Abstract
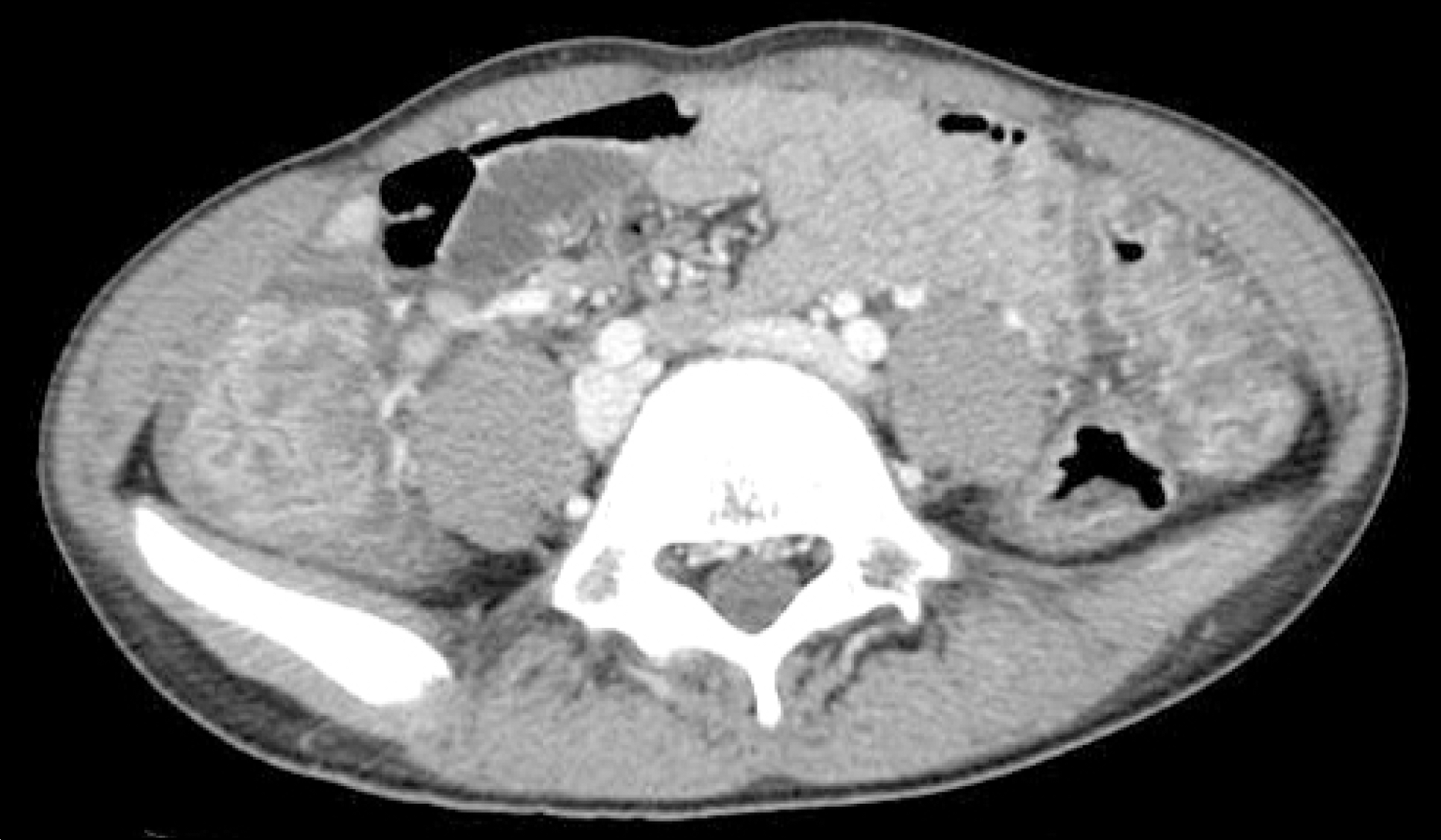
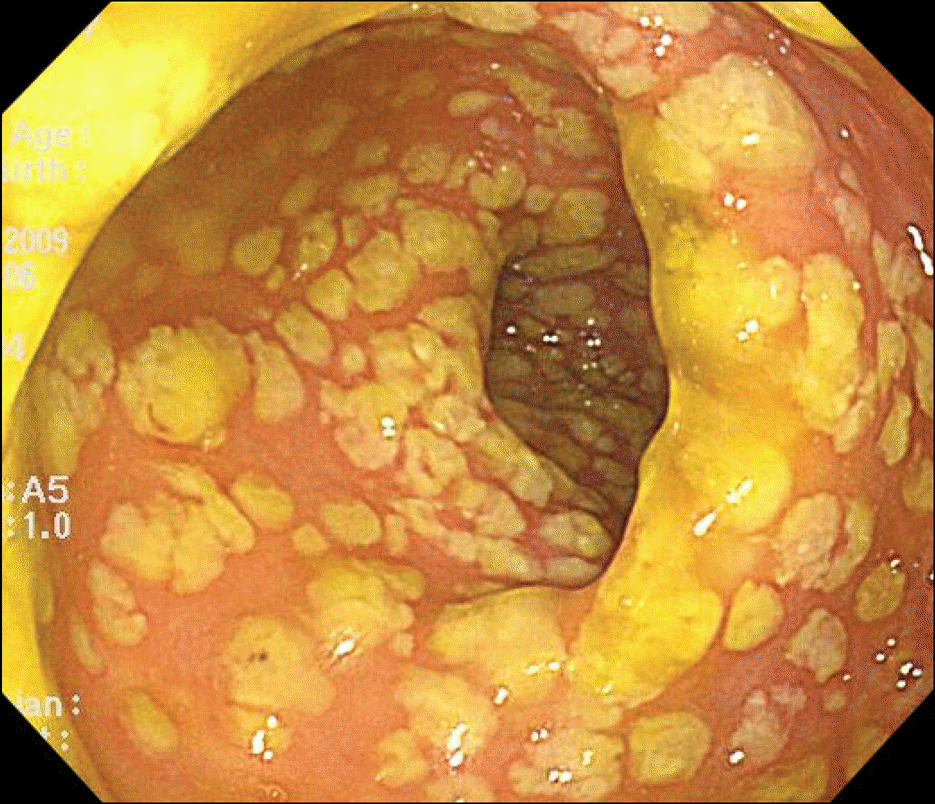
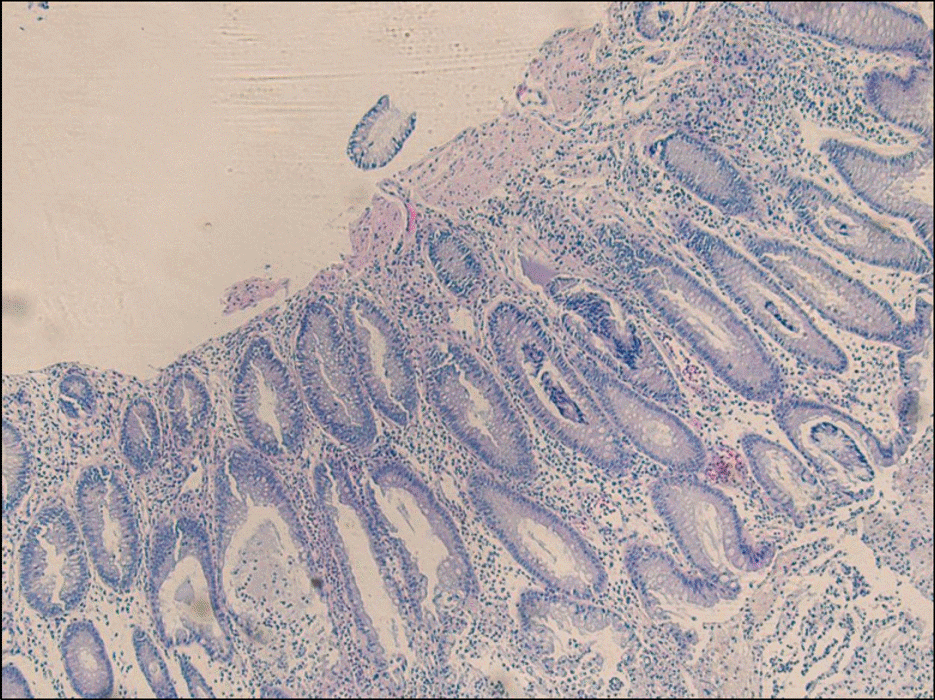
Pseudomembranous colitis is mainly caused by antibiotics and Clostridium difficile infection. But conditions such as gastrointestinal surgery, antacid medication, anti-neoplastic agent or immunosuppressive agent which influences the normal flora of colon can induce colitis without the administration of any antibiotics. We experienced a 13 year-old male who was taking low-dose methotrexate for juvenile rheumatoid arthritis complained diarrhea and abdominal pain for 3 weeks. Sigmoidoscopic findings revealed diffuse patch yellowish pseudomembranes on the rectum. Histologic finding was compatible to pseudomembranous colitis. His symptom was improved after stop taking methotrexate and the administration of metronidazole. If a patient treated with immunosuppressive agents or antineoplastic agents complains diarrhea, fever or abdominal pain and has not improved with conservative care, pseudomembranous colitis should be taken into account as a differential diagnosis and prompt treatment is required for better prognosis.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Feldman M, Friedman LS, Sleisenger MH. Sleisenger & Fordtran's gastrointestinal and liver disease: pathophysiology, diagnosis, management. 8th ed.Philadelphia: Saunders;2006.
2. DuPont HL, Garey K, Caeiro JP, Jiang ZD. New advances in Clostridium difficile infection: changing epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment and control. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2008; 21:500–507.

3. Janvier J, Kuhn S, Church D. Not all pseudomembranous colitis is caused by Clostridium difficile. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2008; 19:256–257.
4. Anand A, Glatt AE. Clostridium difficile infection associated with antineoplastic chemotherapy: a review. Clin Infect Dis. 1993; 17:109–113.
5. Cudmore MA, Silva J Jr, Fekety R, Liepman MK, Kim KH. Clostridium difficile colitis associated with cancer chemotherapy. Arch Intern Med. 1982; 142:333–335.
6. Miller SD, Koornhof HJ. Clostridium difficile colitis associated with the use of antineoplastic agents. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984; 3:10–13.
7. Blot E, Escande MC, Besson D, et al. Outbreak of Clostridium difficile-related diarrhoea in an adult oncology unit: risk factors and microbiological characteristics. J Hosp Infect. 2003; 53:187–192.
8. Cheon SH, Kim KH. Pseudomembranous colitis after 5-fluo-rouracil chemotherapy in rectal cancer patient. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2005; 46:319–320.
9. Yang SW, Moon W. A case of pseudomenbranous colitis after paclitaxel and carboplatin chemotherapy. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2009; 54:328–332.

10. Ramos A, Martí nez-Taboada VM, Fito C, Rodrigué z-Valverde V. Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea in rheumatoid arthritis patients who are receiving therapy with low-dose chlorambucil. Arthritis Rheum. 1997; 40:2090–2091.

11. van Ede AE, Laan RF, Blom HJ, De Abreu RA, van de Putte LB. Methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis: an update with fo-cus on mechanisms involved in toxicity. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1998; 27:277–292.
12. Cappell MS. Colonic toxicity of administered drugs and chemicals. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004; 99:1175–1190.

13. Silva J, Fekety R, Werk C, et al. Inciting and etiologic agents of colitis. Rev Infect Dis. 1984; 6(suppl 1):S214–221.

14. Yamazawa K, Kanno H, Seki K, Kuzuta T, Matsui H, Sekiya S. Life-threatening Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea induced by paclitaxel-carboplatin combination chemotherapy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2001; 80:768–769.
15. Husain A, Aptaker L, Spriggs DR, Barakat RR. Gastrointestinal toxicity and Clostridium difficile diarrhea in patients treated with paclitaxel-containing chemotherapy regimens. Gynecol Oncol. 1998; 71:104–107.
16. Moon SJ, Min CK, Lee DG, et al. Pseudomembranous colitis following bortezomib therapy in a myeloma patient. Acta Haematol. 2007; 117:211–214.

17. Castagnola E, Battaglia T, Bandettini R, et al. Clostridium difficile-associated disease in children with solid tumors. Support Care Cancer. 2009; 17:321–324.
18. Phatak UP, Seo-Mayer P, Jain D, Selbst M, Husain S, Pashankar DS. Mycophenolate mofetil-induced colitis in children. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2009; 43:967–969.

19. Arslan H, Inci EK, Azap OK, Karakayali H, Torgay A, Haberal M. Etiologic agents of diarrhea in solid organ recipients. Transpl Infect Dis. 2007; 9:270–275.

20. Song JH, Shim KN, Jung SA, et al. Antibiotic-associated diarrhea: candidate organisms other than Clostridium difficile. Korean J Intern Med. 2008; 23:9–15.
Go to : 




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download