References
1. Lee SG, Hwang S. How I do it: assessment of hepatic functional reserve for indication of hepatic resection. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2005; 12:38–43.

2. Kubota K, Makuuchi M, Kusaka K, et al. Measurement of liver volume and hepatic functional reserve as a guide to decision-making in resectional surgery for hepatic tumors. Hepatology. 1997; 26:1176–1181.

3. Yokoyama Y, Nagino M, Nimura Y. Mechanisms of hepatic regeneration following portal vein embolization and partial hepatectomy: a review. World J Surg. 2007; 31:367–374.

4. Hwang S, Lee SG, Ko GY, et al. Sequential preoperative ipsilateral hepatic vein embolization after portal vein embolization to induce further liver regeneration in patients with hepatobiliary malignancy. Ann Surg. 2009; 249:608–616.

5. Ko GY, Hwang S, Sung KB, Gwon DI, Lee SG. Interventional oncology: new options for interstitial treatments and intravascular approaches: right hepatic vein embolization after right portal vein embolization for inducing hypertrophy of the future liver remnant. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2010; 17:410–412.
6. Nagino M, Kamiya J, Nishio H, Ebata T, Arai T, Nimura Y. Two hundred forty consecutive portal vein embolizations before extended hepatectomy for biliary cancer: surgical outcome and long-term follow-up. Ann Surg. 2006; 243:364–372.
7. Hwang S, Lee SG, Sung KB, Lee YJ. Hepatectomy for patients with transient hepatic failure after preoperative portal vein embolization. Hepatogastroenterology. 2007; 54:1817–1820.
8. Gruttadauria S, Luca A, Mandala' L, Miraglia R, Gridelli B. Sequential preoperative ipsilateral portal and arterial embolization in patients with colorectal liver metastases. World J Surg. 2006; 30:576–578.

Go to : 
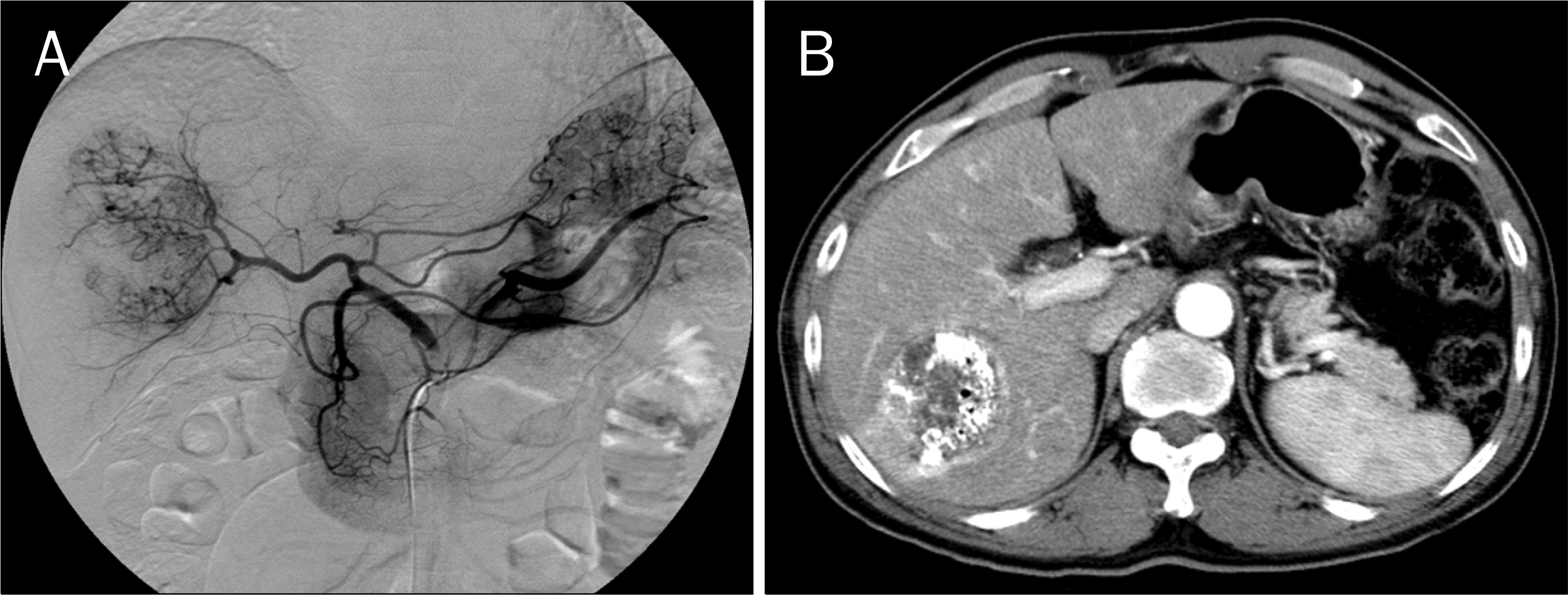 | Fig. 1.Initial application of transarterial chemoembolization. (A) Hepatic arteriogrphy shows a large-sized hypervascular mass at the right liver. (B) Two weeks after embolization, CT showed extensive tumor necrosis but incomplete lipiodol uptake, implica-ting presence of viable tumor cells. |
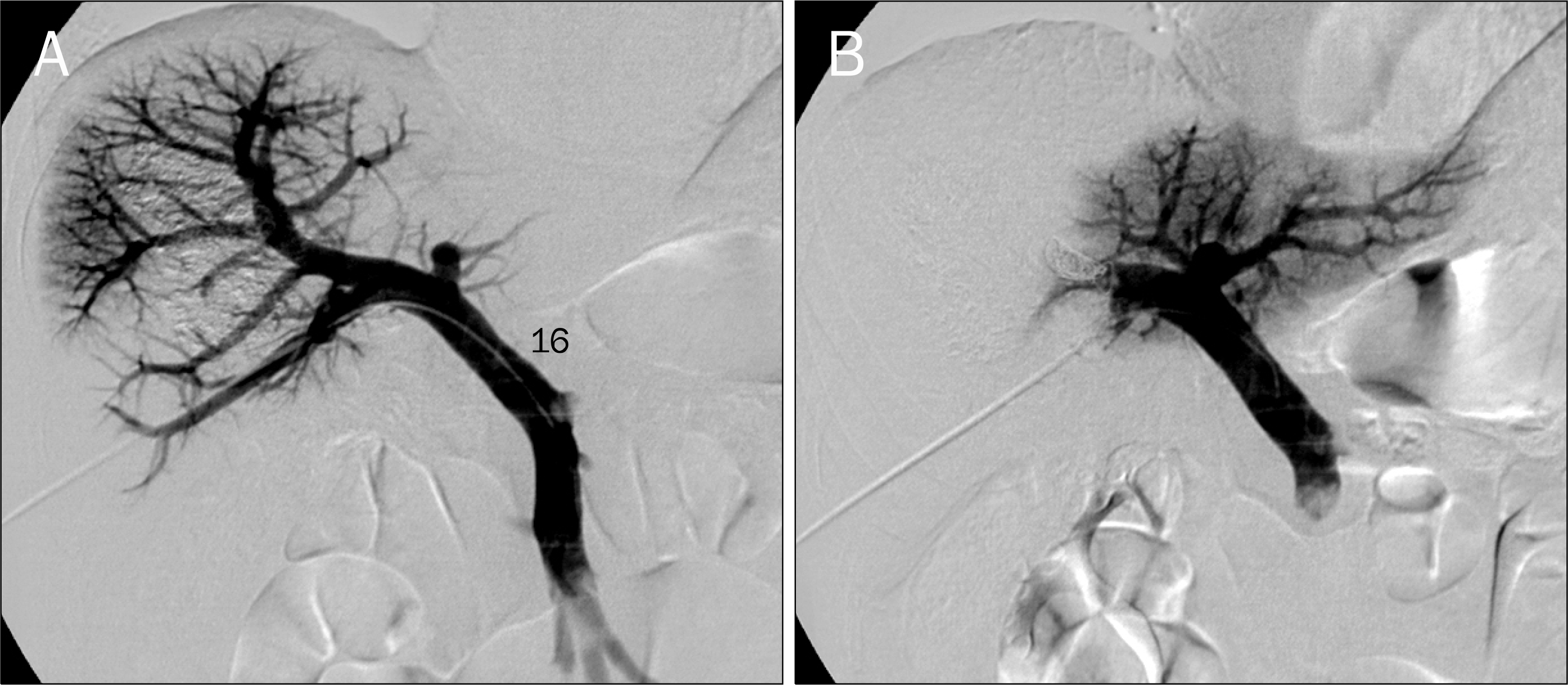 | Fig. 2.Preoperative right portal vein embolization. (A) The portal vein system was visualized through percutaneous ipsilateral approach. (B) After occlusion of the right portal vein with multiple coils and gelfoam, only the left portal vein was visualized. |
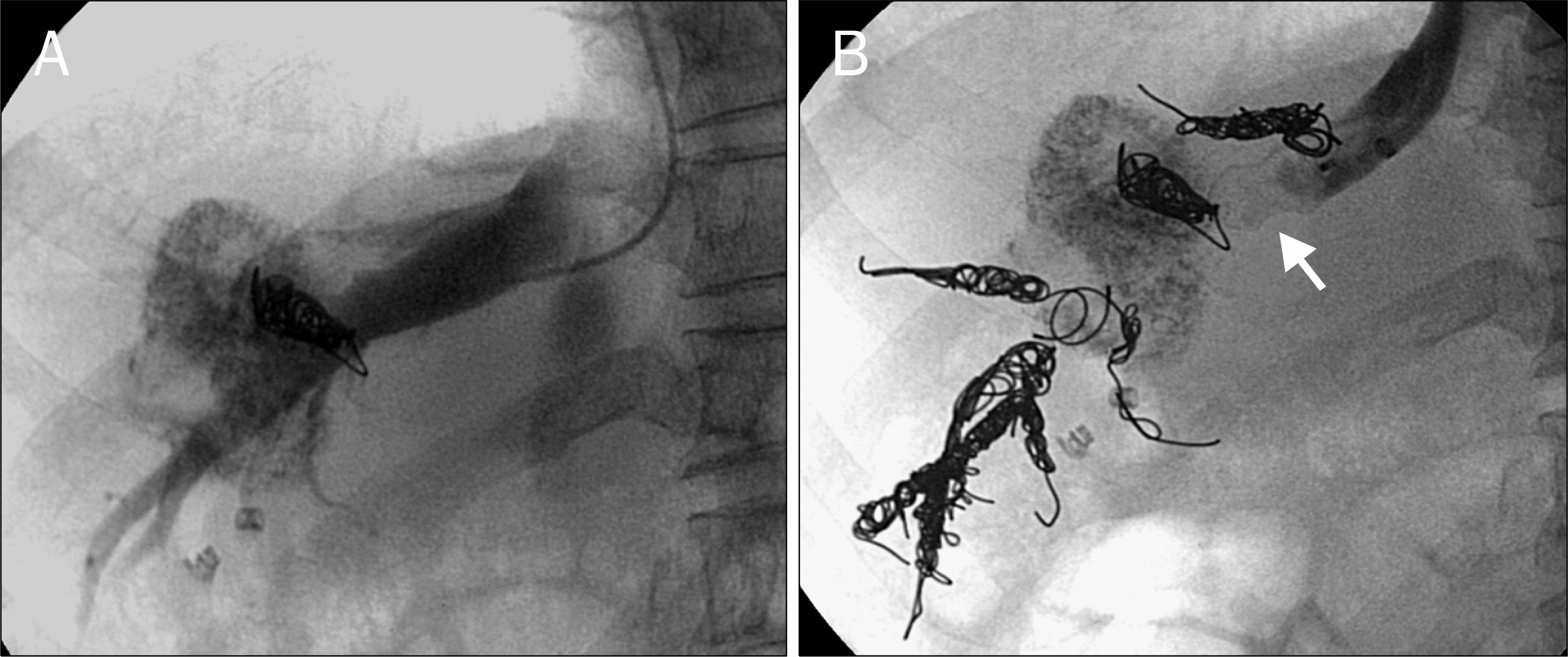 | Fig. 3.Subsequent right hepatic vein embolization following right portal vein embolization. (A) The right hepatic vein was visualized through transjugular approach. (B) The right hepatic vein was occluded with multiple coils and a vascular plug (arrow). |
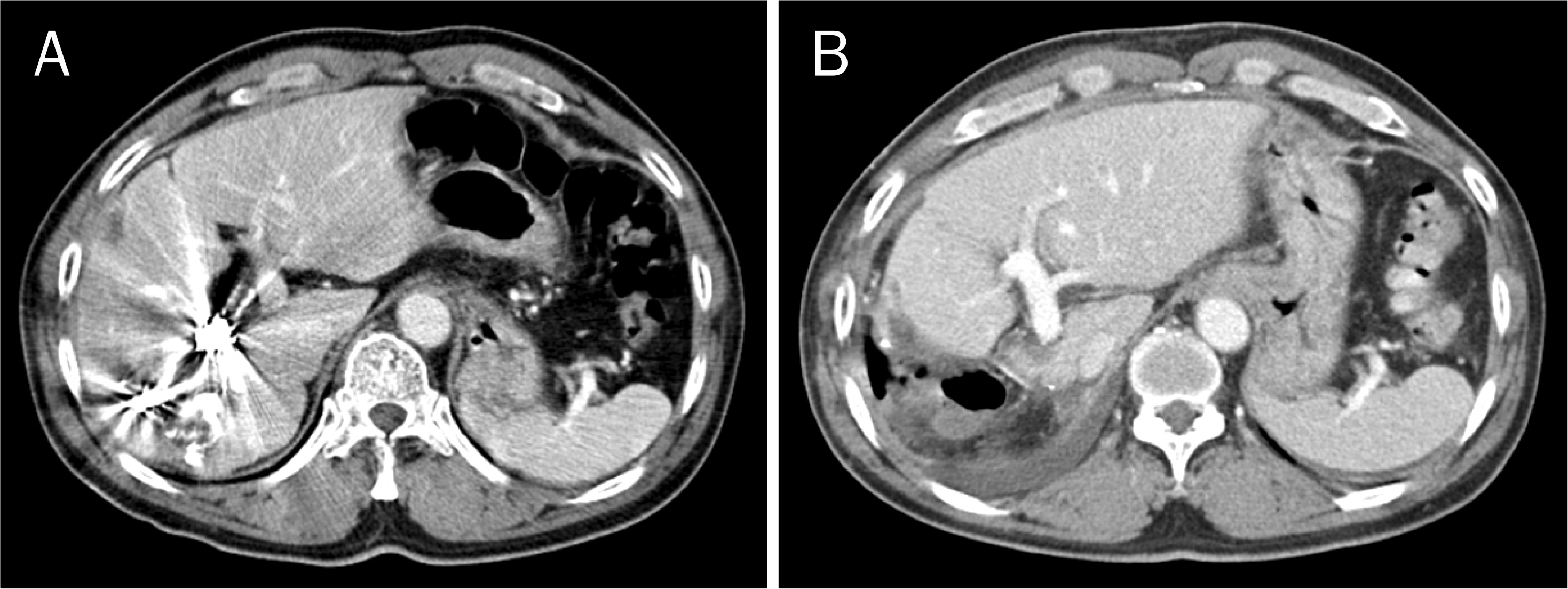
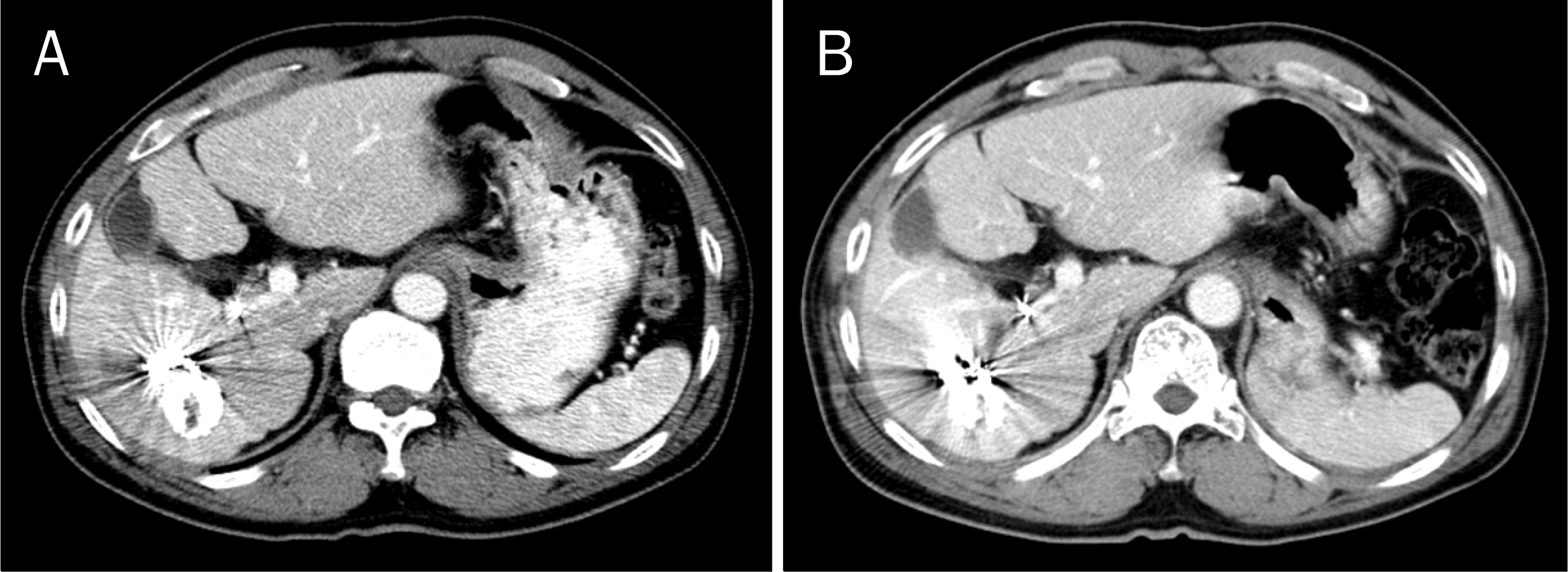 | Fig. 4.Computed tomography images following right portal and hepatic vein embolizations. (A) There were little hemi-liver volume changes 2 weeks after hepatic vein embolization. (B) A slight further atrophy of the right liver was found 2 months after hepatic vein embolization. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download