Abstract
A subcapsular splenic hematoma is a very rare hemorrhagic complication of pancreatitis. We report here on a case of pseudocyst with a large subcapsular splenic hematoma in a 43-year-old man who presented with severe left flank pain for one week. Despite the initial conservative treatment consisting of pain control, bowel rest, intravenous fluids and antibiotics, the pain was not relieved. An abdominal computed tomography (CT) was performed, and it showed a pseudocyst that was increasing in size with a large subcapsular splenic hematoma measuring 6×13 cm compared to the images at admission. Ultrasonography (US)-guided percutaneous drainage was performed without any complications, and splenectomy was avoided. After the discharge, the patient remained asymptomatic for eight months. We suggest that percutaneous drainage of a large subcapsular hematoma complicating pancreatitis might be a useful treatment option in selected patients.
Go to : 
References
2. Kuramitsu T, Komatsu M, Ono T, et al. Ruptured subcapsular giant hematoma of the spleen as a complication of chronic pancreatitis. Intern Med. 1995; 34:564–568.

3. Vyborny CJ, Merrill TN, Reda J, Geurkink RE, Smith SJ. Subacute subcapsular hematoma of the spleen complicating pancreatitis: successful percutaneous drainage. Radiology. 1988; 169:161–162.

4. Malka D, Hammel P, Lévy P, et al. Splenic complications in chronic pancreatitis: prevalence and risk factors in a medical-surgical series of 500 patients. Br J Surg. 1998; 85:1645–1649.

5. Siu TL. Percutaneous drainage of spontaneous subcapsular haematoma of the spleen complicating chronic pancreatitis. Surgeon. 2004; 2:52–55.

6. Patel VG, Eltayeb OM, Zakaria M, Fortson JK, Weaver WL. Spontaneous subcapsular splenic hematoma: a rare complication of pancreatitis. Am Surg. 2005; 71:1066–1069.

7. Tseng CW, Chen CC, Chiang JH, Chang FY, Lin HC, Lee SD. Percutaneous drainage of large subcapsular hematoma of the spleen complicating acute pancreatitis. J Chin Med Assoc. 2008; 71:92–95.

9. Greenstein A, DeMaio EF, Nabseth DC. Acute hemorrhage associated with pancreatic pseudocysts. Surgery. 1971; 69:56–62.
10. Warshaw AL, Chesney TM, Evans GW, McCarthy HF. Intrasplenic dissection by pancreatic pseudocysts. N Engl J Med. 1972; 287:72–75.

11. Sitzmann JV, Imbembo AL. Splenic complications of a pancreatic pseudocyst. Am J Surg. 1984; 147:191–196.

12. Heider R, Behrns KE. Pancreatic pseudocysts complicated by splenic parenchymal involvement: results of operative and percutaneous management. Pancreas. 2001; 23:20–25.

13. Agnifili A, Gianfelice F, Gola P, et al. Subcapsular splenic hematoma complicating chronic relapsing pancreatitis. Case report. Eur J Surg. 1991; 157:63–65.
Go to : 
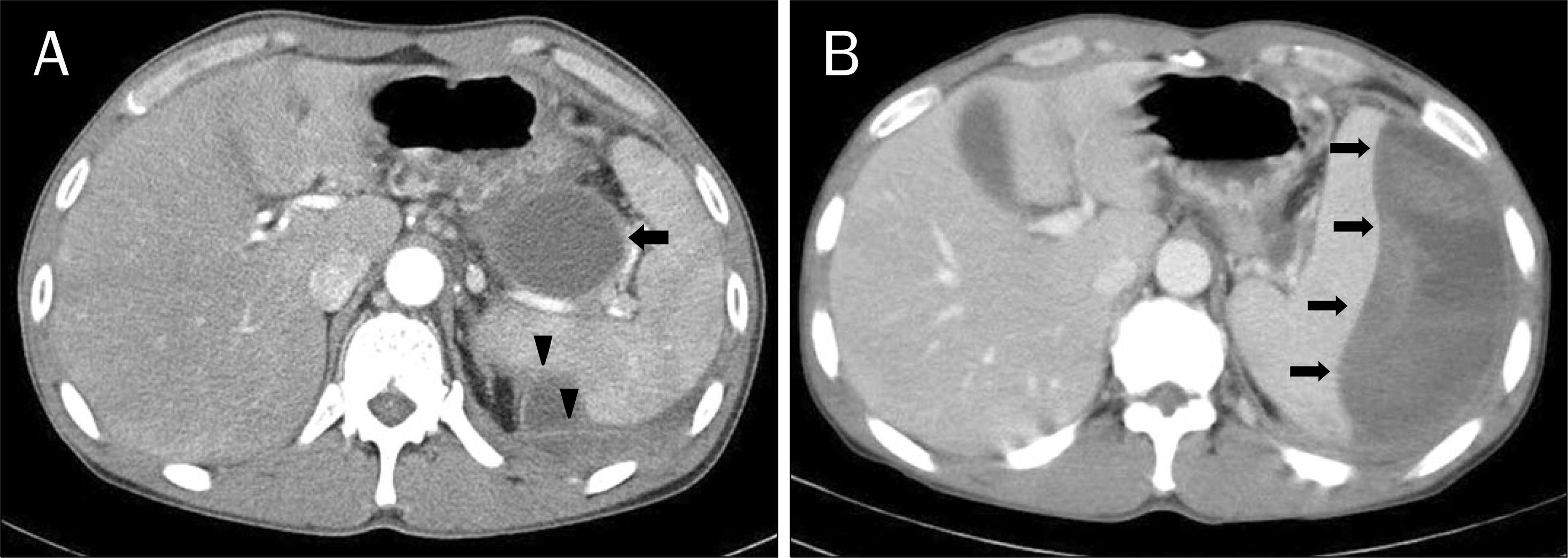 | Fig. 1.Computed tomographic (CT) scan images during the second episode of pancreatitis and in the emergency room. (A) Variable sized multiple pseudocysts in the tail of the pancreas compressed the adjacent structures including splenic vein, gastric fundus (arrow), and splenic parenchyma (arrow heads). (B) A CT scan showed increased size of the pseudocyst with a large subcapsular splenic hematoma (arrows) measuring 5×12 cm in the tail of pancreas. |
 | Fig. 2.CT scan images on hospital day 6 and 3 weeks after US-guided drainage. (A and B) increased size (approximately 6×13 cm) of the psedocyst with subcapsular splenic hematoma is shown (arrows and arrow heads). (C and D) CT images 3 weeks after US-guided percutaneous drainage, the size of the pseudocyst with subcapsular splenic hematoma was markedly decreased. A drainage catheter is shown (arrow head). |
Table 1.
Cases of Successful Percutaneous Drainage of Subcapsular Splenic Hematoma in the Literature
| Vyborny CJ, et al.3 | Siu TL.5 | Tseng CW, et al.7 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Published year | 1988 | 2004 | 2008 |
| Sex | Male | Male | Male |
| Age (year) | 58 | 38 | 32 |
| Previous trauma history | None | NA | NA |
| Previous episodes of pancreatitis | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Presence of pseudocyst | Yes | Yes | NA |
| Number and largest size of pseudocyst | Multiple, 2.5 cm | 1, 3.5 cm | NA |
| Elapsing time a | 1 month | 11 days | 2 weeks |
| Presenting symptoms | Nausea, early satiety, postprandial emesis, LUQ discomfort | LUQ pain | Intermittent epigastric pain with radiating back pain |
| Serum amylase | NA | 366 U/L | 266 U/L |
| Serum lipase | NA | 1505 U/L | 473 U/L |
| Size of hematoma on abdomen CT scan | NA | 8×5×13 cm | 15.0×13.0×9.5 cm |
| Follow-up | Asymptomatic at 2 years follow-up | Pain free 6 months after the procedure | Asymptomatic at 1 year follow-up |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download