Abstract
Hepatitis A virus (HAV) infection is common in developing countries, including Korea. It can be accompanied by extrahepatic complications such as renal failure, arthritis, and vasculitis. Pleural effusion is a very rare complication of HAV infection, which has been reported usually in children, and has benign clinical courses. Here we report a case of pleural effusion with ascites which occurred in an adult hepatitis A patient. A 26-year-old-wom-an presented generalized myalgia and fever and was diagnosed as acute hepatitis A. Despite of the improvement of laboratory findings, fever and cough persisted. Pleural effusion newly appeared on the serial chest radiologic images. After the fever settled down, the pleural effusion resolved spontaneously at 13th day of admission.
REFERENCES
1. Jeong SH. Current status and vaccine indication for hepatitis A virus infection in Korea. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2008; 51:331–337.
2. Song YB, Lee JH, Choi MS, et al. The age-specific seroprevalence of hepatitis A virus antibody in Korea. Korean J Hepatol. 2007; 13:27–33.
3. Lee EJ, Kwon SY, Seo TH, et al. Clinical features of acute hepatitis A in recent two years clinical features of acute hepatitis A in recent two years. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2008; 52:298–303.
4. Tong MJ, el-Farra NS, Grew MI. Clinical manifestations of hepatitis A: recent experience in a community teaching hospital. J Infect Dis. 1995; 171:15–18.

5. Gordon SC, Reddy KR, Schiff L, Schiff ER. Prolonged intrahepatic cholestasis secondary to acute hepatitis A. Ann Intern Med. 1984; 101:635–637.

6. Sjogren MH. Hepatitis A. Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, Sleisenger MH, editors. eds.Sleisenger & Fordtran's gastrointestinal and liver disease. Volume 2. 8th ed.Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier;2006. p. 1642.

7. Kim DI, Park JO, Kim CH. A case of pleural effusion associated with acute hepatitis A. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005; 48:243–246.
8. Hong WS, Kim CY. Seroepidemiology of type A and type B hepatitis in Seoul area. Korean J Intern Med. 1982; 25:19–26.
9. Jeong SH. Current status and vaccine indication for hepatitis A virus infection in Korea. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2008; 51:331–337.
10. Willner IR, Uhl MD, Howard SC, Williams EQ, Riely CA, Waters B. Serious hepatitis A: an analysis of patients hospitalized during an urban epidemic in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 1998; 128:111–114.

11. Alhan E, Yildizdaş D, Ypicioğ lu H, Necmi A. Pleural effusion associated with acute hepatitis A infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1999; 18:1111–1112.

12. Kurt ANC, Bulut Y, Mehmet T, et al. Pleural effusion associated with hepatitis A. J Pediatr Inf. 2008; 2:25–26.
13. Selimoğ lu MA, Ziraatci O, Tan H, Ertekin V. A rare complication of Hepatitis A: pleural effusion. J Emerg Med. 2004; 28:229–230.
14. Bukulmez A, Koken R, Melek H, Dogru O, Ovali F. Pleural effusion: a rare complication of hepatitis A. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2008; 26:87–88.

15. Tesovic G, Vukelić D, Vuković B, Benić B, Bozinovi D. Pleural effusion associated with acute hepatitis A infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2000; 19:585–586.

16. Gü rkan F. Ascites and pleural effusion accompanying hepatitis A infection in a child. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2000; 6:286–287.
17. Vaidya P, Kadam C. Hepatitis A: an unusual presentation. Indian Pediatr. 2003; 40:910–911.
Fig. 1.
Chest radiography. Right pleural effusion appeared at the 6th day in hospital (posteroanterior view).
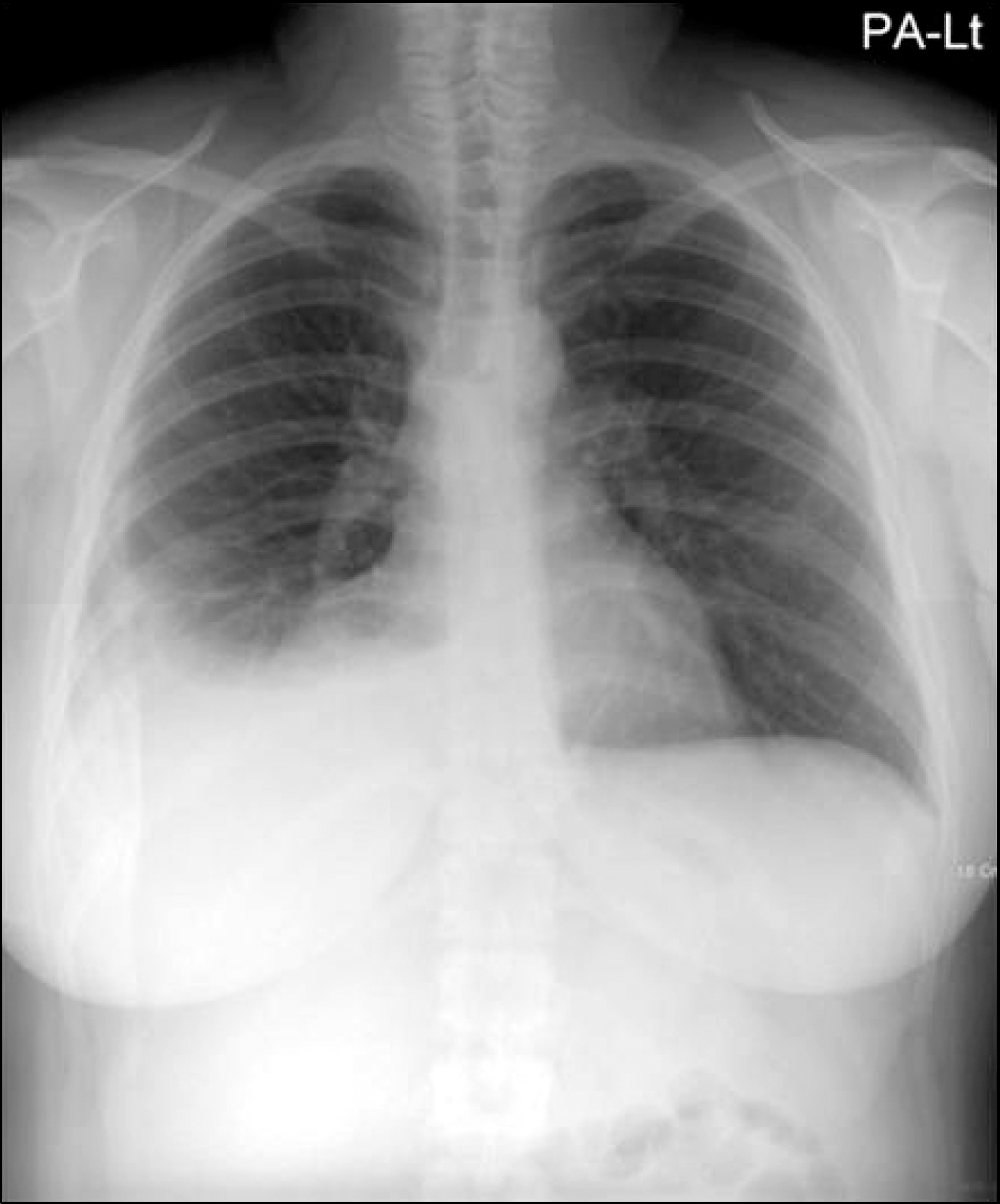
Fig. 2.
Computer tomography. Right side pleural effusion was observed (A). Minimal amount of left side pleural effusion and ascites was observed (B).
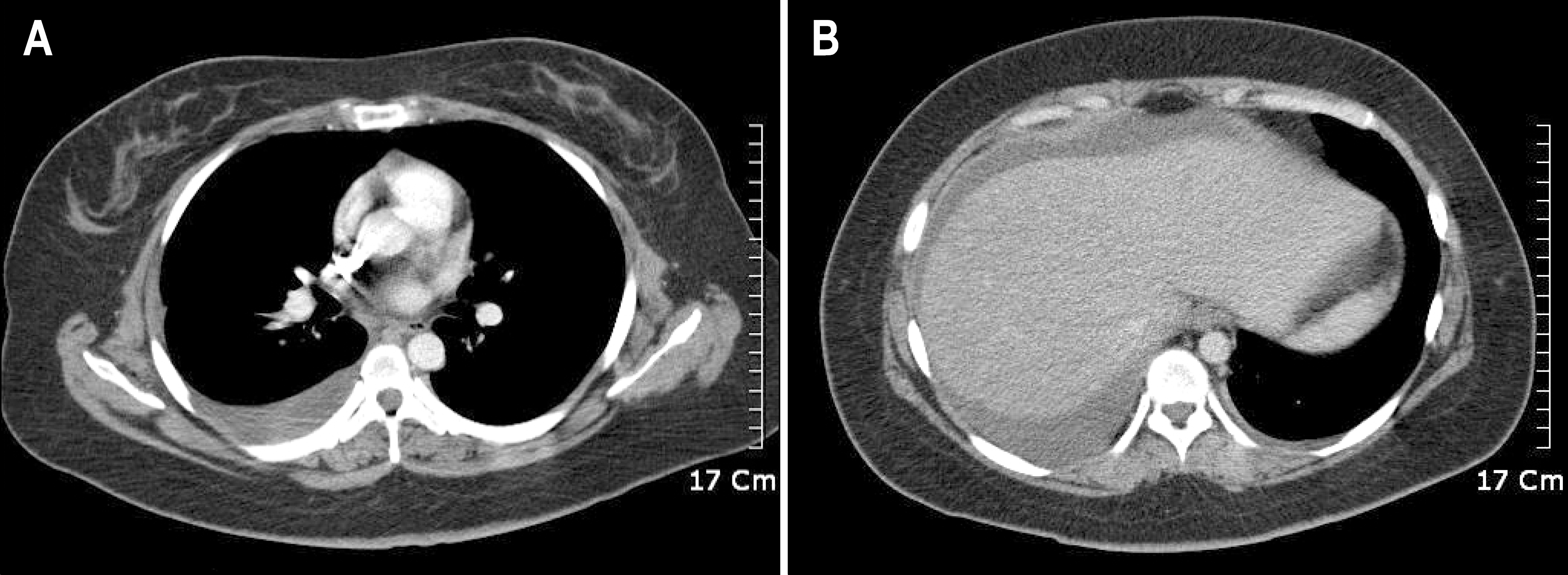
Table 1.
Clinical Features of Pleural Effusion Combined with Hepatitis A




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download