghi T, Solbiati L, Meloni MF, Gazelle GS, Halpern EF, Goldberg SN. Treatment of focal liver tumors with percutaneous radio-frequency ablation: complications encountered in a multicenter study. Radiology. 2003; 226:441–451.

13. Giorgio A, Tarantino L, de Stefano G, Coppola C, Ferraioli G. Complications after percutaneous saline-enhanced radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors:3-year experience with 336 patients at a single center. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 184:207–211.
14. Kong WT, Zhang WW, Qiu YD, et al. Major complications after radiofrequency ablation for liver tumors: analysis of 255 patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2009; 15:2651–2656.

15. Mulier S, Mulier P, Ni Y, et al. Complications of radiofrequency coagulation of liver tumours. Br J Surg. 2002; 89:1206–1222.

16. Munene G, Graham JA, Holt RW, Johnson LB, Marshall HP Jr. Biliary-colonic fistula: a case report and literature review. Am Surg. 2006; 72:347–350.

17. Uppot RN, Silverman SG, Zagoria RJ, Tuncali K, Childs DD, Gervais DA. Imaging-guided percutaneous ablation of renal cell carcinoma: a primer of how we do it. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 192:1558–1570.

18. Satoh H, Matsuyama S, Mashima H, Imoto A, Hidaka K, Hisatsugu T. A case of hepatocolic fistula after percutaneous drainage for a gas-containing pyogenic liver abscess. J Gastroenterol. 1994; 29:782–785.

19. Petersen B, Barkun A, Carpenter S, et al. Technology Assessment Committee, American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Tissue adhesives and fibrin glues. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 60:327–333.

Go to : 
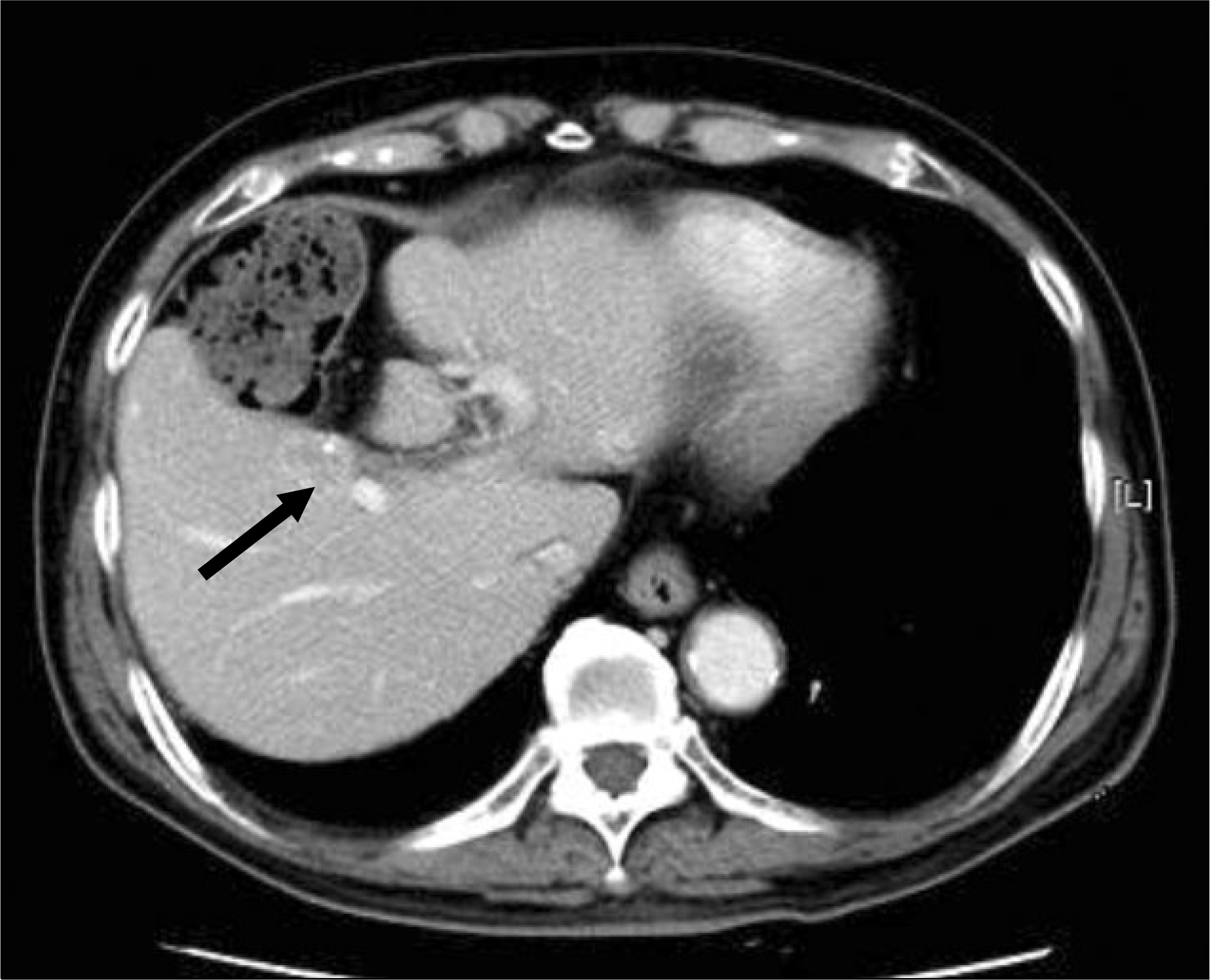 | Fig. 1.CT shows 1.6 cm sized hepatocellular carcinoma Hepatocellular carcinoma in segment V. Black arrow indicates the close proximity of the colon to HCC. |
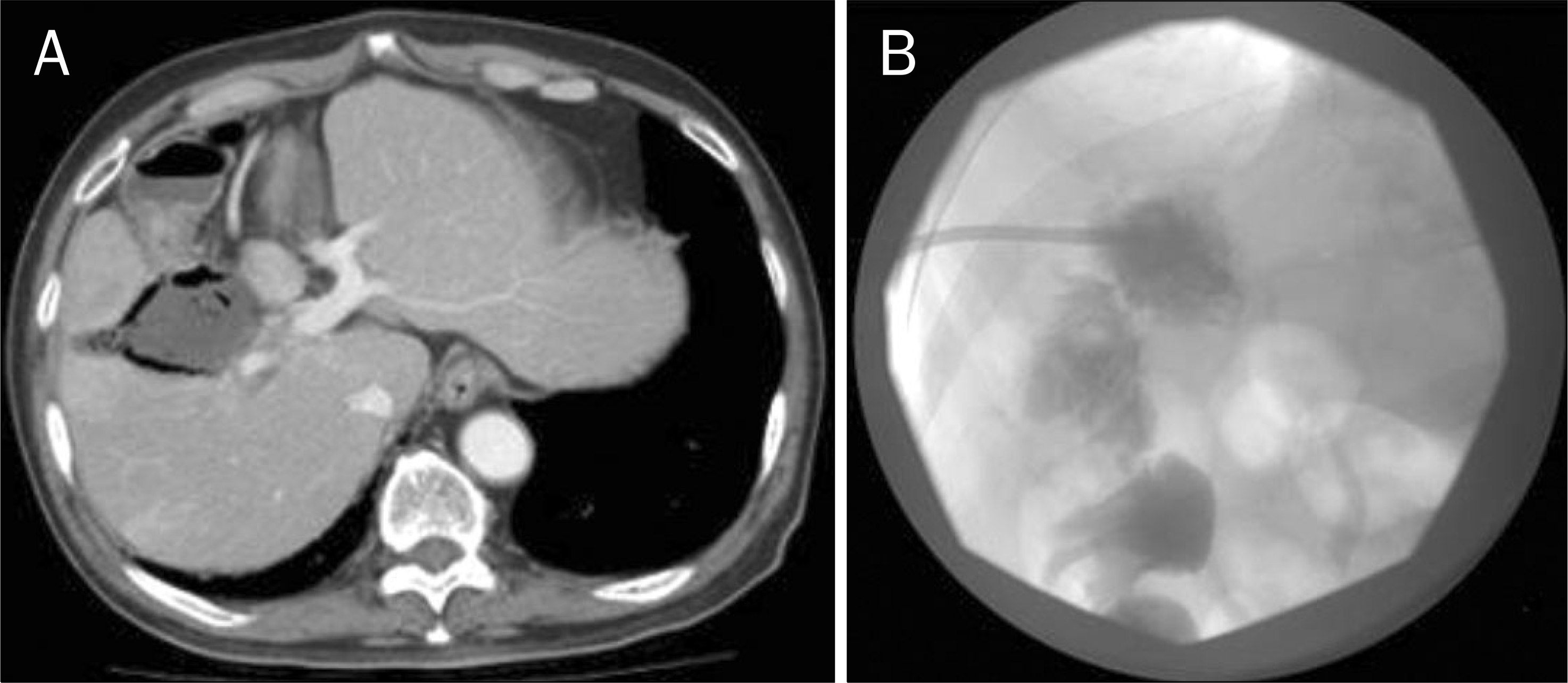 | Fig. 2.(A) CT showed 6 cm sized air-bubble containing liver abscess and communication with hepatic flexure of colon. (B) Contrast study through percutaneous drainage catheter demonstrated communication between the abscess cavity and the ascending colon. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download