Abstract
Background/Aims
A stercoral perforation of the colon (SPC) is a rare, life-threatening disease. The aim of this study was to represent the definition of SPC and help the diagnosis and treatment of this condition.
Methods
We reviewed 92 medical records of patients who underwent operation due to colonic perforation from January 2000 to February 2009 retrospectively. Maurer's diagnostic criteria were used for the diagnosis of SPC.
Results
Eight patients (8.7%) were diagnosed as SPC. The age of the patients ranged from 59 to 85 years old. All of the patients were female and had a history of long-standing constipation. Only two patients (25%) were diagnosed as SPC preoperatively. The site of perforation of all patients was sigmoid colon. The methods of operation were Hartmann's procedure (7 cases), and primary repair with sigmoid loop colostomy (1 case). There were one recurrence and two deaths (25%) due to sepsis and multiple organ failure.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
2. Maurer CA, Renzulli P, Mazzucchelli L, Egger B, Seiler CA, Buchler MW. Use of accurate diagnostic criteria may increase incidence of stercoral perforation of colon. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000; 43:991–998.
3. Berry JA. Dilatation and rupture of the sigmoid flexure. Br Med J. 1894; 1:301.
4. Bauer JJ, Weiss M, Dreiling DA. Stercoraceous perforation of the colon. Surg Clin North Am. 1972; 52:1047–1053.

5. Grinvalsky HT, Bowerman CI. Stercoraceous ulcers of the colon: relatively neglected medical and surgical problem. J Am Med Assoc. 1959; 171:1941–1946.
6. Elliot MS, Jeffery PC. Stercoral perforation of the large bowel. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1980; 25:38–40.
7. Tessier DJ, Harris E, Collins J, Johnson DJ. Stercoral perforation of the colon in a heroin addict. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2002; 17:435–437.

8. Haley TD, Long C, Mann BD. Stercoral perforation of the colon: a complication of methadone maintenance. J Subst Abuse Treat. 1998; 15:443–444.
9. Cass AJ. Stercoral perforation: a case of drug-induced impaction. Br Med J. 1978; 2:932–933.
10. Doughty JC, Donald AK, Keogh G, Cooke TG. Stercoral perforation with verapamil. Postgrad Med J. 1994; 70:525.

11. Penn I, Brettschneider L, Simpson K, Martin A, Starzl TE. Major colonic problem in human homotransplant recipients. Arch Surg. 1970; 100:61–65.
12. Wang SY, Sutherland JC. Colonic perforation secondary to fecal impaction: report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum. 1977; 20:355–356.
13. Beradi RS, Lee S. Stercoraceous perforation of the colon: report of case. Dis Colon Rectum. 1983; 26:283–286.
14. Han SY, Kim BC, Sohn TK, et al. Stercoral perforation of the colon. J Korean Surg Soc. 2004; 67:432–436.
15. Wood CD. Acute perforation of the colon. Dis Colon Rectum. 1977; 20:126–129.
16. Jung GJ, Jeong JS, Choi HJ, Kim YH, Cho SH, Kim SS. A case of cecal perforation by the stercoral ulcer. J Korean Surg Soc. 1992; 43:146–151.
17. Heffernan C, Pachter HL, Megibow AJ, Macari M. Stercoral colitis leading to fatal peritonitis: CT findings. Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 184:1189–1193.

18. Zissin R, Hertz M, Osadchy A, Even-Sapir E, Gayer G. Abdominal CT findings in nontraumatic colorectal perforation. Eur J Radiol. 2008; 65:125–132.

Go to : 
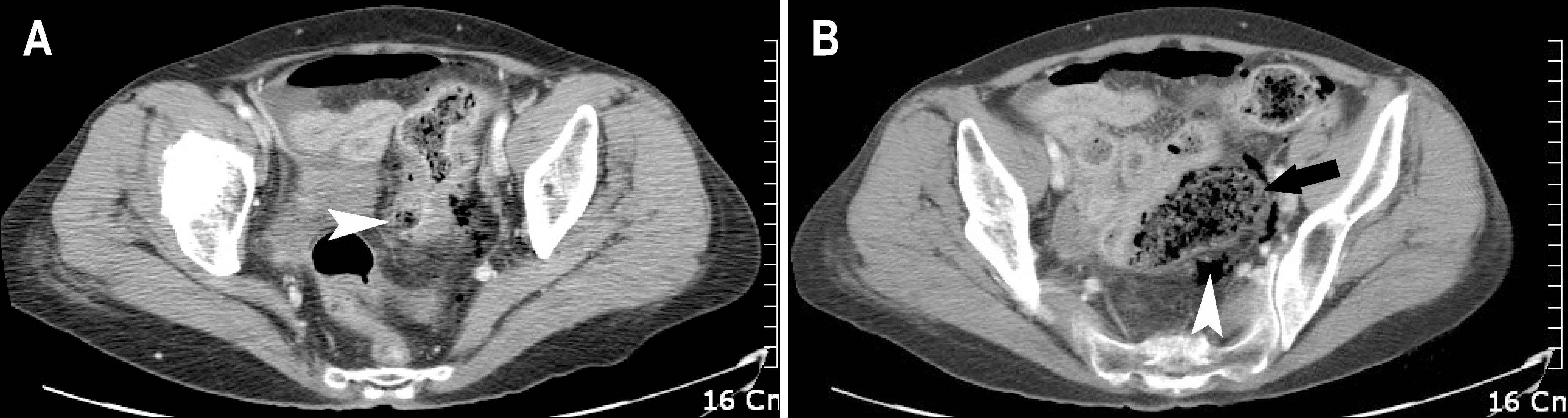 | Fig. 1.68-year-old female with stercoral perforation of colon. (A) Transverse CT image showed fecaloma protruding through the wall defect of the sigmoid colon (arrowhead). (B) Transverse CT image obtained at upper level showed extra-luminal fecal material (arrow) and free gas (arrowhead). |
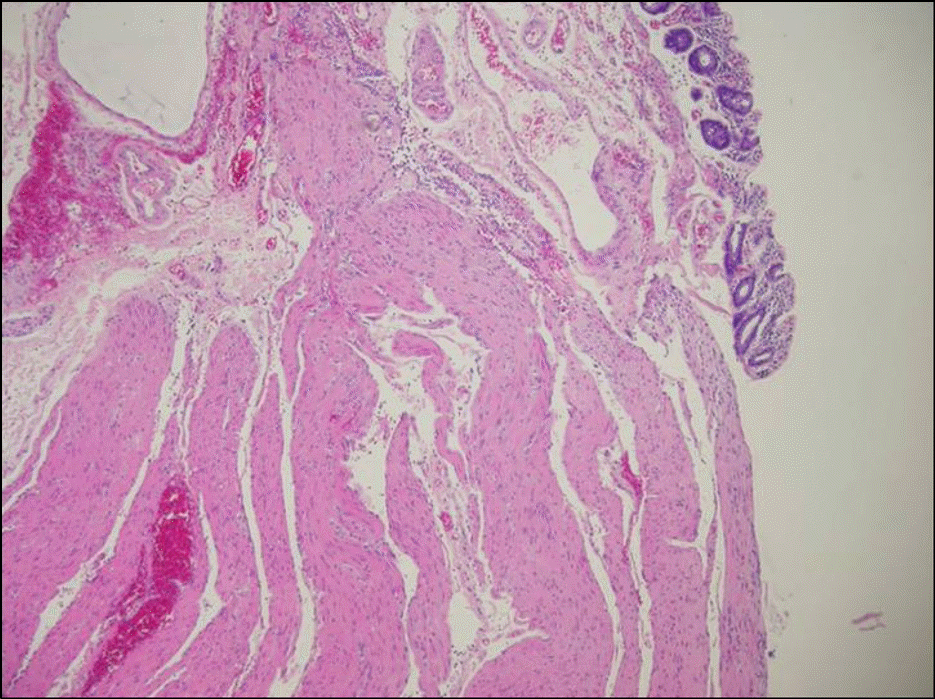 | Fig. 2.Microscopic findings of the colonic wall around the perforation. It showed clear-cut denudation of mucosa and submucosa with exposure of muscular layer. Marked vascular congestion and mild chronic inflammation were noted (H&E stain, ×100). |
Table 1.
Diagnostic Criteria of Stercoral Perforation of the Colon2
| 1) The colonic perforation is round or ovoid, exceeds 1 cm in diameter, and lies antimesenterial |
|---|
| 2) Fecalomas are present within the colon, protruding through the perforation site or lying within the abdominal cavity |
| 3) Pressure necrosis or ulcer and chronic inflammatory reaction around the perforation site are present microscopically |
| 4) Colonic perforations associated with an abdominal trauma or with another colonic pathology∗ were excluded |
Table 2.
Causes of Colonic Perforation from Jan 2000 to Feb 2009
| Causes | Number (%) |
|---|---|
| Diverticulitis | 34 (37.0) |
| Iatrogenic | 19 (20.7) |
| Trauma | 14 (15.2) |
| Cancer | 9 (9.8) |
| Stercoral | 8 (8.7) |
| Idiopathic | 4 (4.3) |
| Others | 4 (4.3) |
| Total | 92 (100) |
Table 3.
Clinical Findings of Stercoral Perforation Patients
Table 4.
Radiologic Findings of Stercoral Perforation Patients
| Case | Free air below the diaphragm at X-ray∗ | CT findings | Preoperative diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | − | Faecal accumulation at the perforation level, pericolic fat stranding, | Perforated appendicitis |
| interloopal free gas | |||
| 2 | + | Faecal accumulation at the perforation level, pericolic fat stranding, | Unknown colon perforation |
| subphrenic and interloopal free gas | |||
| 3 | + | Faecal accumulation at the perforation level, pericolic fat stranding, | Unknown colon perforation |
| subphrenic and interloopal free gas | |||
| 4 | + | Faecal accumulation at the perforation level, colonic wall defect, | Unknown colon perforation |
| pericolic fat stranding, subphrenic and interloopal free gas | |||
| 5 | − | Wall thickening of duodenal 2nd portion | Duodenal ulcer perforation |
| 6 | + | Faecal accumulation at the perforation level, colonic wall defect, | Stercoral perforation |
| pericolic fat stranding, subphrenic and interloopal free gas | |||
| 7 | − | Faecal accumulation at the perforation level, pericolic fat stranding, | Rectal cancer perforation |
| interloopal free gas | |||
| 8 | + | Faecal accumulation at the perforation level, colonic wall defect, | Stercoral perforation |
| pericolic fat stranding, subphrenic and interloopal free gas |
Table 5.
Operative Findings, Procedures, and Outcomes




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download