REFERENCES
1. Kim HG, Han J, Kim MH, et al. Prevalence of clonorchiasis in patients with gastrointestinal disease: A Korean nationwide multicenter survey. World J Gastroenterol. 2009; 15:86–94.

2. Joo CY, Chung MS, Kim SJ, Kang CM. Changing patterns of clonorchis sinensis infections in Kyongbuk, Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 1997; 35:155–164.

3. Kim YH. Extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma associated with clonorchiasis: CT evaluation. Abdom Imaging. 2003; 28:68–71.

6. Park YH, Choi SK. A clinical review on biliary clonorchiasis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1986; 18:145–152.
7. Song HY, Rhee KS, Lee ST, Kim DK, Ahn DS. Clinical features in clonorchiasis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1995; 27:64–71.
8. Kang DH, Choi SH, Chun KJ, et al. ERCP findings in hepatic clonorchiasis. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 1993; 13:121–126.
Go to : 
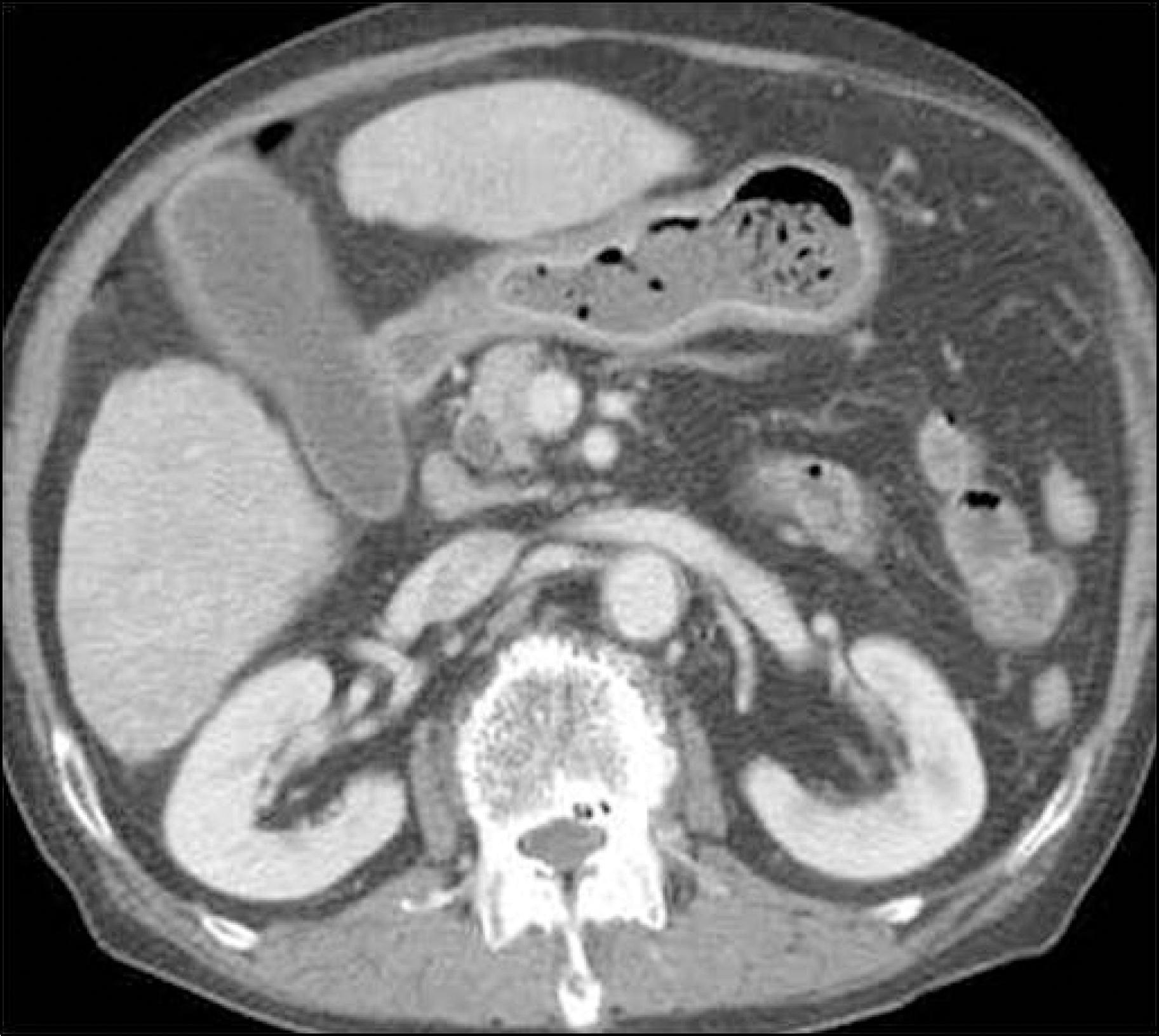 | Fig. 1.Contrast-enhanced CT finding of the patient. There were gallbladder distension and wall thickening, and dilated common bile duct. |
 | Fig. 2.Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatographic finding. Major papilla looked normal in endoscopic view. |
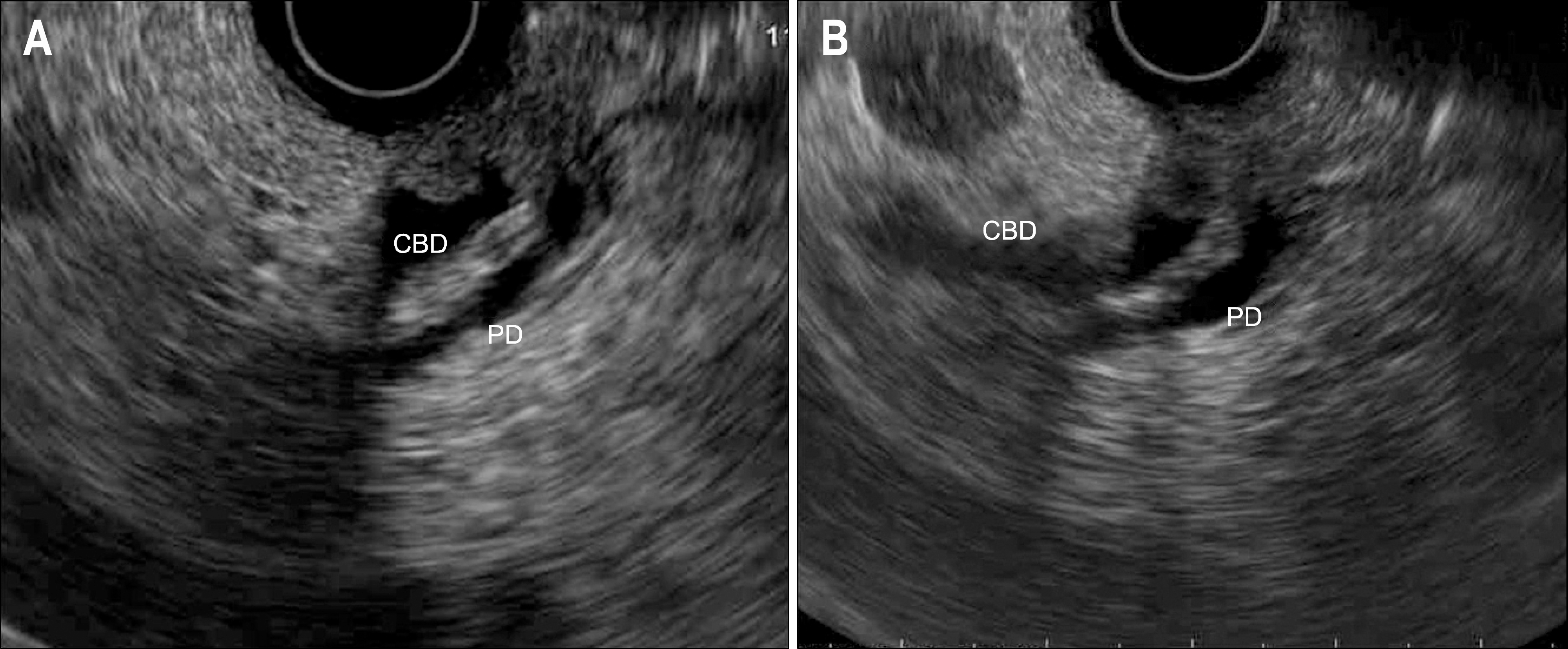
 | Fig. 3.Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatographic findings. (A) A filling defect was noted at the distal common bile duct. (B) Threre was diffuse mild dilatation at peripheral intrahepatic bile ducts. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download