Abstract
Primary natural killer (NK) cell like T cell lymphoma of the terminal ileum is extremely rare. It most frequently occurs in the nasal or paranasal areas and less frequently in the skin, the soft tissue, and the gastrointestinal tract. NK/T cell lymphoma involving gastrointestinal tract has characteristic endoscopic features of Inflammatory bowel disease. We herein describe a first case of primary NK/T cell lymphoma misdiagnosed as Behcet's enteritis of the terminal ileum colonoscopically and complicated by cecal bleeding and perforation.
Go to : 
References
1. Kwong YL, Anderson BO, Advani R, Kim WS, Levine AM, Lim ST. Management of T-cell and natural-killer-cell neoplasms in Asia: consensus statement from the Asian Oncology Summit 2009. Lancet Oncol. 2009; 10:1093–1101.

2. Kim HS, Lee DK, Baik SK, Kwon SO, Cho MY, Ko YH. Primary CD56+ T/NK cell lymphoma of the colon. J Gastroenterol. 2002; 37:939–946.

3. Evereklioglu C. Diagnostic dilemma between intestinal Behçet disease and inflammatory bowel disease with pyoderma gangrenosum. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:5748–5751.

4. Otter R, Bieger R, Kluin PM, Hermans J, Willemze R. Primary gastrointestinal non-Hodgkin's lymphoma in a population-based registry. Br J Cancer. 1989; 60:745–750.

5. Gale J, Simmonds PD, Mead GM, Sweetenham JW, Wright DH. Enteropathy-type intestinal T-cell lymphoma: clinical features and treatment of 31 patients in a single center. J Clin Oncol. 2000; 18:795–803.

6. Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, et al. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood. 2009; 114:937–951.

7. Ko YH, Cho EY, Kim JE, et al. NK and NK-like T-cell lymphoma in extranasal sites: a comparative clinicopathological study according to site and EBV status. Histopathology. 2004; 44:480–489.

8. Tung CL, Hsieh PP, Chang JH, Chen RS, Chen YJ, Wang JS. Intestinal T-cell and natural killer-cell lymphomas in Taiwan with special emphasis on 2 distinct cellular types: natural killer-like cytotoxic T cell and true natural killer cell. Hum Pathol. 2008; 39:1018–1025.

9. Son HJ, Rhee PL, Kim JJ, et al. Primary T-cell lymphoma of the colon. Korean J Intern Med. 1997; 12:238–241.

10. Kim YS, Choi YS, Park JS, et al. Case of small bowel perforation due to enteropathy-type T-cell lymphoma. Yonsei Med J. 2009; 50:859–861.

11. Inagaki N, Asaoka D, Mori KL, et al. Enteropathy-type T-cell lymphoma expressing NK-cell intraepithelial lymphocyte (NK-IEL) phenotype. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004; 45:1471–1474.

12. Chim CS, Au WY, Shek TW, et al. Primary CD56 positive lymphomas of the gastrointestinal tract. Cancer. 2001; 91:525–533.

13. Jaffe ES. Classification of natural killer (NK) cell and NK-like T-cell malignancies. Blood. 1996; 87:1207–1210.
Go to : 
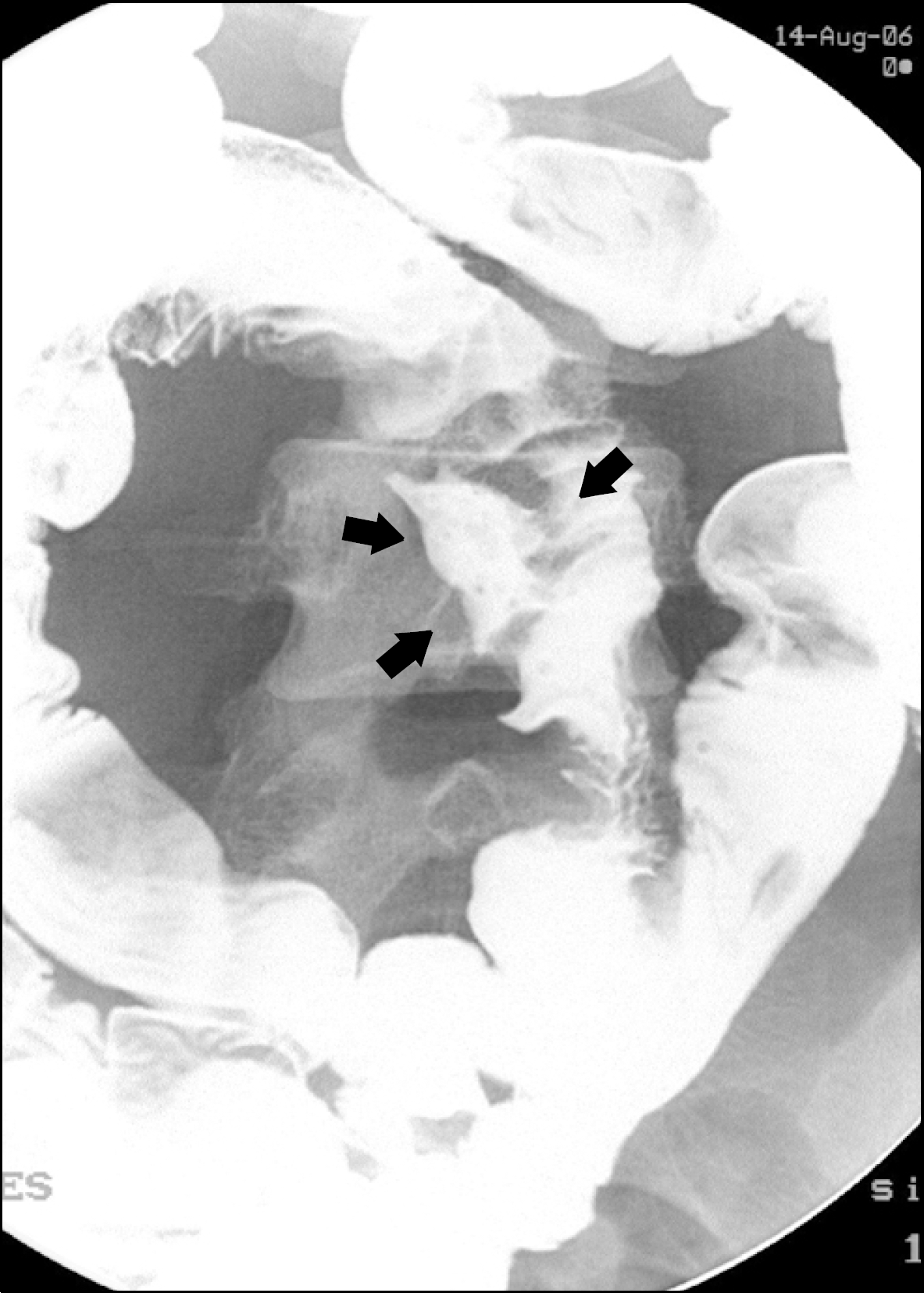 | Fig. 1.Barium enema showing a single deep penetrating ulcer (arrows) in the terminal ileum. Converging fold and mucosal thickening were seen around the ulcer. |
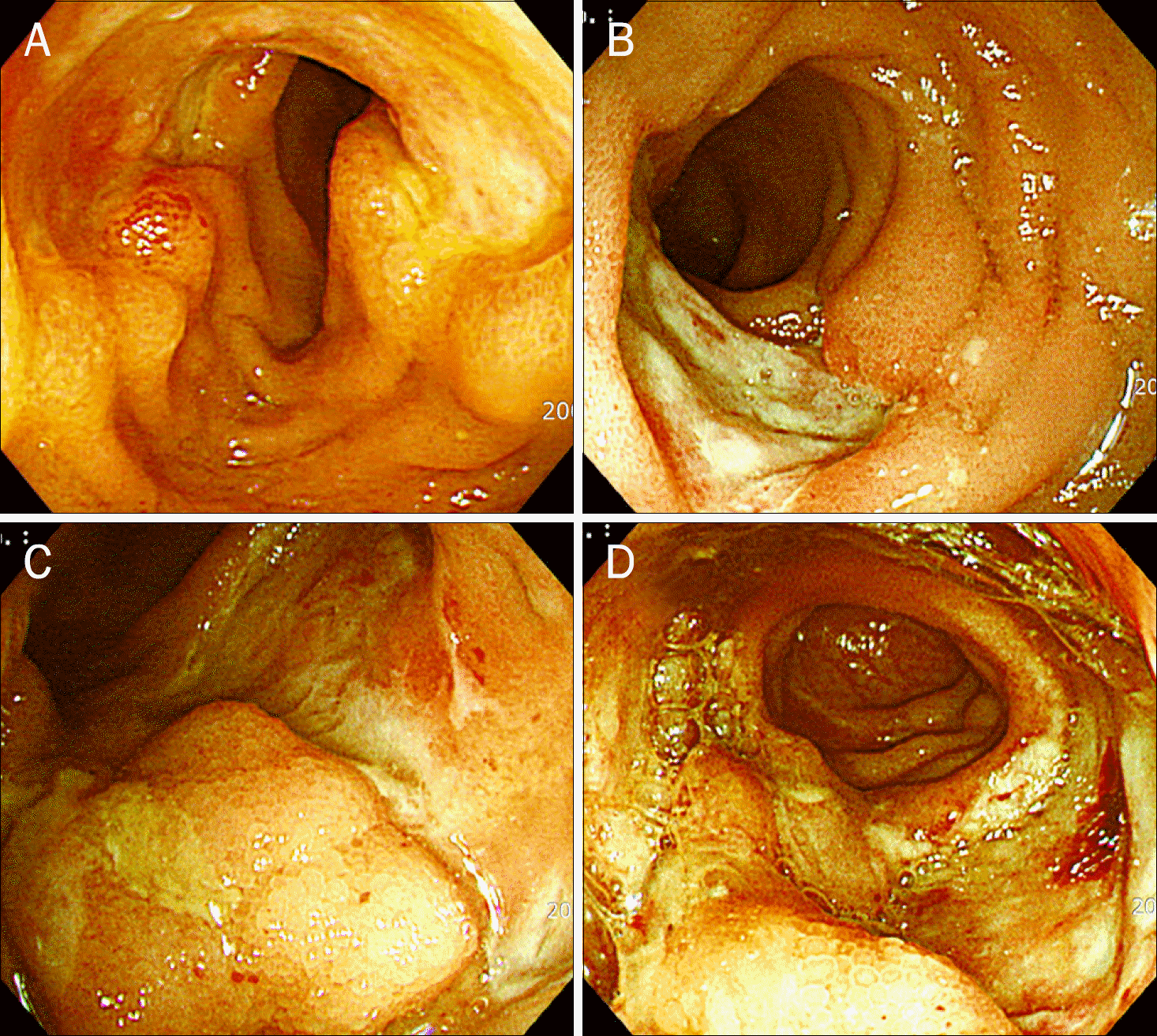 | Fig. 2.Endoscopic photographs of the natural killer cell like T cell lymphoma of the terminal ileum. (A) Single deep penetrating ulcers mimicking Behcet's ileitis in the terminal ileum at initial presentation.(B) Somewhat healing changes at the second colonoscopic examination after short term (2 weeks) steroid treatment. (C) Extensive infilatrating ulcerative mass lesion mimicking Crohn's disease with a marginal oozing was observed on 6-month follow-up colonoscopy. (D) Still remained ulcerative mass lesion after short term antituberculosis medication. |
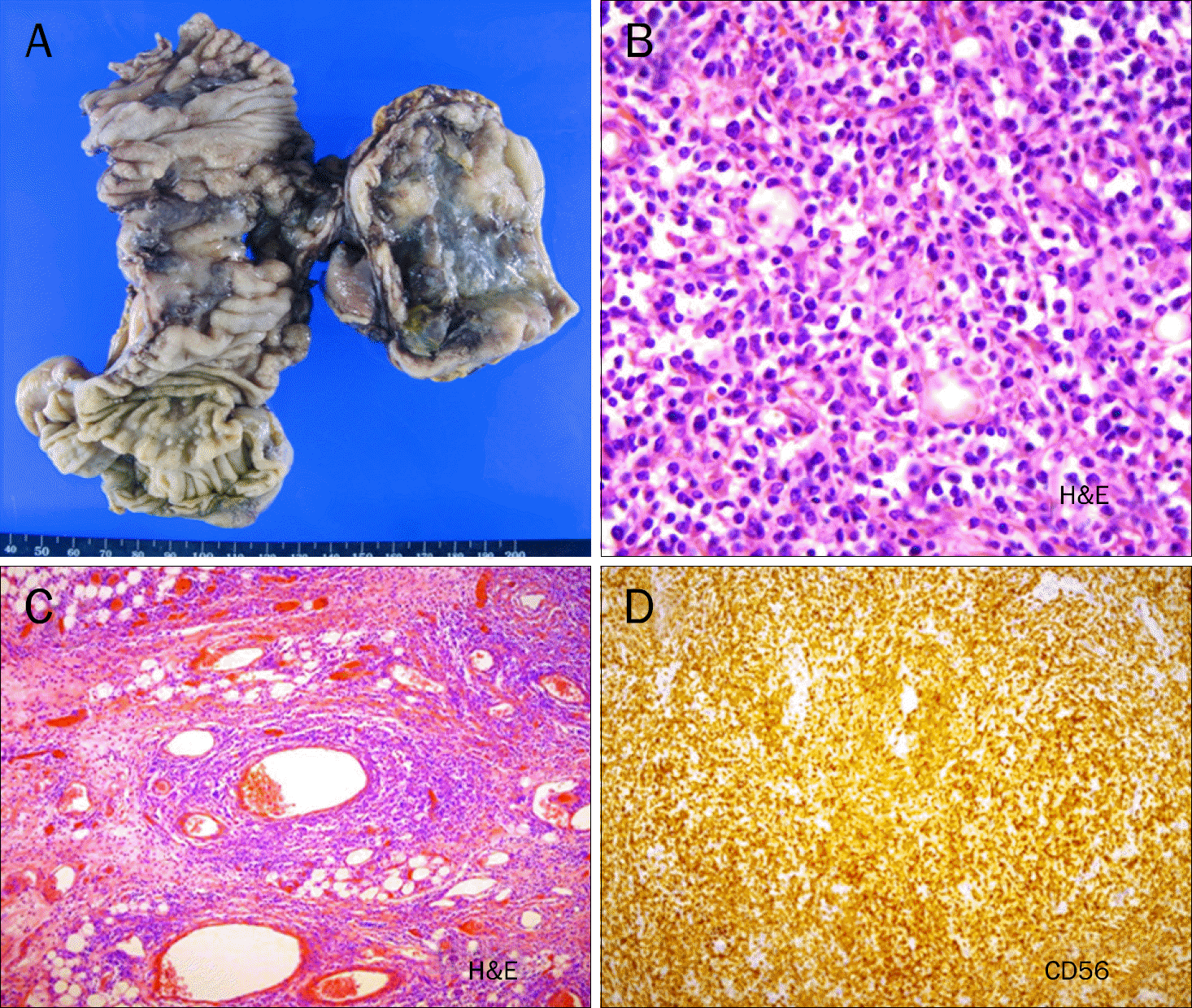 | Fig. 3.(A) Gross appearance of the resected terminal ileum, showing hemorrhage and perforation. (B) Medium to large size atypical lymphocyte infiltration was seen, and high mitotic index (72/10 HPF) was noted (H&E, ×400). (C) Angiocentric growth pattern of medium to large lymphoid cells (H&E, ×100). (D) Immunochemical staining of the tumor cells, showing strong reactivity to both CD3 and CD56 monoclonal antibody (H&E, ×100). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download