Abstract
Erythema nodosum is the most common form of septal panniculitis and the most frequent skin manifestation associated with inflammatory bowel disease, affecting up to 15% of Crohn's disease patients. Since the development of erythema nodosum is closely related with a variety of disorders and condition, it can serve as an important early sign of systemic disease. Here, we present the occurrence of erythema nodosum as an early sign of Cronh's disease in a 16-year-old woman.
Go to : 
References
2. Schwartz RA, Nervi SJ. Erythema nodosum: a sign of systemic disease. Am Fam Physician. 2007; 75:695–700.
3. Greenstein AJ, Janowitz HD, Sachar DB. The extraintestinal complications of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis: a study of 700 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 1976; 55:401–412.

4. Requena L, Yus ES. Panniculitis. Part I. Mostly septal panniculitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001; 45:163–183.

6. Veloso FT, Carvalho J, Magro F. Immune-related systemic manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease. A prospective study of 792 patients. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1996; 23:29–34.
7. Hanauer SB. How do I treat erythema nodosum, aphthous ulcerations, and pyoderma gangrenosum? Inflamm Bowel Dis. 1998; 4:70.

8. Farhi D, Cosnes J, Zizi N, et al. Significance of erythema nodosum and pyoderma gangrenosum in inflammatory bowel diseases: a cohort study of 2402 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2008; 87:281–293.
9. Barreiro-de Acosta M, Domínguez-Muñoz JE, Núñez-Pardo de Vera MC, Lozano-León A, Lorenzo A, Peña S. Relationship between clinical features of Crohn's disease and the risk of developing extraintestinal manifestations. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007; 19:73–78.

10. Orchard TR, Wordsworth BP, Jewell DP. Peripheral arthropathies in inflammatory bowel disease: their articular distribution and natural history. Gut. 1998; 42:387–391.

11. Christodoulou DK, Katsanos KH, Kitsanou M, Stergiopoulou C, Hatzis J, Tsianos EV. Frequency of extraintestinal manifestations in patients with inflammatory bowel disease in Northwest Greece and review of the literature. Dig Liver Dis. 2002; 34:781–786.

12. Bernstein CN, Blanchard JF, Rawsthorne P, Yu N. The prevalence of extraintestinal diseases in inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001; 96:1116–1122.

13. Lebwohl M, Lebwohl O. Cutaneous manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 1998; 4:142–148.

14. Mir-Madjlessi SH, Taylor JS, Farmer RG. Clinical course and evo-lution of erythema nodosum and pyoderma gangrenosum in chronic ulcerative colitis: a study of 42 patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 1985; 80:615–620.
15. Jwa SW, Jang HS, Park JH, et al. A case of erythema nodosum associated with Crohn's disease. Korean J Dermatol. 2006; 44:899–901.
16. Park YD, Cho JW, Lee KS. A case of erythema nodosum associated with Crohn's disease. Korean J Dermatol. 2009; 47:986–988.
Go to : 
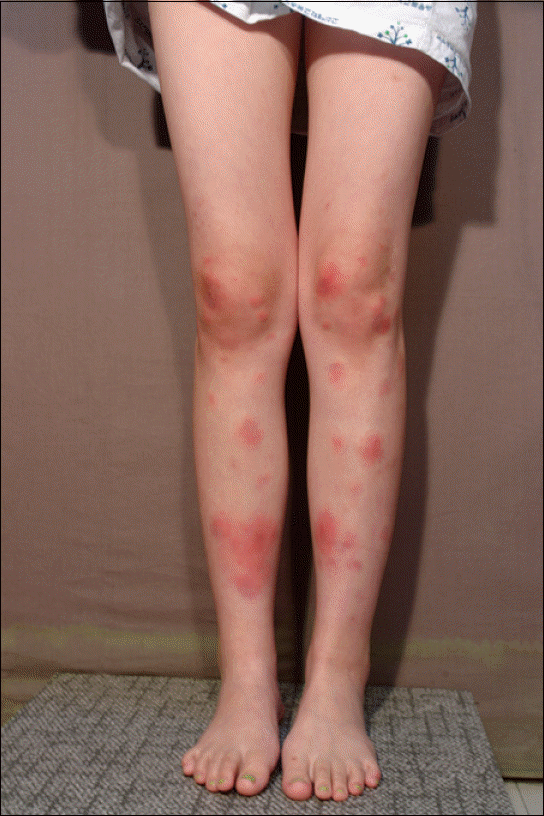 | Fig. 1.Photograph of lower extremities on the first admission. It showed 1–5 cm sized multiple erythematous indurated subcutaneous nodules on the anterior aspect of the both lower extrimities. |
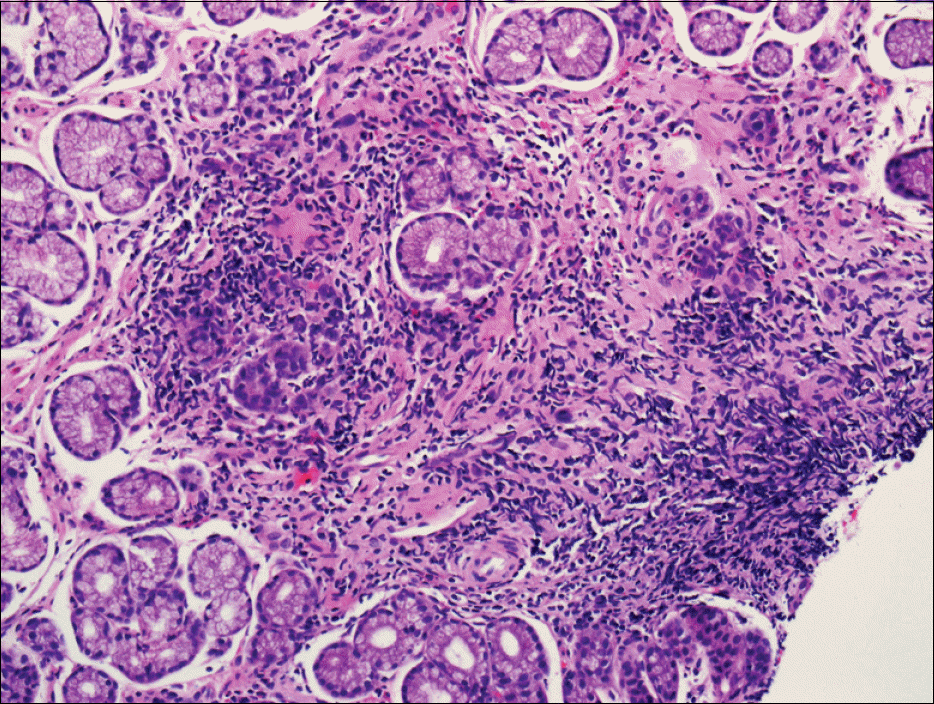
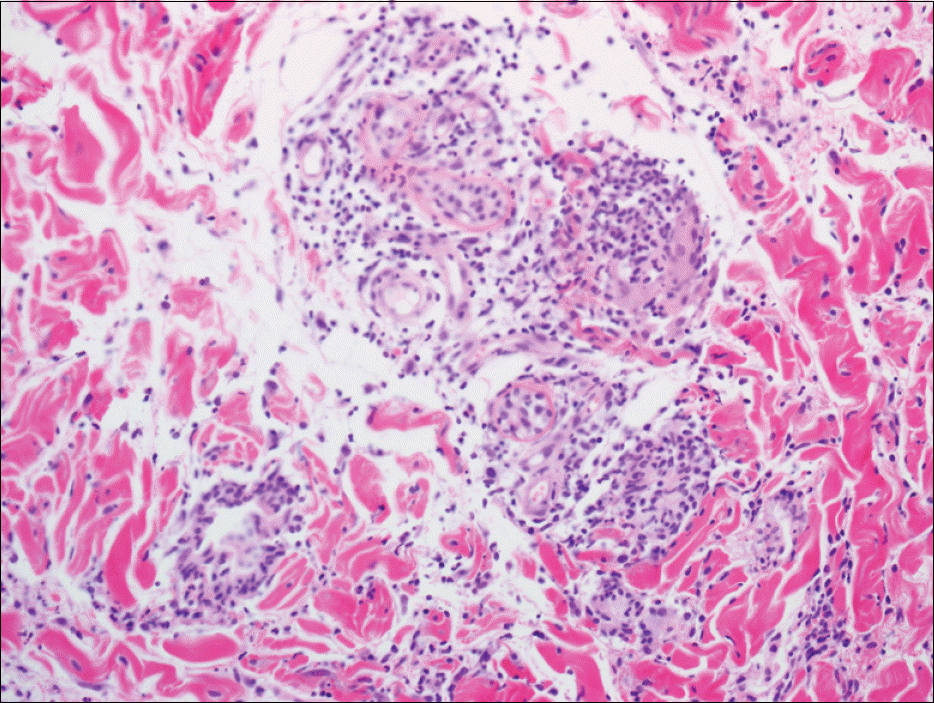 | Fig. 2.Histopathologic finding of skin punch biopsy. It revealed the small and medium sized vessels infiltrated by lymphocytic aggregation in the deep dermis (H&E, ×200). |
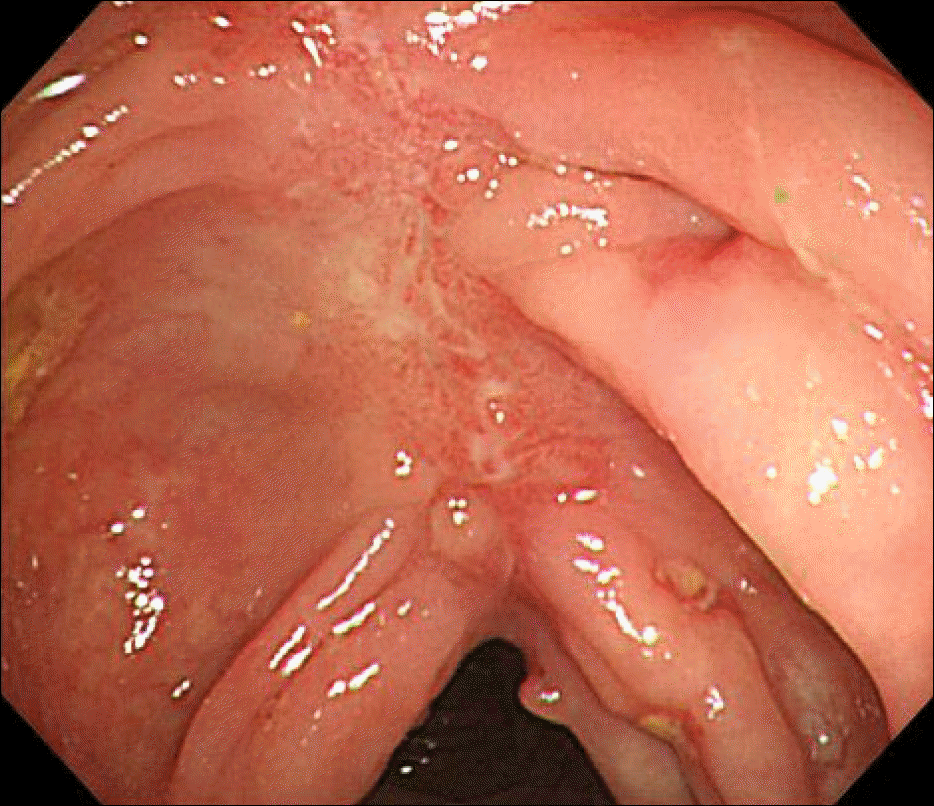 | Fig. 3.Colonoscopic finding of the transverse colon. It showed longitudinally arrayed, linear, active ulcers with several inflammatory pseudopolyps and normal looking background mucosa. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download