Abstract
Background/Aims
The combination therapy with peginterferon and ribavirin is a standard treatment for patients with chronic hepatitis C. However, because of the long duration of the treatment and many complications, the reduction of adherence frequently occur. This study aimed to assess influences of reduced medication adherence in the combination therapy of chronic hepatitis C patients.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 82 patients with chronic hepatitis C who received a combination therapy with peginterferon and ribavirin. The patients were categorized into 3 subgroups on the basis of medication adherence. Group 1 comprised patients who received ≥80% of the recommended dosage of both peginterferon and ribavirin. Group 2 comprised those patients who received ≥80% of the recommended dosage of only 1 drug. The patients of Group 3 received <80% of the recommended dosage of both the drugs.
Results
Sustained virologic response (SVR)s of patients in Group 1, 2 and 3 were 85.4% (41/48), 85.7% (18/21), and 38.5% (5/13), respectively (p=0.002). SVRs of genotype 1 patients in Group 1, 2 and 3 were 84.2% (16/19), 75% (9/12), and 14.3% (1/7), respectively (p=0.003). SVRs of genotype non-1 patients in Group 1, 2 and 3 were 86.2% (25/29), 100% (9/9), and 66.7% (4/6), respectively (p=0.196). Furthermore are SVRs significantly differed with the degree of medication adherence to either peginterferon or ribavirin (p=0.003 and 0.021, respectively). In multivariate analysis, the peginterferon dose was a significant independent factor associated with SVR.
Go to : 
References
1. Alter MJ, Kruszon-Moran D, Nainan OV, et al. The prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States, 1988 through 1994. N Engl J Med. 1999; 341:556–562.

3. Hu KQ, Tong MJ. The long-term outcomes of patients with compensated hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis and history of parenteral exposure in the United States. Hepatology. 1999; 29:1311–1316.

4. Serfaty L, Aumaître H, Chazouillères O, et al. Determinants of outcome of compensated hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1998; 27:1435–1440.

5. Hwang SG. Current clinical practice: KASL guideline of management of chronic hepatitis C. Korean J Med. 2005; 69:713–717.
6. McHutchison JG, Poynard T, Pianko S, et al. The impact of interferon plus ribavirin on response to therapy in black patients with chronic hepatitis C. The International Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group. Gastroenterology. 2000; 119:1317–1323.
7. Strader DB, Wright T, Thomas DL, Seeff LB. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2004; 39:1147–1171.

8. Paterson DL, Swindells S, Mohr J, et al. Adherence to protease inhibitor therapy and outcomes in patients with HIV infection. Ann Intern Med. 2000; 133:21–30.

9. Chesney MA, Ickovics J, Hecht FM, Sikipa G, Rabkin J. Adherence: a necessity for successful HIV combination therapy. AIDS. 1999; 13(Suppl A):S271–S278.
10. Stone VE. Strategies for optimizing adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy: lessons from research and clinical practice. Clin Infect Dis. 2001; 33:865–872.

11. Eisen SA, Miller DK, Woodward RS, Spitznagel E, Przybeck TR. The effect of prescribed daily dose frequency on patient medication compliance. Arch Intern Med. 1990; 150:1881–1884.

12. Dimitroulopoulos D, Petroulaki E, Manolakopoulos S, et al. Peginterferon/ribavirin treatment achieves a higher compliance rate than interferon/ribavirin combination in patients chronically infected with HCV on methadone maintenance. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 21:1407–1412.

13. Glue P, Fang JW, Rouzier-Panis R, et al. Pegylated interferon-alpha2b: pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, and preliminary efficacy data. Hepatitis C Intervention Therapy Group. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2000; 68:556–567.
14. Zeuzem S, Feinman SV, Rasenack J, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a in patients with chronic hepatitis C. N Engl J Med. 2000; 343:1666–1672.

15. Lindsay KL, Trepo C, Heintges T, et al. A randomized, double-blind trial comparing pegylated interferon alfa-2b to interferon alfa-2b as initial treatment for chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2001; 34:395–403.

16. Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Reddy KR, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:975–982.

17. Manns MP, McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, et al. Peginterferon al-fa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2001; 358:958–965.

18. Jeong SW, Kim JD, Woo HY, et al. Impact of adherence to peginterferon-ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C patients on achieving a sustained virologic response. Korean J Hepatol. 2009; 15:338–349.

19. National Institutes of Health. National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference Statement: Management of hepatitis C:2002–June 10–12, 2002. Hepatology. 2002; 36(5 Suppl 1):S3–S20.
20. Lee SS, Heathcote EJ, Reddy KR, et al. Prognostic factors and early predictability of sustained viral response with peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD). J Hepatol. 2002; 37:500–506.

21. Ferenci P, Fried MW, Shiffman ML, et al. Predicting sustained virological responses in chronic hepatitis C patients treated with peginterferon alfa-2a (40 KD)/ribavirin. J hepatol. 2005; 43:425–433.
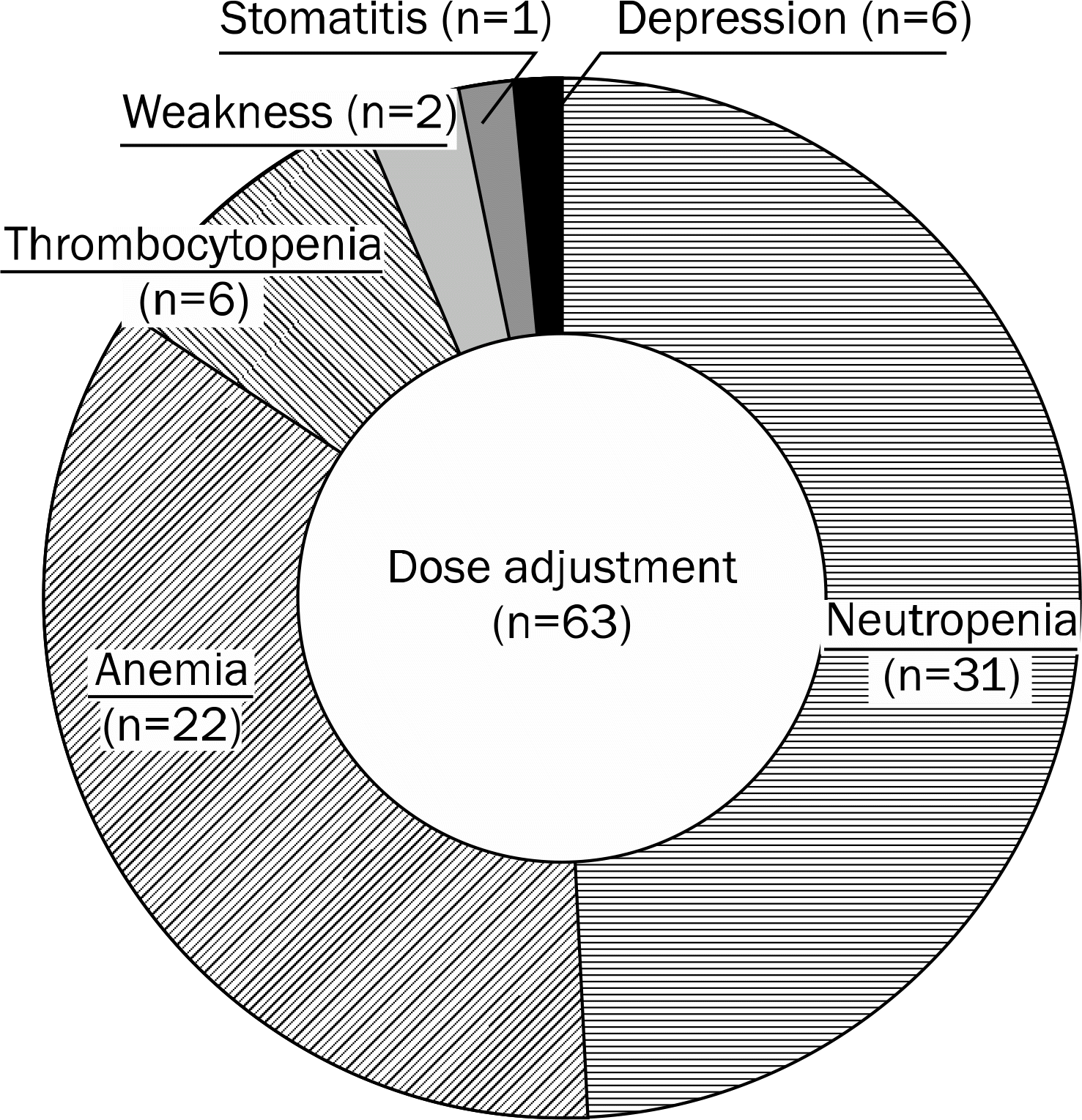
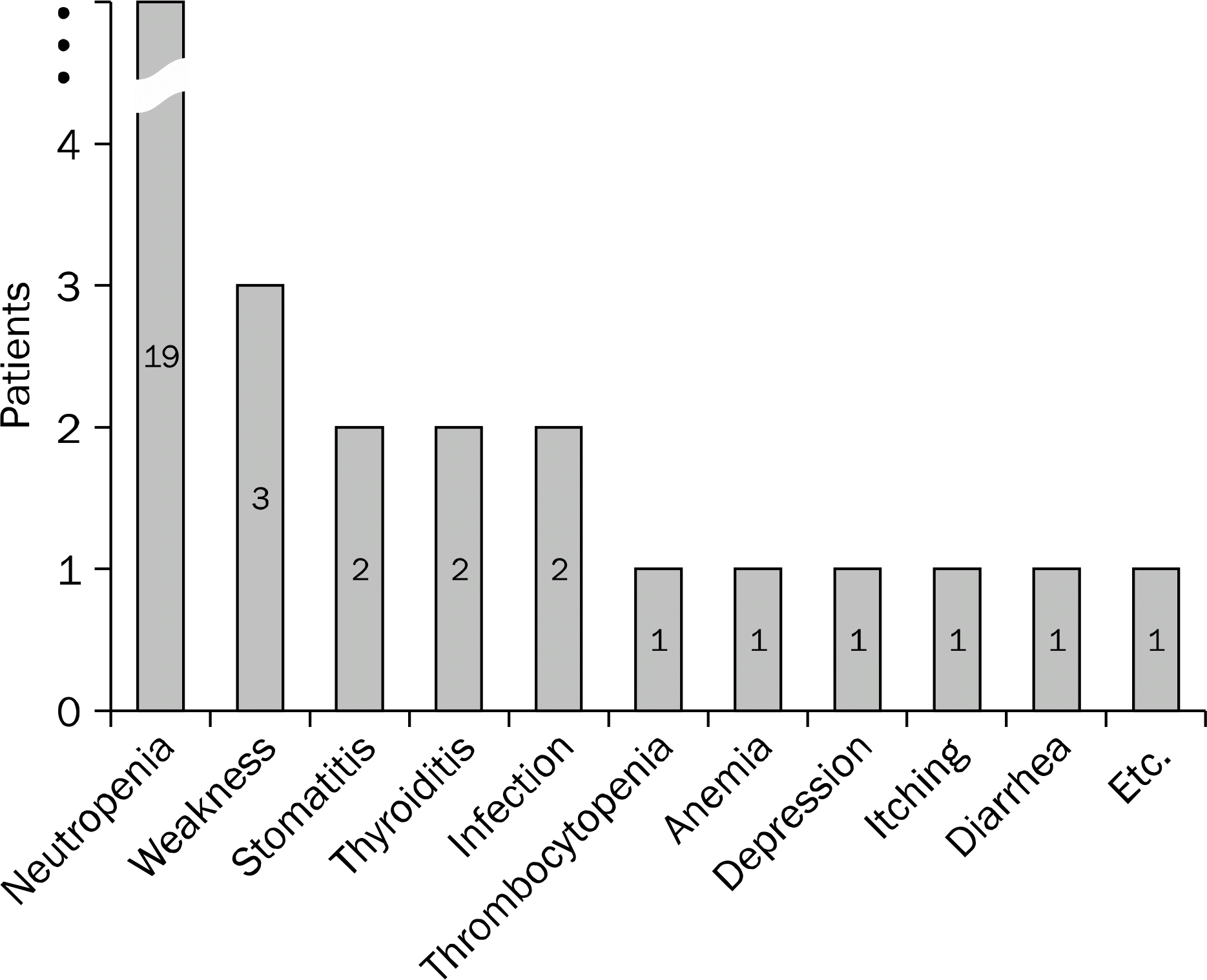
22. Russo MW, Fried MW. Side effects of therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2003; 124:1711–1719.

23. Fried MW. Side effects of therapy of hepatitis C and their management. Hepatology. 2002; 36(5 Suppl 1):S237–S244.

24. Manns MP, Wedemeyer H, Cornberg M. Treating viral hepatitis C: efficacy, side effects, and complications. Gut. 2006; 55:1350–1359.

25. Manns MP. Adherence to combination therapy: influence on sustainedvirologic response and economic impact. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2004; 33(1 Suppl):S11–S24.
Go to : 
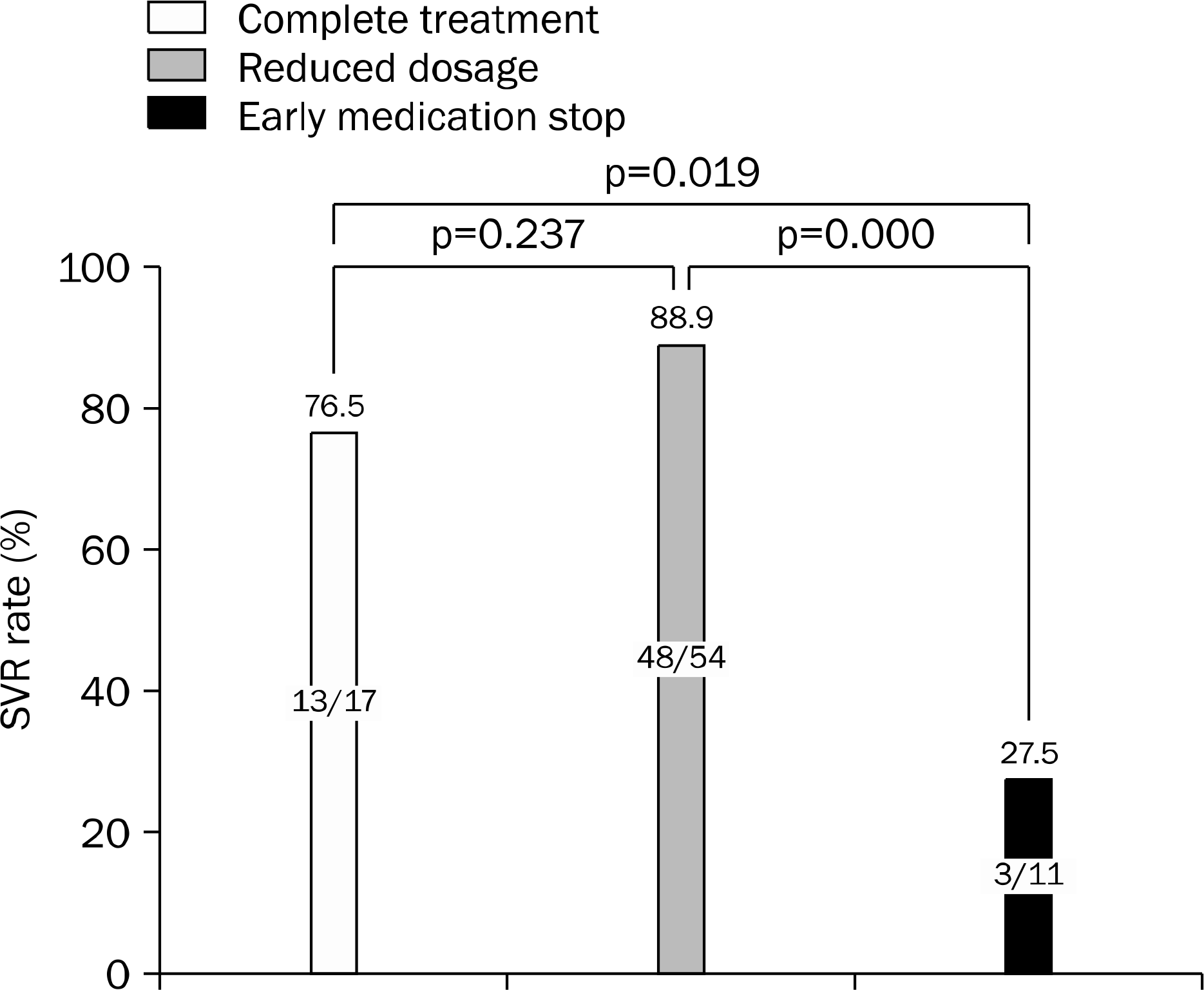 | Fig. 2.SVR rate according to the level of treatment accomplishment. SVR, sustained virologic response. |
Table 1.
Characteristics of Patients at Baseline
Table 2.
SVR Rate according to Medication Adherence
| Medication adherence | Patients achieving SVR | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| n All patients (n=82) | Genotype 1 patients (n=38) | Genotype non-1 patients (n=44) | |
| Group 1 a | 41/48 (85.4%) | 16/19 (84.2%) | 25/29 (86.2%) |
| Group 2 b | 18/21 (85.7%) | 9/12 (75%) | 9/9 (100%) |
| Group 3 c | 5/13 (38.5%) | 1/7 (14.3%) | 4/6 (66.7%) |
| p-value | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.196 |
Table 3.
Univariate Analysis for Factors Influencing SVR




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download