Abstract
Infliximab, the monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor, is indicated for refractory luminal and fistulizing Crohn's disease and rheumatoid arthritis. Infliximab treatment has adverse events including infusion reactions, op-portunistic infections, and the potential for the event such as reactivation of latent tuberculosis. Cutaneous adverse reactions of TNF-α agents include skin rash, urticaria, pruritus, lupus-like eruption, and injection site reactions. Most of all, psoriasis or psoriasiform dermatitis induced by infliximab treatment for Crohn's disease is rarely reported in Korea. We report a case of psoriasis induced by infliximab treatment for Crohn's disease with a review of world literature.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Sandborn WJ, Hanauer SB. Infliximab in the treatment of Crohn's disease: a user's guide for clinicians. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002; 97:2962–2972.

2. Rutgeerts P, Van Assche G, Vermeire S. Review article: infliximab therapy for inflammatory bowel disease–seven years on. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006; 23:451–463.
3. Fidder H, Schnitzler F, Ferrante M, et al. Longterm safety of infliximab for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: a single-centre cohort study. Gut. 2009; 58:501–508.

4. Wollina U, Hansel G, Koch A, Schö nlebe J, Köstler E, Haroske G. Tumor necrosis factoralpha inhibitor-induced psoriasis or psoriasiform exanthemata: first 120 cases from the literature including a series of six new patients. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2008; 9:1–14.
5. de Gannes GC, Ghoreishi M, Pope J, et al. Psoriasis and pustular dermatitis triggered by TNF-alpha inhibitors in patients with rheumatologic conditions. Arch Dermatol. 2007; 143:223–231.

6. Takahashi H, Hashimoto Y, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Ashida T, Kohgo Y, Iizuka H. Psoriasiform and pustular eruption induced by infliximab. J Dermatol. 2007; 34:468–472.

7. Severs GA, Lawlor TH, Purcell SM, Adler DJ, Thompson R. Cutaneous adverse reaction to infliximab: report of psoriasis developing in 3 patients. Cutis. 2007; 80:231–237.
8. Umeno J, Matsumoto T, Jo Y, Ichikawa M, Urabe K, Iida M. Psoriasis during anti-tumor necrosis factoralpha therapy for Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2007; 13:1188–1189.

9. Peramiquel L, Puig L, Dalmau J, Ricart E, Roe E, Alomar A. Onset of flexural psoriasis during infliximab treatment for Crohn's disease. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2005; 30:713–714.

10. Angelucci E, Cocco A, Viscido A, Vernia P, Caprilli R. Another paradox in Crohn's disease: new onset of psoriasis in a patient receiving tumor necrosis factoralpha antagonist. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2007; 13:1059–1061.
11. Cohen JD, Bournerias I, Buffard V, et al. Psoriasis induced by tumor necrosis factoralpha antagonist therapy: a case series. J Rheumatol. 2007; 34:380–385.
12. Sfikakis PP, Iliopoulos A, Elezoglou A, Kittas C, Stratigos A. Psoriasis induced by anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: a paradoxical adverse reaction. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 52:2513–2518.

13. Park BC, Lim HJ, Kim BS, Lee WJ, Kim DW, Lee SJ. Repeated paradoxical aggravation of preexisting psoriasis during infliximab treatment for Crohn's disease. Ann Dermatol. 2009; 21:60–62.

14. Choi YJ, Kim DS, Park JM, Oh SH, Park YK, Lee JH. A case of psoriasiform eruption triggered by tumor necrosis factoralpha antagonist therapy. Korean J Dermatol. 2008; 46:721–723.
15. Choi KD, Song HJ, Kim JS, Jung HC, Song IS. Efficacy and safety of treatment with Infliximab in Crohn's disease-the experience of single center in Korea. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2005; 46:48–55.
16. Borrás-Blasco J, Navarro-Ruiz A, Borrás C, Casterá E. Adverse cutaneous reactions induced by TNF-alpha antagonist therapy. South Med J. 2009; 102:1133–1140.
17. Mease P. TNFalpha therapy in psoriasis arthritis and psoriasis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004; 63:755–758.
Go to : 
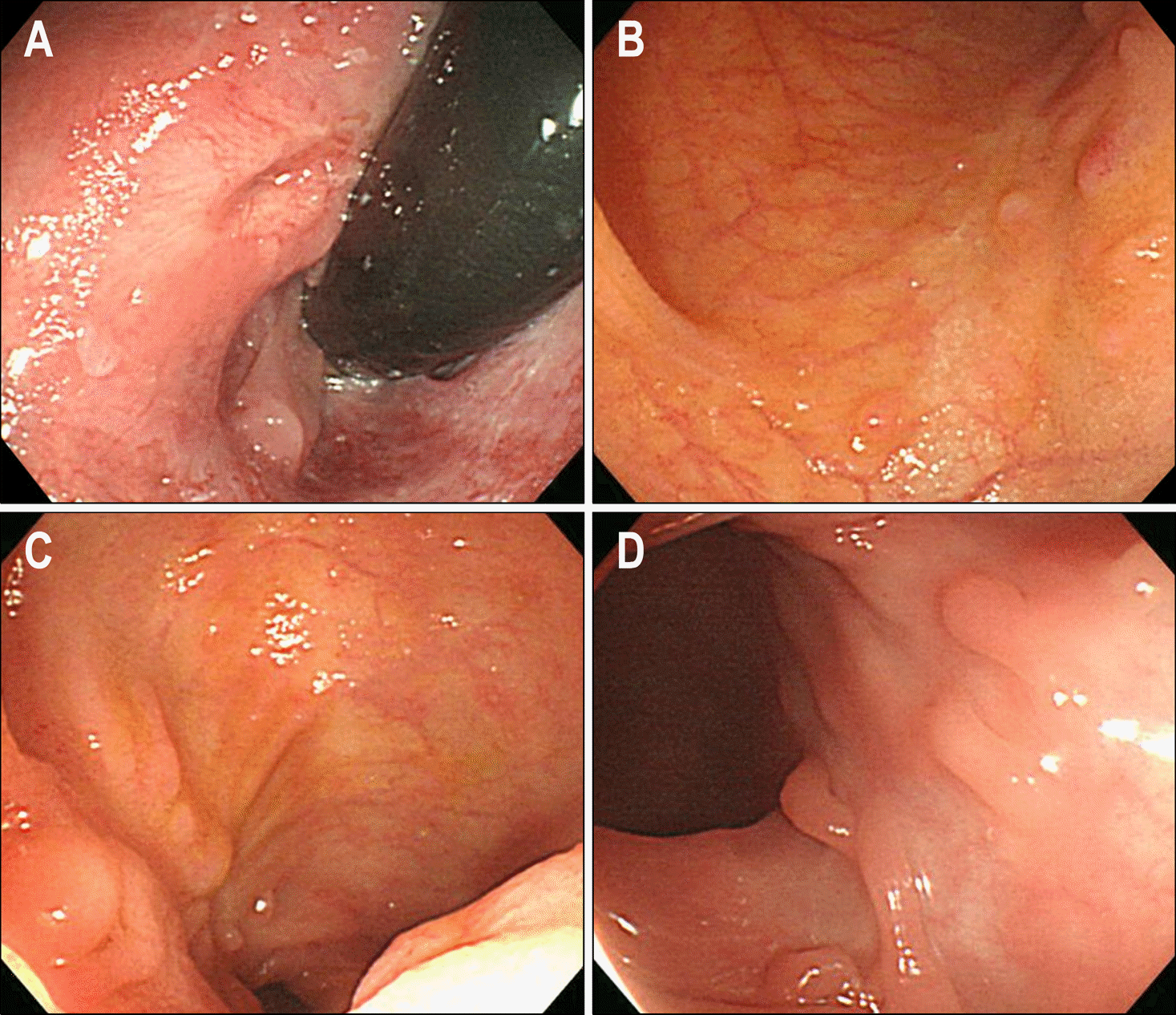
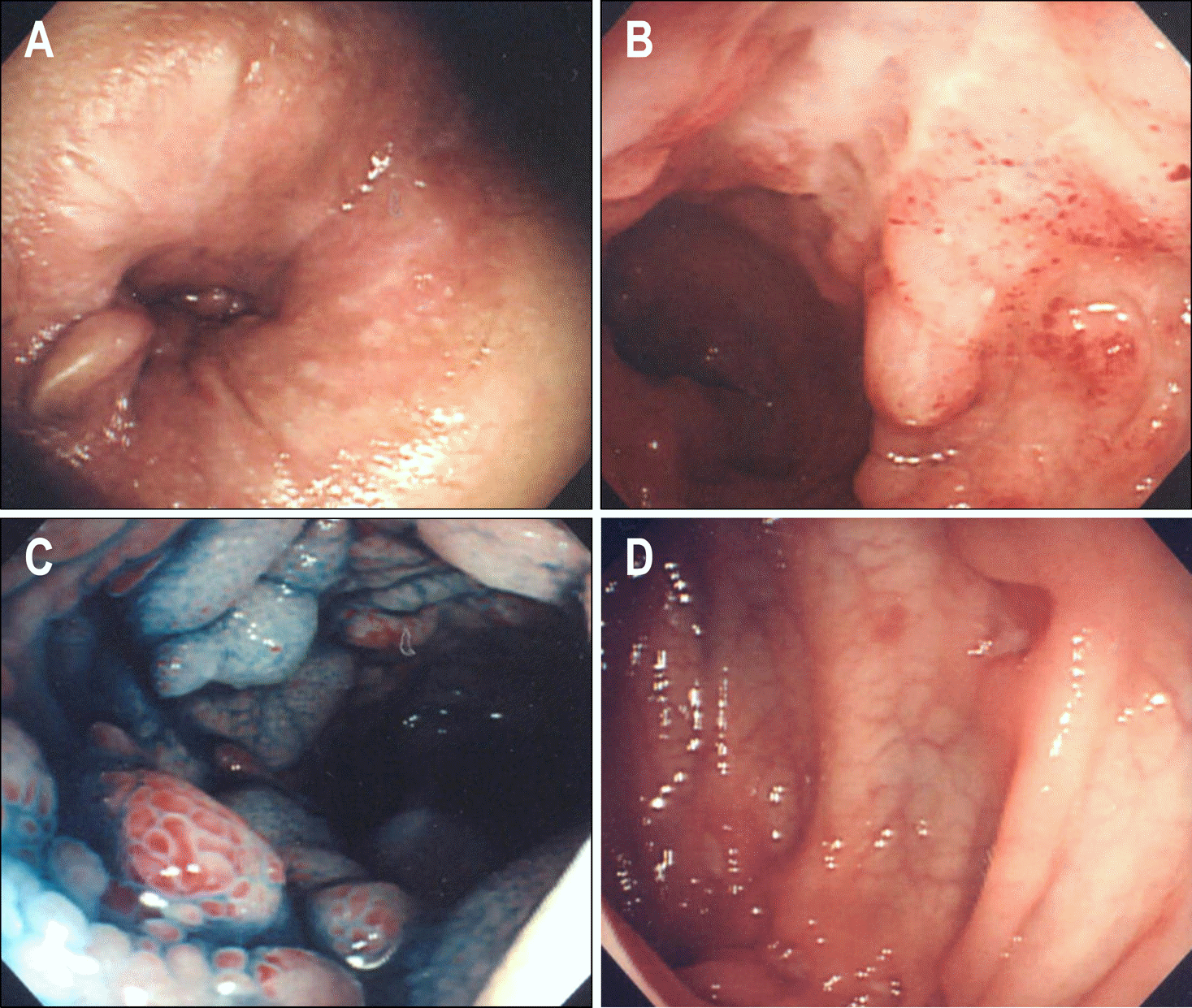 | Fig. 1.Initial colonoscopic findings. (A) Perianal fistula was seen. (B, C) Longitudinal ulcers with cobble stone appearance were observed at the terminal ileum. (D) Another apthous ulcers were noted at the descending colon. |
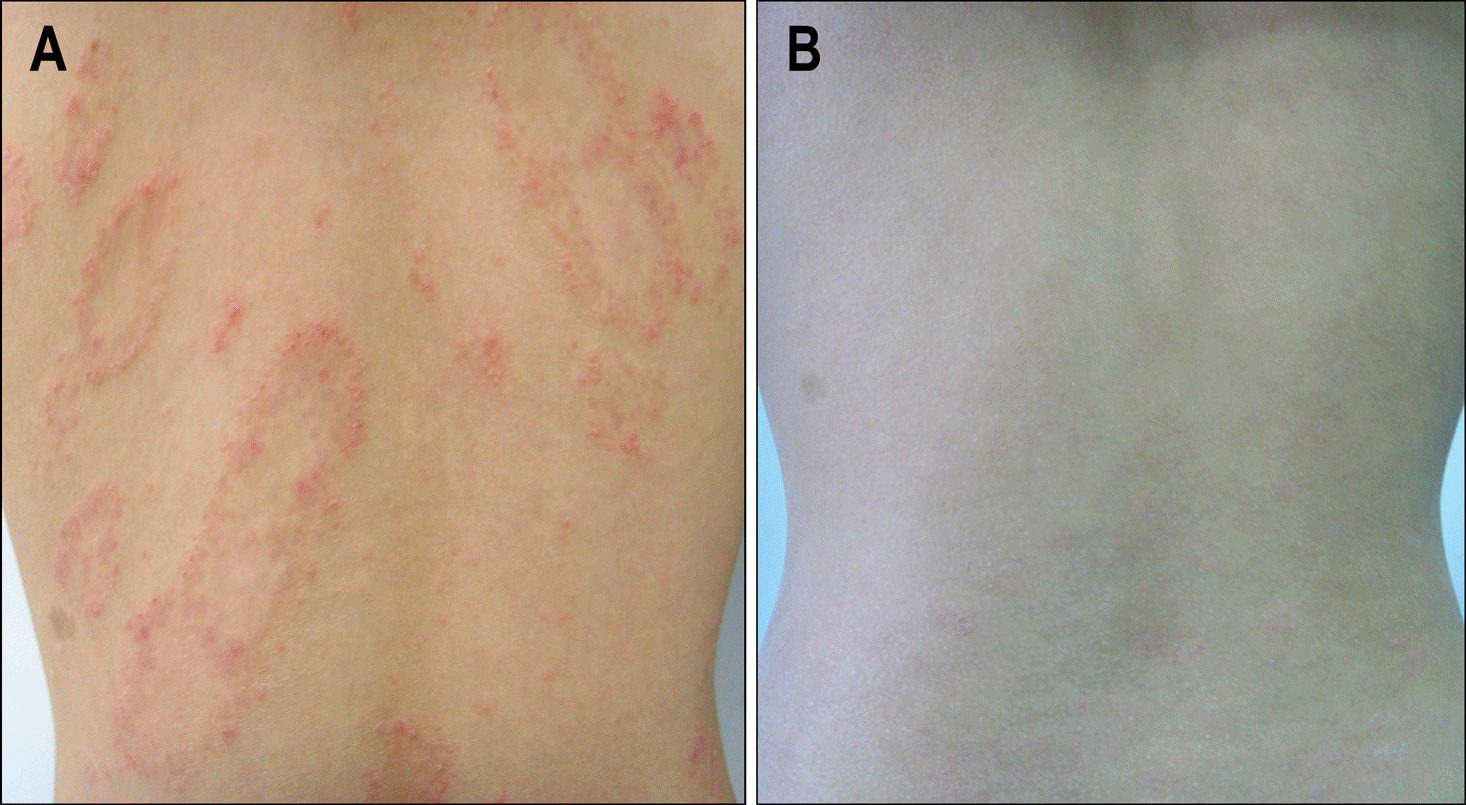 | Fig. 2.Photographs of the skin lesion. (A) Psoriasis with reddened skin and pustules was developed on the back. (B) After treatment, the skin lesion was completely healed, with no signs of discoloration or scarring. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download