Abstract
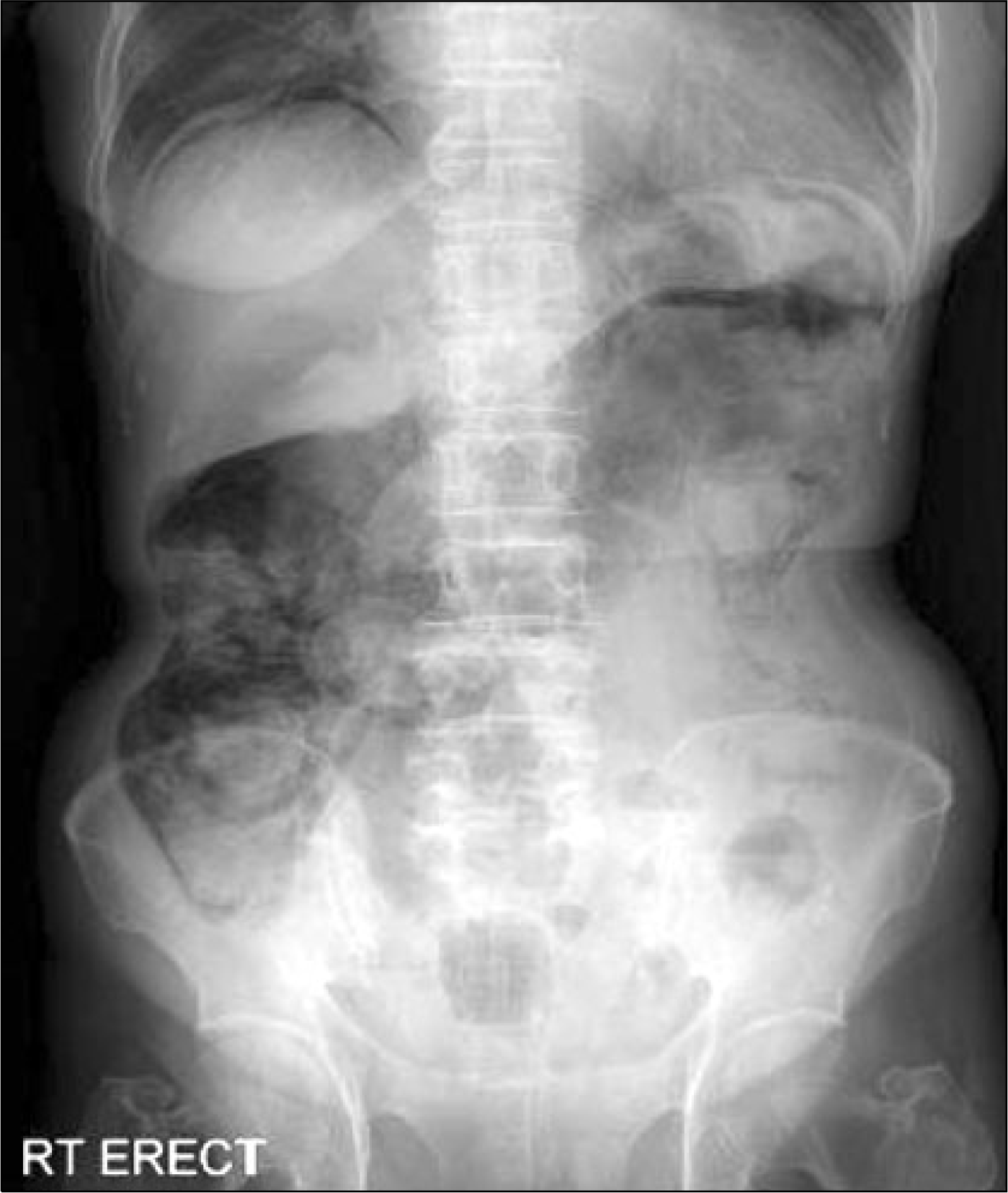
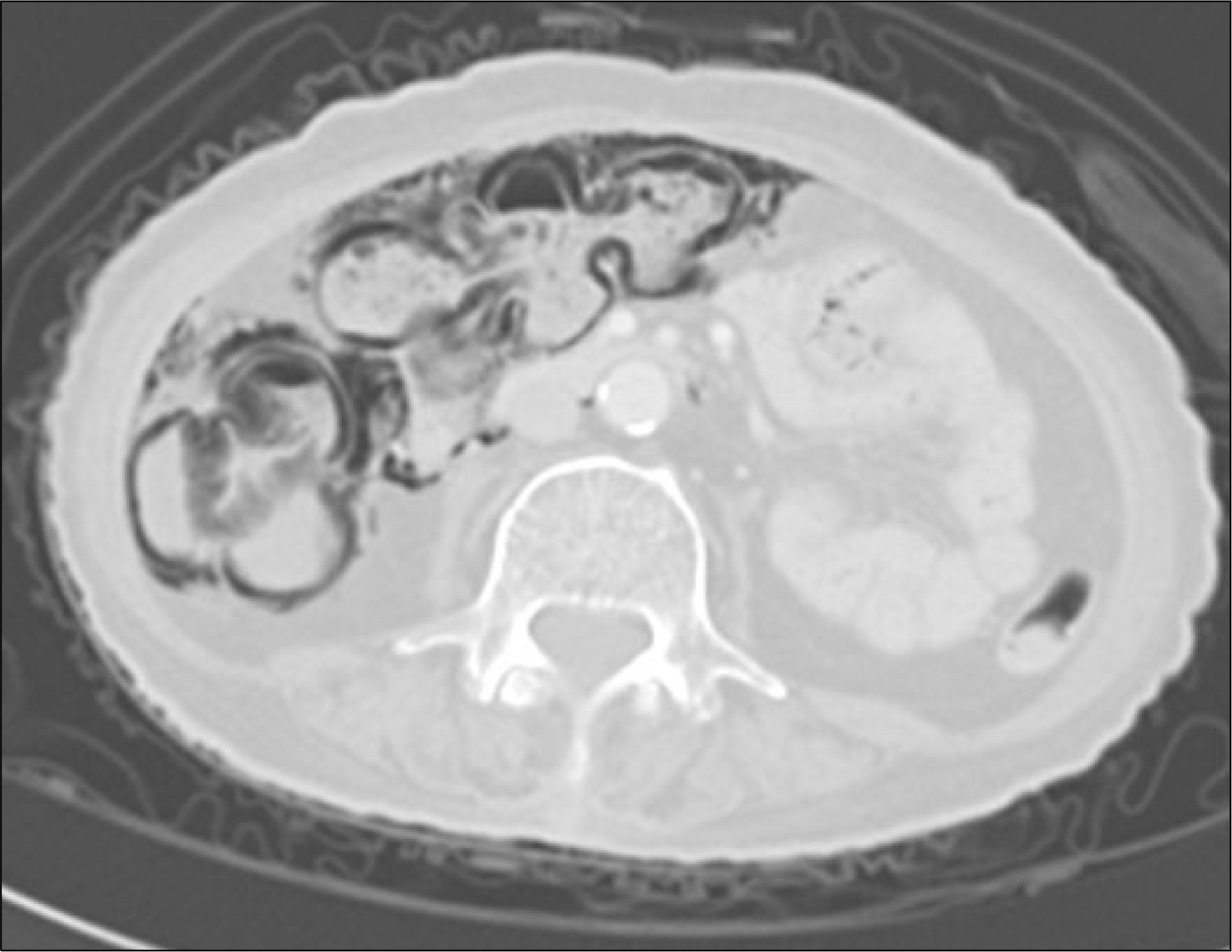
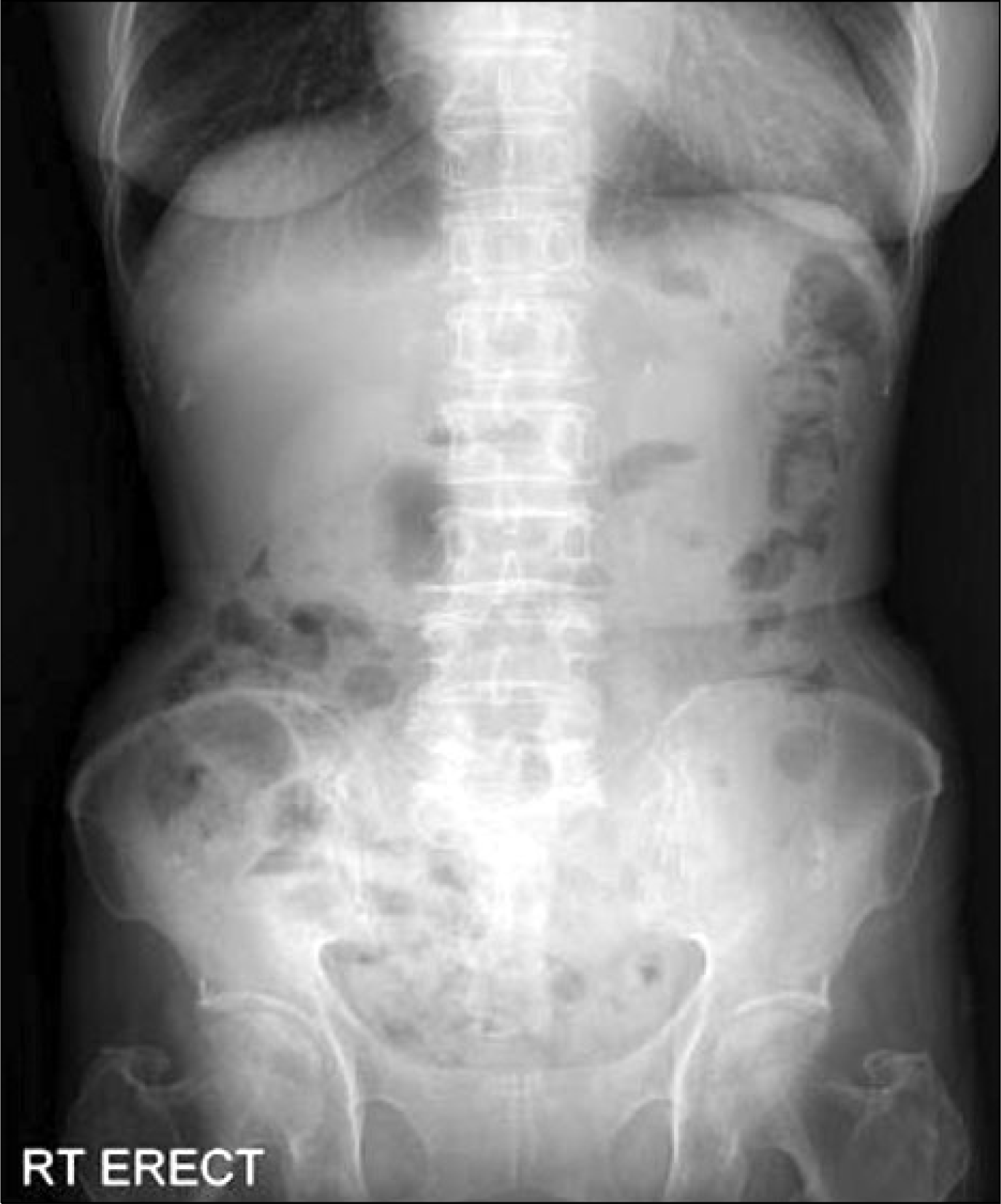
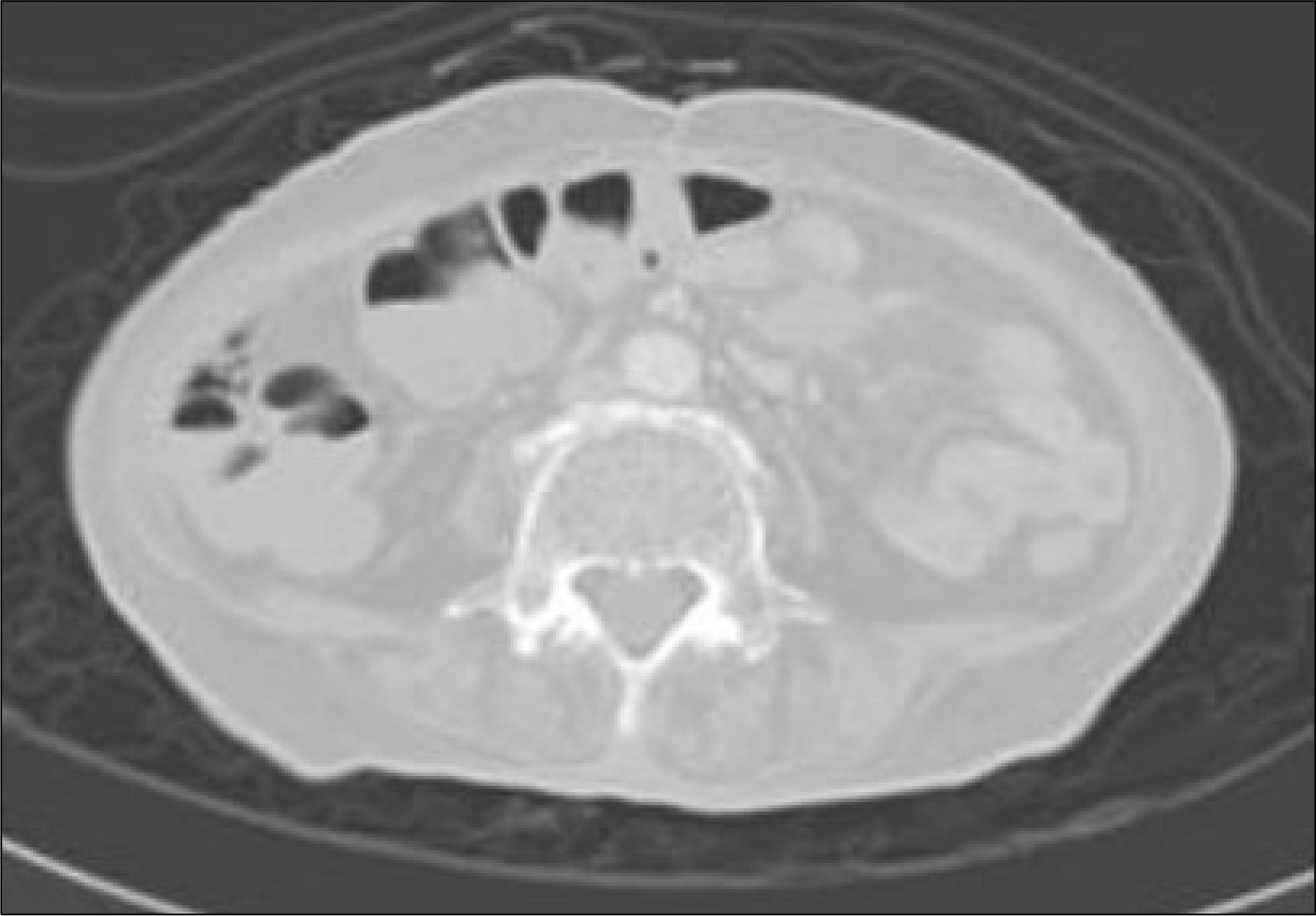
Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis (PCI), characterized by presence of intramural gas cyst in the intestinal wall is associated with various medical condition. Polymyosistis, however, is rarely associated with PCI. Few cases are reported in the world, and none has not been reported previously in Korea. A 67-year-old woman with polymyositis developed mild abdominal pain and abdominal distension during treatment with steroid and azathioprine. Radiographic findings including CT scan showed intraperitoneal free gas and intramural air, compatible with PCI. The patient's symptom and clinical findings improved after the treatment with antibiotics and high-dose oxygen therapy.
Go to : 
References
1. Wada Y, Murayama N, Hirose S, et al. A case of pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis in a patient with polymyositis and interstitial pneumonia. Mod Rheumatol. 2004; 14:260–263.

2. Kuroda T, Ohfuchi Y, Hirose S, Nakano M, Gejyo F, Arakawa M. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis in a patient with polymyositis. Clin Rheumatol. 2001; 20:49–52.

3. Zülke C, Ulbrich S, Graeb C, et al. Acute pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis following allogeneic transplantation – the surgeon's dilemma. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002; 29:795–798.

4. Kim YJ, Jeon EK, Cho BS, et al. A case of pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis in an allogenic stem cell transplant recipient who had bronchiolitis obliterans and pulmonary infection by Mycobacterium abscessus. Infect Chemother. 2008; 40:271–275.
5. Turan M, Sen M, Egilmez R. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis: report of two cases. Acta Chir Belg. 2004; 104:742–744.

6. Selva-O'Callaghan A, Martínez-Costa X, Solans-Laque R, Mauri M, Capdevila JA, Vilardell-Tarrés M. Refractory adult dermatomyositis with pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis treated with infliximab. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2004; 43:1196–1197.
7. Park MJ. A case of nonspecific interstitial pneumonia complicated with spontaneous pneumomediastinum, subcutaneous emphysema and pneumatosis interstinalis. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2008; 64:138–143.

8. Antosz Z, Zaniewski M. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis–a report of two cases. Pol J Pathol. 2004; 55:177–180.
9. Tsujimoto T, Shioyama E, Moriya K, et al. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis following alpha-glucosidase inhibitor treatment: a case report and review of the literature. World J Gastroenterol. 2008; 14:6087–6092.

10. Heng Y, Schuffler MD, Haggitt RC, Rohrmann CA. Pneumatosis intestinalis: a review. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995; 90:1747–1758.
11. St Peter SD, Abbas MA, Kelly KA. The spectrum of pneumatosis intestinalis. Arch Surg. 2003; 138:68–75.

12. Knechtle SJ, Davidoff AM, Rice RP. Pneumatosis intestinalis. Surgical management and clinical outcome. Ann Surg. 1990; 212:160–165.
Go to : 




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download