Abstract
Background/Aims
Liver stiffness (LS) measurement by transient elastography can estimate the degrees of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic liver disease. However, longitudinal data of LS after recovery of acute viral hepatitis are still lacking. In the present study, we aimed to evaluate among LS of patients at various stages of viral hepatitis and normal control.
Methods
Patients who had admitted at Korea University Ansan Hospital between January 2006 and January 2007 due to acute viral hepatitis and recovered were recruited (group A, n=22). We compared the liver biochmistry and LS of group A with those of healthy control group (group B, n=23), current acute viral hepatitis group (group C, n=49), and chronic viral hepatitis group (group D, n=66).
Results
Mean ALT, total bilirubin, and LS level of group A were not different from group B (p=0.318, p=0.116, p=0.125, respectively). However, group A had lower ALT, total bilirubin, and LS values compared to group C (all p <0.001), and lower ALT and LS values compared to group D (p=0.007, p<0.001). The mean total bilirubin was not significantly different from group D (p=0.117).
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Kang HM, Jeong SH, Kim JW, et al. Recent etiology and clinical features of acute viral hepatitis in a single center of Korea. Korean J Hepatol. 2007; 13:495–502.

4. Cadranel JF, Rufat P, Degos F. Practices of liver biopsy in France: results of a prospective nationwide survey. For the Group of Epidemiology of the French Association for the Study of the Liver (AFEF). Hepatology. 2000; 32:477–481.
5. Maharaj B, Maharaj RJ, Leary WP, et al. Sampling variability and its influence on the diagnostic yield of percutaneous needle biopsy of the liver. Lancet. 1986; 1:523–525.

7. Saadeh S, Cammell G, Carey WD, Younossi Z, Barnes D, Easley K. The role of liver biopsy in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2001; 33:196–200.

8. Poynard T, Ratziu V, Bedossa P. Appropriateness of liver biopsy. Can J Gastroenterol. 2000; 14:543–548.

9. Regev A, Berho M, Jeffers LJ, et al. Sampling error and intraobserver variation in liver biopsy in patients with chronic HCV infection. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002; 97:2614–2618.

10. Bedossa P, Dargere D, Paradis V. Sampling variability of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2003; 38:1449–1457.

11. Soloway RD, Baggenstoss AH, Schoenfield LJ, Summerskill WH. Observer error and sampling variability tested in evaluation of hepatitis and cirrhosis by liver biopsy. Am J Dig Dis. 1971; 16:1082–1086.

12. Standish RA, Cholongitas E, Dhillon A, Burroughs AK, Dhillon AP. An appraisal of the histopathological assessment of liver fibrosis. Gut. 2006; 55:569–578.

13. Ganne-Carrie N, Ziol M, de Ledinghen V, et al. Accuracy of liver stiffness measurement for the diagnosis of cirrhosis in patients with chronic liver diseases. Hepatology. 2006; 44:1511–1517.

14. Rockey DC. Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis and portal hypertension with transient elastography. Gastroenterology. 2008; 134:8–14.

15. Sandrin L, Fourquet B, Hasquenoph JM, et al. Transient elastography: a new noninvasive method for assessment of hepatic fibrosis. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2003; 29:1705–1713.

16. Ziol M, Handra-Luca A, Kettaneh A, et al. Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis by measurement of stiffness in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2005; 41:48–54.

17. Castera L, Vergniol J, Foucher J, et al. Prospective comparison of transient elastography, Fibrotest, APRI, and liver biopsy for the assessment of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2005; 128:343–350.

18. Colletta C, Smirne C, Fabris C, et al. Value of two noninvasive methods to detect progression of fibrosis among HCV carriers with normal aminotransferases. Hepatology. 2005; 42:838–845.

19. Foucher J, Chanteloup E, Vergniol J, et al. Diagnosis of cirrhosis by transient elastography (FibroScan): a prospective study. Gut. 2006; 55:403–408.

20. Kazemi F, Kettaneh A, N'Kontchou G, et al. Liver stiffness measurement selects patients with cirrhosis at risk of bearing large oesophageal varices. J Hepatol. 2006; 45:230–235.

21. Sagir A, Erhardt A, Schmitt M, Haussinger D. Transient elastography is unreliable for detection of cirrhosis in patients with acute liver damage. Hepatology. 2008; 47:592–595.

22. Coco B, Oliveri F, Maina AM, et al. Transient elastography: a new surrogate marker of liver fibrosis influenced by major changes of transaminases. J Viral Hepat. 2007; 14:360–369.

23. Castera L, Forns X, Alberti A. Non-invasive evaluation of liver fibrosis using transient elastography. J Hepatol. 2008; 48:835–847.

24. Fraquelli M, Rigamonti C, Casazza G, et al. Reproducibility of transient elastography in the evaluation of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic liver disease. Gut. 2007; 56:968–973.

25. Arena U, Vizzutti F, Corti G, et al. Acute viral hepatitis increases liver stiffness values measured by transient elastography. Hepatology. 2008; 47:380–384.

26. Cho SW, Cheong JY. Clinical application of non-invasive diagnosis for hepatic fibrosis. Korean J Hepatol. 2007; 13:129–137.
27. Jung HS, Kim YS, Kwon OS, et al. Usefulness of liver stiffness measurement for predicting the presence of esophageal varices in patients with liver cirrhosis. Korean J Hepatol. 2008; 14:342–350.

28. Jung MK, Cho HJ, Lee HC, et al. Comparison of transient elastography and hepatic fibrosis assessed by histology in chronic liver disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2008; 51:241–247.
29. Kang JK, Cheong JY, Cho SW, et al. Liver stiffness measurement for the diagnosis of hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic viral hepatitis. Korean J Hepatol. 2007; 13:521–529.

30. Kim HS, Kim JK, Park YN, et al. Non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis by measuring the liver stiffness and biochemical markers in chronic hepatitis B patients. Korean J Med. 2007; 72:459–469.
31. Lee HS, Byun JH, Kim CY. Etiology and outcome of acute viral hepatitis in Korean adults. J Korean Med Sci. 1990; 5:149–154.

32. Lee D, Cho YA, Park Y, et al. Hepatitis a in Korea: epidemiological shift and call for vaccine strategy. Intervirology. 2008; 51:70–74.

33. Song MH, Lim YS, Song TJ, et al. The etiology of acute viral hepatitis for the last 3 years. Korean J Med. 2005; 68:256–260.
34. Jeong SH. Current status and vaccine indication for hepatitis a virus infection in Korea. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2008; 51:331–337.
35. Byun KS. Recent epidemiologic changes of acute and chronic hepatitis in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 2005; 48:423–427.

36. Roulot D, Czernichow S, Le Clesiau H, Costes JL, Vergnaud AC, Beaugrand M. Liver stiffness values in apparently healthy subjects: influence of gender and metabolic syndrome. J Hepatol. 2008; 48:606–613.

Go to : 
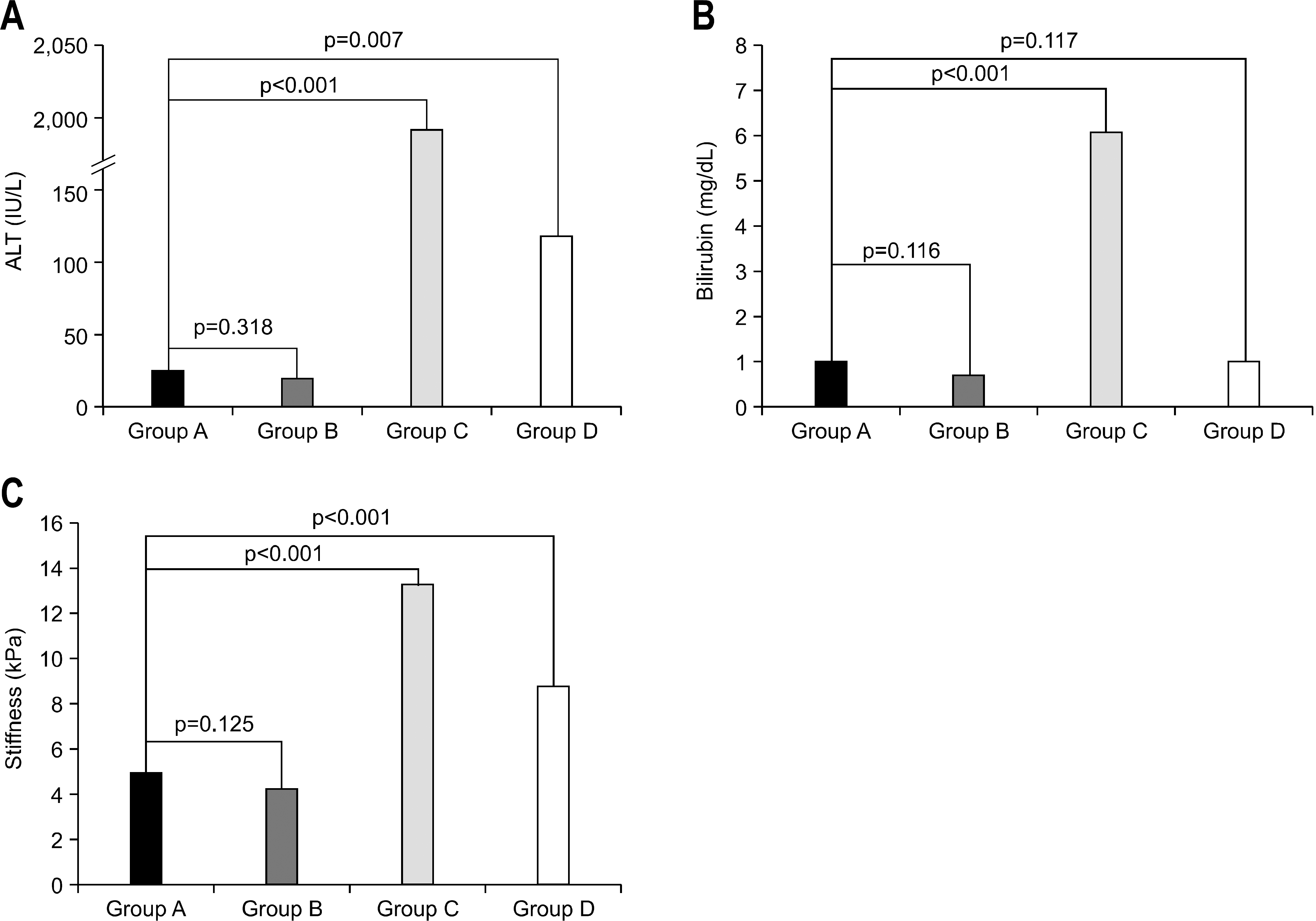 | Fig. 1.Comparison of biochemistry and liver stiffness among recovered group (group A) and other groups (group B, C, or D). (A) ALT: Group A showed significant difference compared with group C and group D, but not with group B. (B) Total bilirubin: Group A showed significant difference compared with group C, but not with group B and group D. (C) Liver stiffness: Group A showed significant difference compared with group C and group D, but not with group B. Group A, recovered group; Group B, healthy control group; Group C, current acute hepatitis group; Group D, chronic hepatitis group. |
Table 1.
Baseline Characteristics
| Variables | Group A (n=22) | Group B (n=23) | Group C (n=49) | Group D (n=66) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male∗ | 12 (54.5%) | 8 (34.8%) | 30 (61.2%) | 50 (75.8%) |
| Age (years) | 34±8.0 (19-59) | 48.7±16.4 (20-77) | 33.0±7.9 (16-60) | 40.2±9.9 (17-68) |
| AST (IU/L) | 37.5±30.1 (11-127) | 22.4±6.6 (12-40) | 1016.9±1008.8 (30-4,802) | 77.9±76.4 (17-706) |
| ALT (IU/L) | 24.4±12.9 (8-51) | 19.3±10.6 (8-50) | 1914.8±1784.7 (16-5,586) | 117.7±116.2 (7-928) |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.0±0.7 (0.6-1.7) | 0.7±0.3 (0.3-1.3) | 6.1±3.4 (0.9-15.6) | 1.0±0.4 (0.3-2.4) |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.4±0.3 (3.7-4.8) | 4.3±0.3 (3.8-4.9) | 3.7±0.3 (3.0-4.4) | 4.3±0.4 (2.8-4.9) |
| Stiffness (kPa) | 5.02±1.2 (3.3-7.2) | 4.4±1.1 (1.8-6.3) | 13.3±7.4 (6.3-44.3) | 8.8±7.0 (3.2-48.8) |
Table 2.
Factors Correlated with Liver Stiffness Adjusted by Gender
| Variables | Correlation coefficient | p-value |
|---|---|---|
| Age | −0.002 | 0.985 |
| AST | 0.179 | 0.049 |
| ALT | 0.211 | 0.02 |
| Total bilirubin | 0.452 | <0.001 |
| ALP∗ | 0.224 | 0.014 |
| γ-GT | 0.287 | 0.001 |
| Albumin | −0.415 | <0.001 |
| Platelet | −0.087 | 0.341 |
Table 3.
Linear Regression Analysis of Continuous Variables with Liver Stiffness




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download