Abstract
Neuroendocrine carcinoma of the colon can be classified into small cell carcinoma and large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. The incidence of neuroendocrine carcinoma is so low that the guideline for the treatment of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the colon are not established. The prognosis of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the colon is worse than that of conventional adenocarcinoma of the colon. We report a case of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the colon that treated with right hemicolectomy and 6th sequential combination chemotherapy of 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin. There has been no evidence of the recurrence or metastasis of tumor for 6 months.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Bernick PE, Klimstra DS, Shia J, et al. Neuoendocrine carcinoma of the colon and rectum. Dis Colon Rectum. 2004; 47:163–169.
2. Jeong MH, Kang BW, Son CM, Kim HS. Neuroendocrine tumor of the colon. J Korean Surg Soc. 2007; 73:178–182.
3. Jung SH, Kim HC, Yu CS, et al. Clinicopathologic characteristics of colorectal neuroendocrine tumor. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2006; 48:97–103.
4. Saclarides TJ, Szeluga D, Staren ED. Neuroendocrine cancers of the colon and rectum. Results of a ten-year experience. Dis Colon Rectum. 1994; 37:635–642.
5. Hamilton SR, Aaltonen LA. WHO classification of tumors. Pathology and genetics of tumours of the digestive system. Lyon: IARC Press;2000.
6. Travis WD, Colby TV, Corrin B, et al. Histological typing of lung and pleural tumors. 3rd ed.Berlin: Springer Verlag;1999.
7. Kato T, Terashima T, Tomida S, et al. Cytokeratin 20-positive large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the colon. Pathol Int. 2005; 55:524–529.

8. Hiroshima K, Iyoda A, Shibuya K, et al. Genetic alterations in early-stage pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. Cancer. 2004; 100:1190–1198.

9. Iyoda A, Hiroshima K, Moriya Y, et al. Prospective study of adjuvant chemotherapy for pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. Ann Thorac Surg. 2006; 82:1802–1807.

10. Yamazaki S, Sekine I, Matsuno Y, et al. Clinical responses of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung to cispla-tin-based chemotherapy. Lung Cancer. 2005; 49:217–223.

11. Okuyama T, Korenaga D, Tamura S, et al. The effectiveness of chemotherapy with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil for recurrent small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the rectum: report of a case. Jpn J Surg. 1999; 29:165–169.

12. Susumu S, Matsuo S, Tsutsumi R, et al. A case of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the colon responding to FOLFOX. Acta Med Nagasaki. 2007; 52:67–70.
13. Kim JR, Kim JY, Hong KH, Chang ES, Song KS, Yoon WH. Neuroendocrine neoplasm of the colon and rectum. J Korean Surg Soc. 2000; 59:237–245.
Go to : 
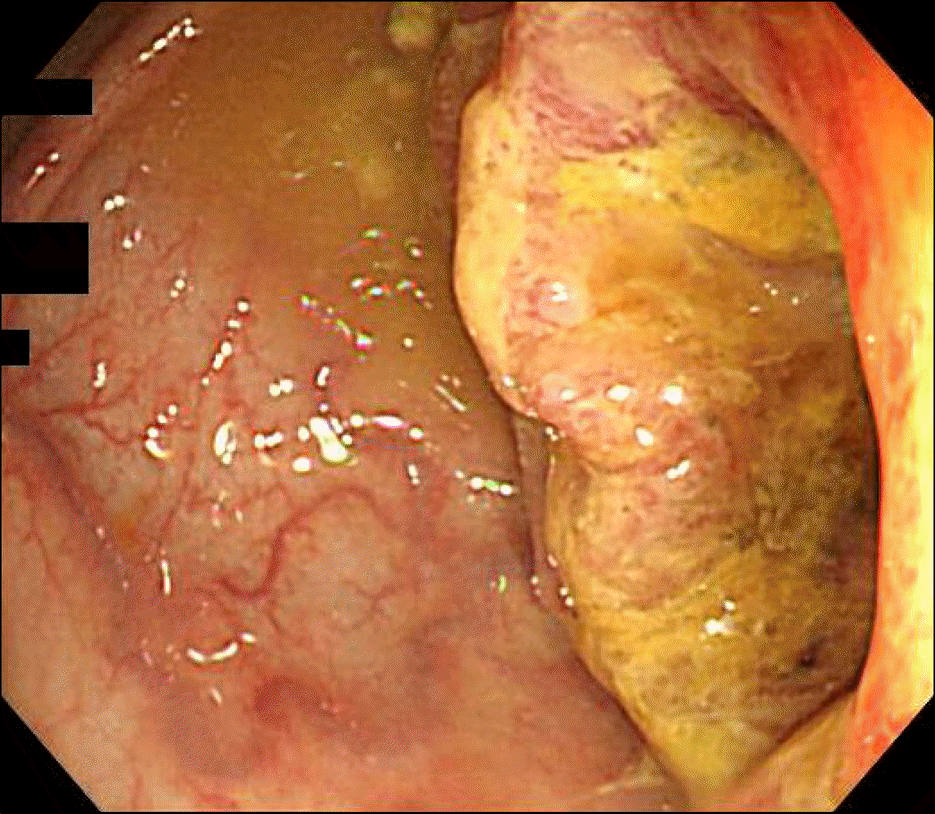 | Fig. 1.Colonoscopic finding showed the ulceroinfiltrative mass with luminal narrowing at hepatic flexure. |
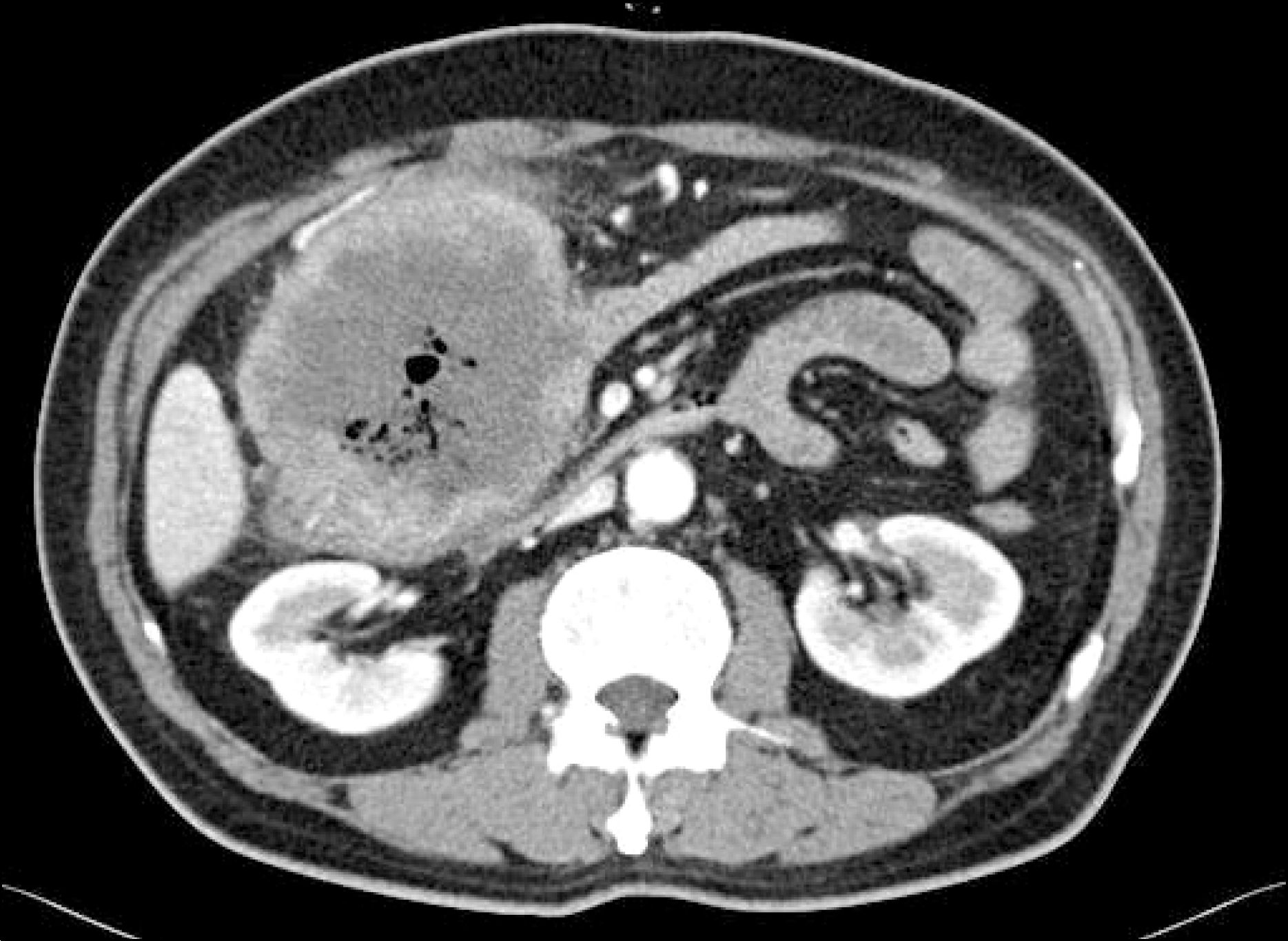 | Fig. 2.Enhanced abdominal CT scan showed a huge necrotic mass located in distal ascending colon with multiple regional lymphadenopathy around mesentery and small amount of ascites. |
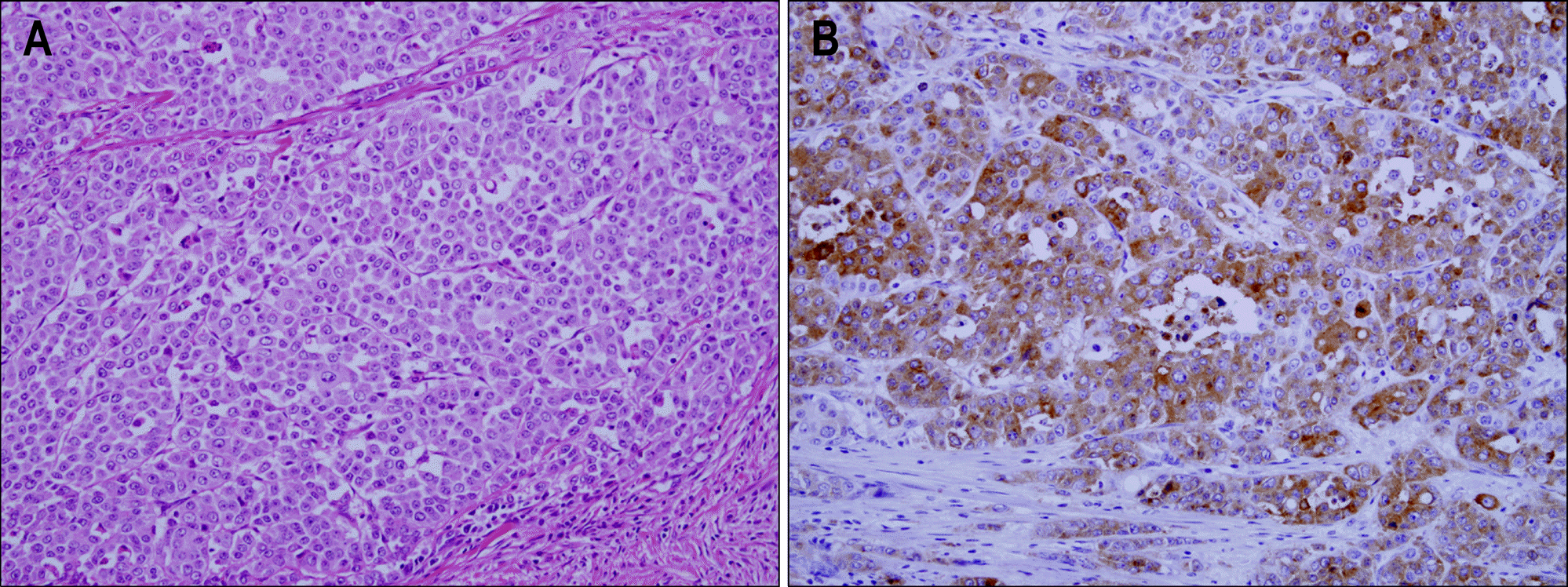 | Fig. 3.Microscopic finding and immunohistochemical stain. Tumor cells featuring abundunt cytoplasm, prominent nucleoli, frequent mi-totic rate showed the organoid, nesting, trabecular and palisadng pattern (H&E, ×200) (A) and positive immunohistochemical stain for synaptophysin (Synaptophysin, ×200) (B). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download