Abstract
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is an inherited disease characterized by the development of hundreds of colorectal adenomas, leading to a 100% lifetime risk of colorectal cancer. A prophylactic colectomy is recom-mended for patients with FAP to prevent colorectal cancer. Four surgical strategies are available for patients with FAP: proctocolectomy with permanent ileostomy, colectomy with ileorectal anastomosis, proctocolectomy with Koch's pouch continent ileostomy (Koch), and restorative proctocolectomy with ileal pouch-anal anastomosis (IPAA). Koch and IPAA, which make ileal pouch, have theoretical advantage of the elimination of the risk of colorectal cancer and adenomas and good functional outcome of reduced defecation frequency. However, recent reports have shown frequent development of adenomas and carcinomas in the ileal pouch after Koch or IPAA. We experienced 2 cases of multiple pouch adenomas after pouch surgery in FAP patients. Both patients were treated with endoscopic mucosal resection without complications. We report these 2 cases with a review of literatures.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Bussey HJ, Veale AM, Morson BC. Genetics of gastrointestinal polyposis. Gastroenterology. 1978; 74:1325–1330.

2. Jagelman DG. Choice of operation in familial adenomatous polyposis. World J Surg. 1991; 15:47–49.

3. Wu JS, McGannon EA, Church JM. Incidence of neoplastic polyps in the ileal pouch of patients with familial adenomatous polyposis after restorative proctocolectomy. Dis Colon Rectum. 1998; 41:552–557.

4. Thompson-Fawcett MW, Marcus VA, Redston M, Cohen Z, Mcleod RS. Adenomatous polyposis develop commonly in the ileal pouch of patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Dis Colon Rectum. 2001; 44:347–353.
5. Parc YR, Olschwang S, Desaint B, Schmitt G, Parc RG, Tiret E. Familial adenomatous polyposis: prevalence of adenomas in the ileal pouch after restorative proctocolectomy. Ann Surg. 2001; 233:360–364.

6. Moussata D, Nancey S, Lapalus MG, et al. Frequency and severity of ileal adenomas in familial adenomatous polyposis after colectomy. Endoscopy. 2008; 40:120–125.

7. Groves CJ, Beveridge G, Swain DJ, et al. Prevalence and morphology of pouch and ileal adenomas in familial adenomatous polyposis. Dis Colon Rectum. 2005; 48:816–823.

8. Tajika M, Nakamura T, Nakahara O, et al. Prevalence of adenomas and carcinomas in the ileal pouch after proctocolectomy in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. J Gastrointest Surg. 2009; 13:1266–1273.

9. Clausen MR, Tveda M, Mortensen PB. Short-chain fatty acids in pouch contents from patients with and without pouchitis after ileal pouch-anal anastomosis. Gastroenterology. 1992; 103:1144–1153.

10. Nasmyth DG, Godwin PG, Dixon MF, Williams NS, Johnston D. Ileal ecology after pouch-anal anastomosis or ileostomy. A study of mucosal morphology, fecal bacteriol-ogy, fecal volatile fatty acids, and their interrelationship. Gastroenterology. 1989; 96:817–824.
11. Natori H, Utsunomiya J, Yamamura T, Benno Y, Uchida K. Fecal and stomal bile acid composition after ileostomy or ileoanal anastomosis in patients with chronic ulcerative colitis and adenomatous coli. Gastroenterology. 1992; 102:1278–1288.
12. Corfield AP, Warren BF, Bartolo DC, Wagner SA, Clamp JR. Mucin changes in ileoanal pouches monitored by metabolic labeling and histochemistry. Br J Surg. 1992; 79:1209–1212.
13. de Silva HJ, Millard PR, Kettlewell M, Mortensen NJ, Prince C, Jewell DP. Mucosal characteristics of pelvic ileal pouches. Gut. 1991; 32:61–65.

14. Bassuini MM, Billings PJ. Carcinoma in an ileoanal pouch after restorative proctocolectomy for familial adenomatous polyposis. Br J Surg. 1996; 83:506.

15. Palkar VM, deSouza LJ, Jagannath P, Naresh KN. Adenocarcinoma arising in “J” pouch after total proctocolectomy for familial polyposis coli. Indian J Cancer. 1997; 34:16–19.
16. Cherki S, Glehen O, Moutardier V, Franç ois Y, Gilly FN, Vignal J. Pouch adenocarcinoma after restorative proctocolectomy for familial adenomatous polyposis. Colorectal Dis. 2003; 5:592–594.

17. Ulas M, Nessar G, Bostanoğ lu A, et al. Development of two cancers in the same patient after ileorectal and ileal pouch anal anastomosis for familial adenomatous polyposis. Med Princ Pract. 2006; 15:83–86.

18. Linehan G, Cahill RA, Kalimuthu SN, O'Connell F, Redmond HP, Kirwan WO. Adenocarcinoma arising in the ileoanal pouch after restorative proctocolectomy for familial adenomatous polyposis. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2008; 23:329–330.

19. Kim HR, Kim DY, Kim YJ. Carcinoma in an ileal pouch after proctocolectomy with ileal pouch-anal anastomosis for familial adenomatous polyposis. J Korean Soc Coloproctol. 1997; 13:623–628.
Go to : 
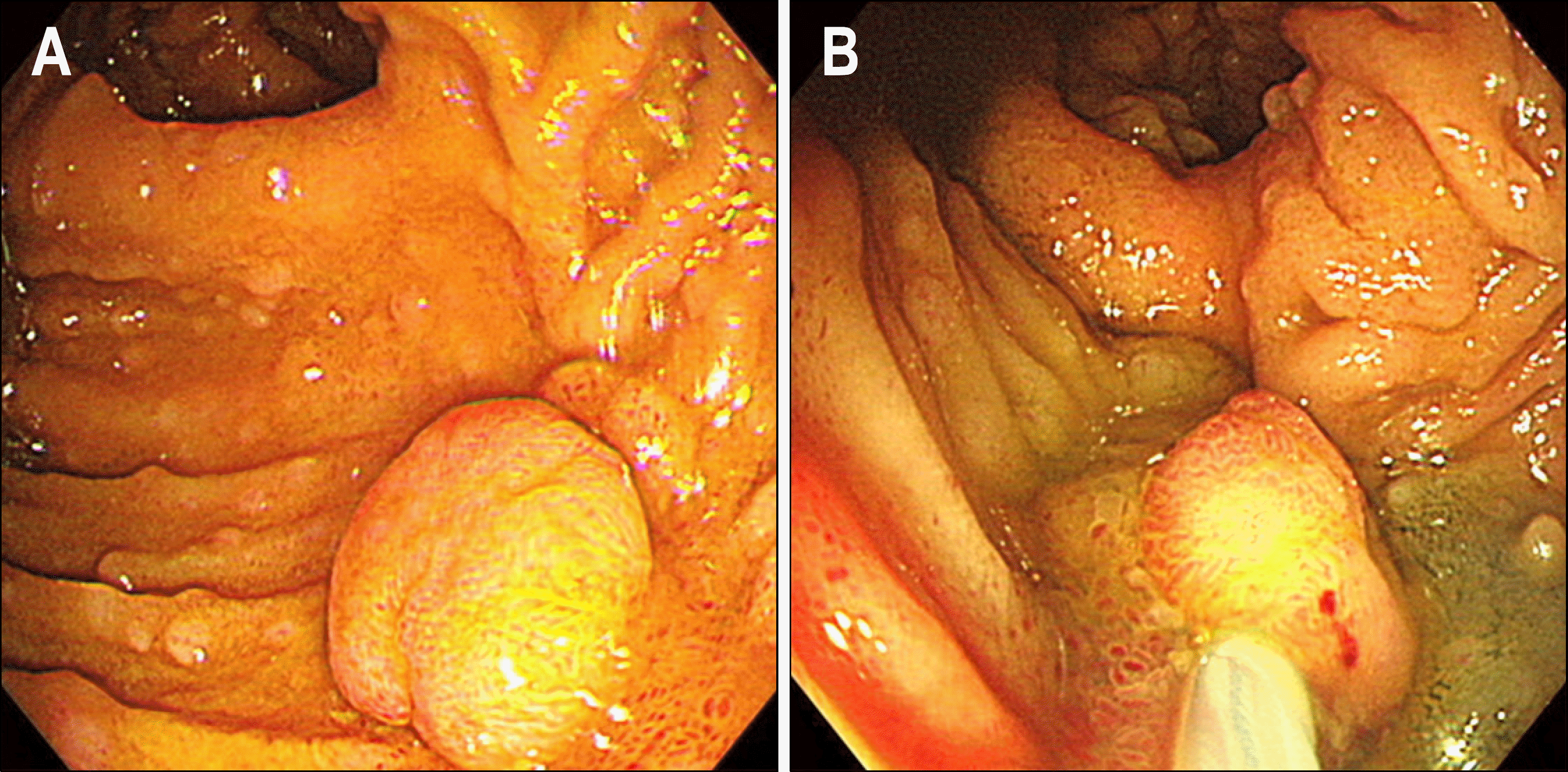
 | Fig. 1.Case 1. (A) Endoscopic findings of ileal pouch. Various sized multiple polyps were noted in the ileal pouch in a patient with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) after Koch's pouch continent ileostomy. The largest one was 15 mm in diameter. (B) Snare polypectomy was performed after submucosal injection of normal saline. (C) Multiple ulcers due to polypectomy were noted. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download