Abstract
Background/Aims
Pegylated interferon plus ribavirin combination therapy has been the standard of therapy for patients with chronic hepatitis C. Although previous studies have reported long term durability after the sustained virologic response (SVR) with standard therapy for chronic hepatitis C, it is still unclear in Korea. The aim of this study was to evaluate the relapse rate and related factors after SVR to pegylated interferon therapy in Korean patients with chronic hepatitis C.
Methods
A total of 119 chronic hepatitis C patients were treated with pegylated interferon plus ribavirin, and 73 patients achieved SVR (61.3%). Among 73 patients who achieved SVR, 68 patients (genotype 1, n=40; genotype non-1, n=28) were evaluated for virological response after SVR.
Results
SVR rate in genotype 1 and genotype non-1 were 52.5%, and 65.1%, respectively. Relapse after SVR occurred in 5 patients (7.4%) with genotype 1, and the median time to relapse from SVR was 10 months. Univariate analysis revealed that the dose reduction of pegylated interferon (p=0.005) and cirrhosis (p=0.03) were significantly associated with relapse.
Go to : 
References
1. Armstrong GL, Wasley A, Simard EP, McQuillan GM, Kuhnert WL, Alter MJ. The prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States, 1999 through 2002. Ann Intern Med. 2006; 144:705–714.

2. Suh DJ, Jeong SH. Current status of hepatitis C virus infection in Korea. Intervirology. 2006; 49:70–75.

3. McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, Schiff ER, et al. Interferon alfa-2b alone or in combination with ribavirin as initial treatment for chronic hepatitis C. Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group. N Engl J Med. 1998; 339:1485–1492.
4. Poynard T, Marcellin P, Lee SS, et al. Randomised trial of interferon alpha2b plus ribavirin for 48 weeks or for 24 weeks versus interferon alpha2b plus placebo for 48 weeks for treatment of chronic infection with hepatitis C virus. International Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group (IHIT). Lancet. 1998; 352:1426–1432.
5. Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Reddy KR, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:975–982.

6. Desmond CP, Roberts SK, Dudley F, et al. Sustained virological response rates and durability of the response to interferon-based therapies in hepatitis C patients treated in the clinical setting. J Viral Hepat. 2006; 13:311–315.

7. Formann E, Steindl-Munda P, Hofer H, et al. Longterm follow-up of chronic hepatitis C patients with sustained virological response to various forms of interferon-based anti-viral therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006; 23:507–511.

8. Khokhar N. Late relapse in chronic hepatitis C after sustained viral response to interferon and ribavirin. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004; 19:471–472.

9. Reichard O, Glaumann H, Frydén A, et al. Two-year biochemical, virological, and histological follow-up in patients with chronic hepatitis C responding in a sustained fashion to interferon al-fa-2b treatment. Hepatology. 1995; 21:918–922.

10. Tsuda N, Yuki N, Mochizuki K, et al. Longterm clinical and virological outcomes of chronic hepatitis C after successful interferon therapy. J Med Virol. 2004; 74:406–413.

11. Kim CH, Park BD, Lee JW, et al. Durability of a sustained virologic response in combination therapy with interferon/peginterferon and ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C. Korean J Hepatol. 2009; 15:70–79.

12. Rodriguez-Torres M, Jeffers LJ, Sheikh MY, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin in Latino and non-Latino whites with hepatitis C. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360:257–267.

Go to : 
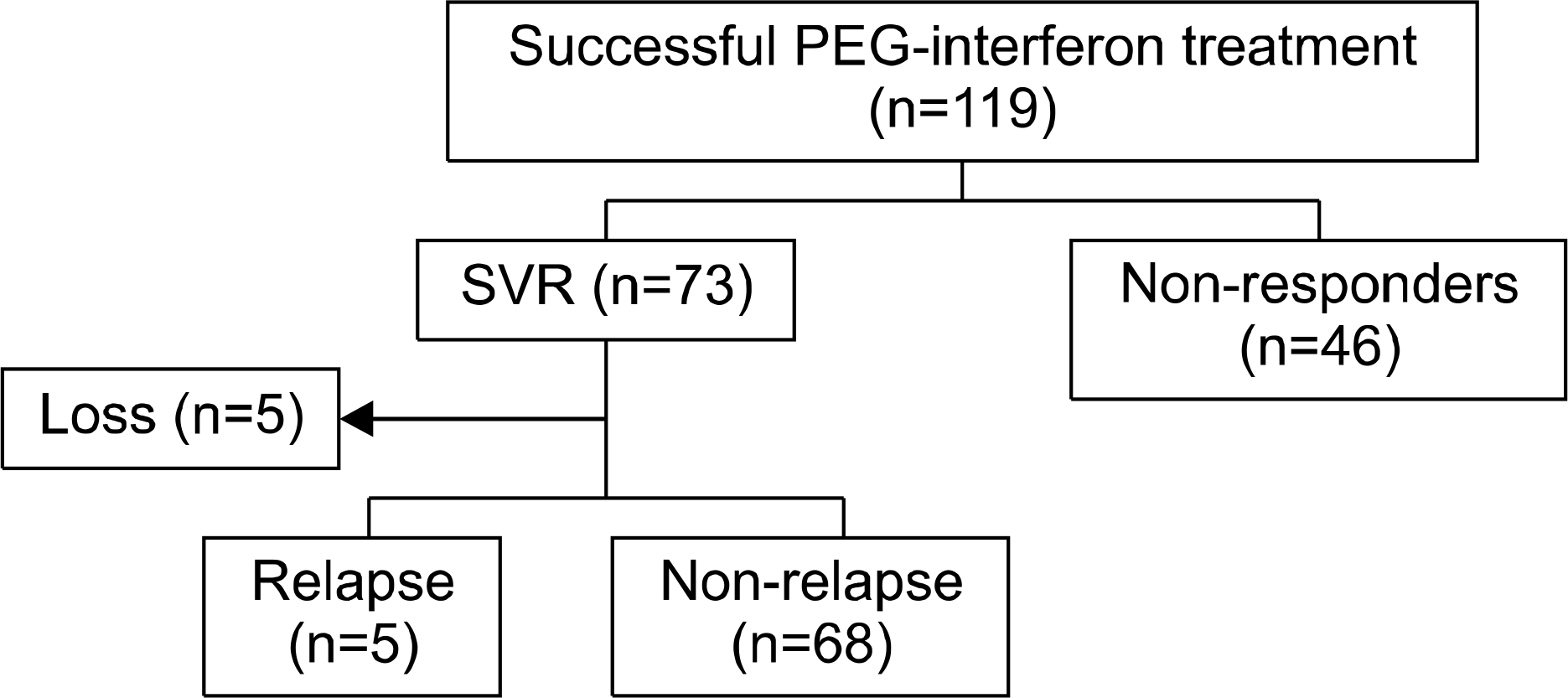 | Fig. 1.Flow diagram for enrolled patients. SVR, sustained virologic response; PEG, pegylated. |
Table 1.
Baseline Characteristics of Patients
| Relapsed (n=5) | Non-relapsed (n=63) | p-value a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, male (%) | 2 (40) | 40 (63) | 0.36 |
| Age (years) | 54 (40–67) | 55 (31–75) | 0.90 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.8 | 23.3 | 0.45 |
| Genotype, type 1 (%) | 5 (100) | 35 (55.6) | 0.05 |
| Platelet count (*109/L) | 155 (82–197) | 159 (65–284) | 0.40 |
| PT INR | 0.95 (0.92–1.1) | 1.0 (0.9–1.19) | 0.30 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 57 | 63 | 0.42 |
| HCV RNA (*105 IU/mL) | 18 (8.5–211) | 8.5 (0.01–210) | 0.05 |
| Cirrhosis (%) | 2 (40) | 4 (6.3%) | 0.03 |
| Treatment-naïve | 5 | 55 | 0.99 |
Table 2.
Characteristics of Patients with Relapse after SVR
| Sex | Age | Geno_type | PEG-interferon | Liver biopsy (fibrosis) a | Dose of interferon (%) | Dose of ribavirin (%) | EVR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | 67 | 1b | α-2b | 3 | 60.8 | 100 | + |
| F | 51 | 1b | α-2b | 0 | 75 | 93.7 | + |
| F | 54 | 1b | α-2a | 1 | 53.1 | 80 | + |
| F | 56 | 1b | α-2a | 4 | 62.5 | 33 | + |
| M | 40 | 1b | α-2a | 4 | 70 | 93 | + |
Table 3.
Univariate Logistic Analysis: Predictors of Relapse after SVR
| Relapsed (n=5) | Non-relapse (n=63) | ed p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype, type 1 | 5 | 35 | 0.05 |
| High viral load (>8*105 IU/mL) | 5 | 33 | 0.06 |
| DM or IFG | 2 | 23 | 1.00 |
| Fibrosis score a (cirrhosis) | 2 | 4 | 0.03 |
| Reduced ribavirin dose (<75%) | 1 | 30 | 1.00 |
| Reduced PEG-interferon dose (<75%) | 4 | 10 | 0.005 |
| Treatment-naïve (n) | 5 | 53 | 0.63 |
| Species of interferon (α-2a/α-2b) | 3/2 | 45/18 | 0.67 |
Table 4.
Predictors of Relapse after SVR in Genotype 1
| Relapsed (n=5) | Non-relapsed (n=35) | d p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| High viral load (>8*105 IU/mL) | 5 | 15 | 0.98 |
| DM or IFG Fibrosis scorea (cirrhosis) | 2 2 | 15 1 | 1.00 0.66 |
| Reduced ribavirin dose (<75%) | 1 | 22 | 0.09 |
| Reduced PEG-interferon dose (<75%) | 4 | 6 | 0.01 |
| Treatment-naïve | 5 | 28 | 0.99 |
| Species of interferon (α-2a/α-2b) | 3/2 | 24/11 | 0.73 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download