Abstract
Protein C is an important physiological anticoagulant factor. Protein C deficiency has been linked to venous thrombosis at unusual sites, including the cerebral and mesenteric veins. Hereditary protein C deficiency is in-herited primarily as an autosomal dominant trait with incomplete penetrance. Protein C and S deficiencies are known to increase the risk of venous thrombosis and pulmonary thromboembolism. Testing for protein C levels and function is necessary for the detection of both type I and type II protein C deficiency. In this article, we report a case of pulmonary embolism and mesentery ischemia due to type 1 protein C deficiency.
REFERENCES
1. Jin PP, Wang XF, Dai J, Ding QL, Wang HL. Hereditary protein C deficiency: a case report. Pathology. 2007; 39:290–291.

2. Kim HJ, Kim DK, Koh KC, Kim JY, Kim SH. Severe protein C deficiency from compound heterozygous mutations in the PROC gene in two Korean adult patients. Thromb Res. 2008; 123:412–417.

3. Yoshida M, Mukohara N, Obo H, Ozaki N, Shida T, Okita Y. Pulmonary thromboendarterectomy for chronic pulmonary thromboembolism in protein C deficiency. Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006; 54:70–74.

4. Rackoff A, Shores N, Willner I. Mesenteric venous thrombosis in a patient with pancreatitis and protein C deficiency. South Med J. 2005; 98:232–234.

5. Vrabec JP, Levin LA. Type II protein C deficiency in a 16-year-old girl with central retinal vein occlusion. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007; 143:341–342.

6. Cho JH, Park CW, Cho BR, et al. A case of pulmonary thromboembolism associated with protein C deficiency. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 2003; 14:125–128.
7. Cho YP, Lee DH, Jung SM, Jang HJ, Kim JS, Han MS. Vascular diseases associated with protein C and/or deficiencies. J Korean Surg Soc. 2002; 62:181–186.
8. Demir T, Celkan T, Ahunbay G, Babaoglu A, Besikci R. Venous and intrapericardial thrombosis: secondary to transient protein C deficiency. Pediatr Cardiol. 2006; 27:497–499.
9. Hoshi S, Hijikata M, Togashi Y, et al. Protein C deficiency in a family with thromboembolism and identified gene mutations. Intern Med. 2007; 46:997–1003.

10. Paç FA, Cağdaş DN. Treatment of massive cardiac thrombi in a patient with protein C and protein S deficiency. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2007; 18:699–702.

11. Imberti D, Pierfranceschi MG. Successful protein C concen10. Paç FA, Cağdaş DN. Treatment of massive cardiac thrombi in a patient with protein C and protein S deficiency. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2007; 18:699–702.
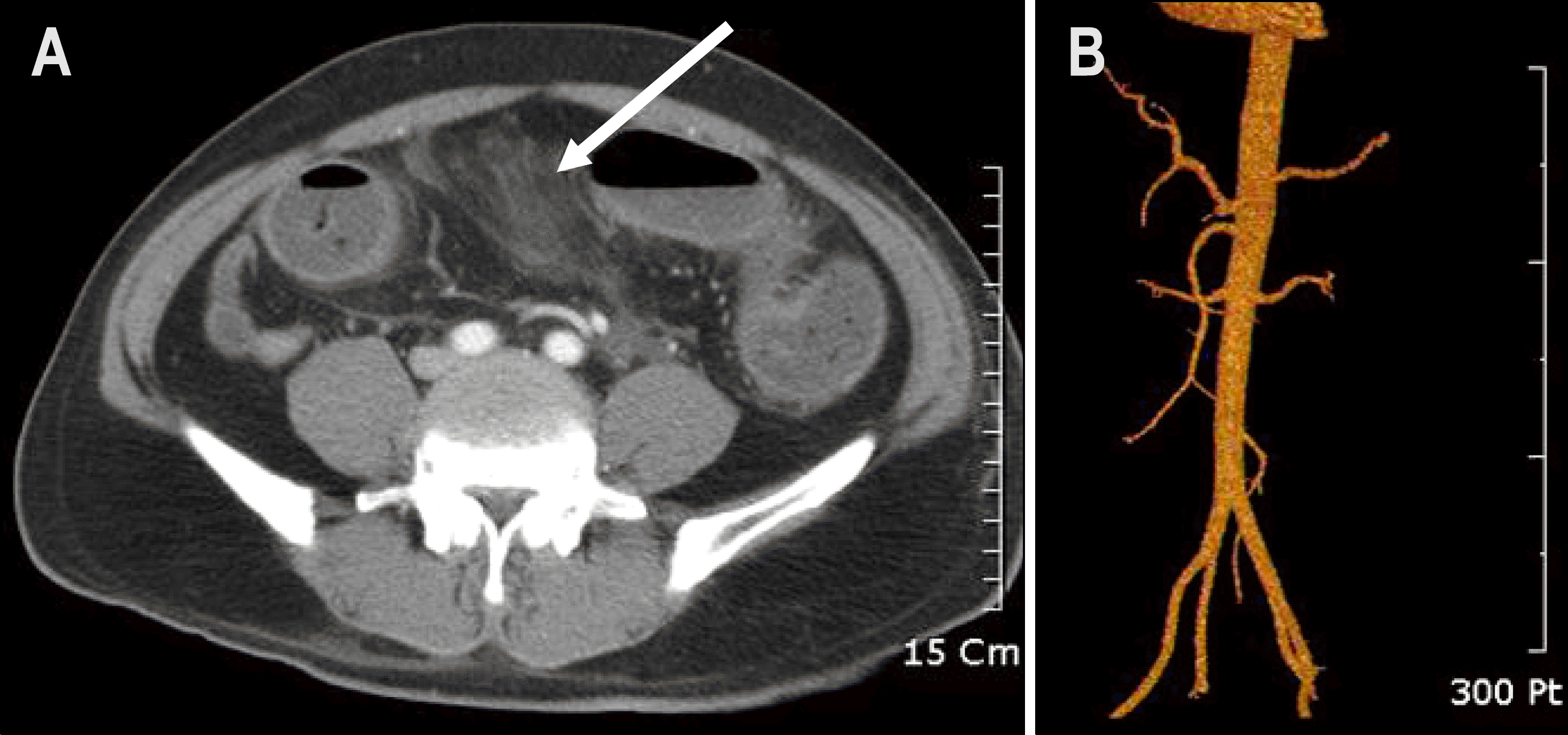
Fig. 1.
(A) Computed tomogram of abdomen showed dilatation of sigmoid colon associated with per-icolic fatty stranding (arrow) and small amount of fluid collection. (B) Surface rendering reconstruction image of abdomen showed no evidence of mesenteric artery occlusion.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download