REFERENCES
1. Behar J, Corassiari E, Guelrud M, Hogan W, Sherman S, Toouli J. Functional gallbladder and sphincter of Oddi disorders. Gastroenterology. 2006; 133:1498–1509.

2. Toouli J, Di Francesco V, Saccone G, Kollias J, Schloithe A, Shanks N. Division of the sphincter of Oddi for treatment of dysfunction associated with recurrent pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 1996; 83:1205–1210.

3. Tarnasky PR, Palesch YY, Cunningham JT, Mauldin PD, Cotton PB, Hawes RH. Pancreatic stenting prevents pancreatitis after biliary sphincterotomy in patients with sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. Gastroenterology. 1998; 115:1518–1524.

4. Elton E, Howell DA, Parsons WG, Qaseem T, Hanson BL. Endoscopicpancreatic sphincterotomy: indications, outcome and a safe stentless technique. Gastrointest Endosc. 1998; 47:240–249.
Go to : 
 | Fig. 1.Contrast-enhanced CT finding of the patient. Pancreas was normal looking without edema, peripancreatic infiltration, or fluid collection. |
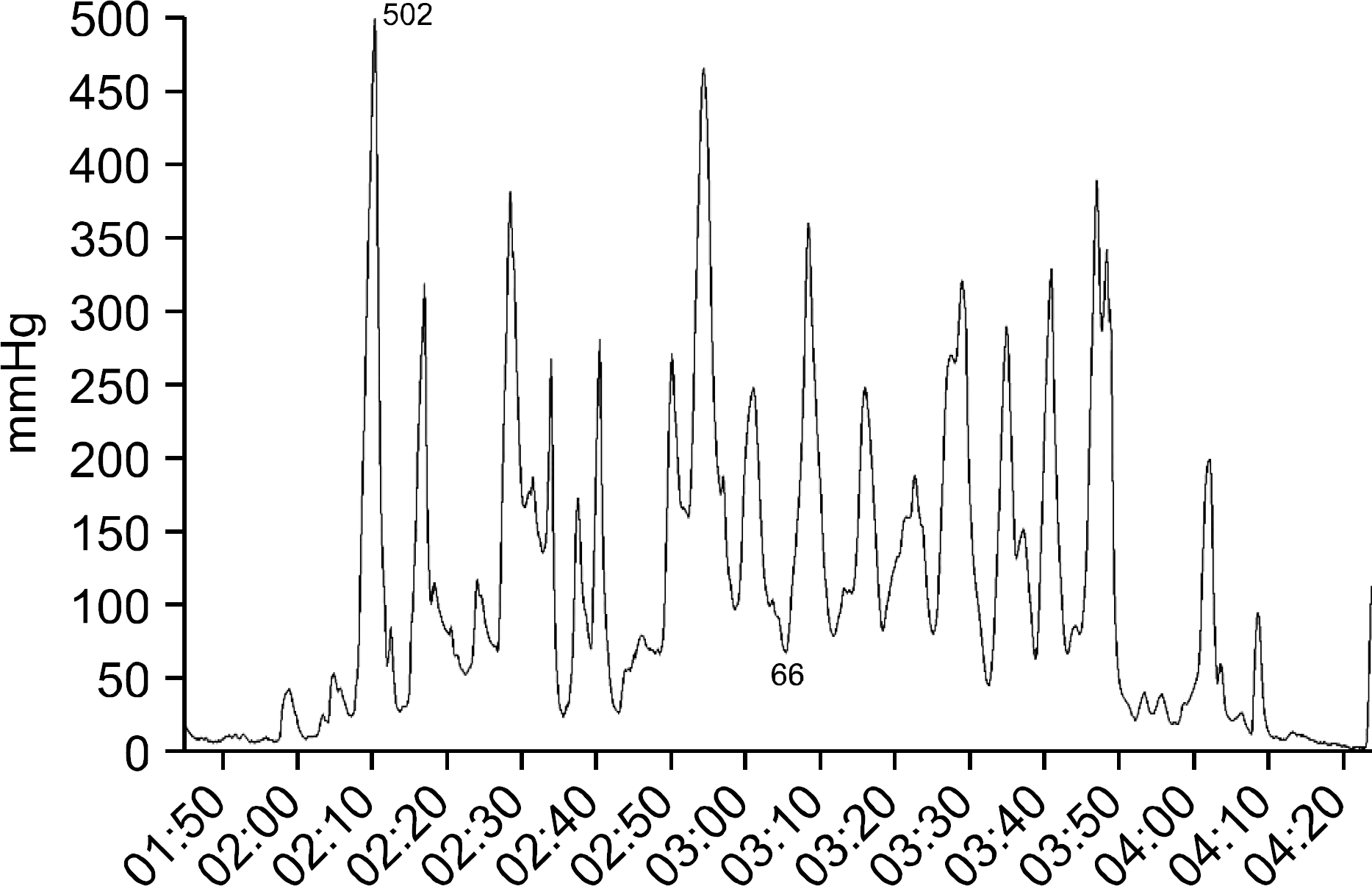
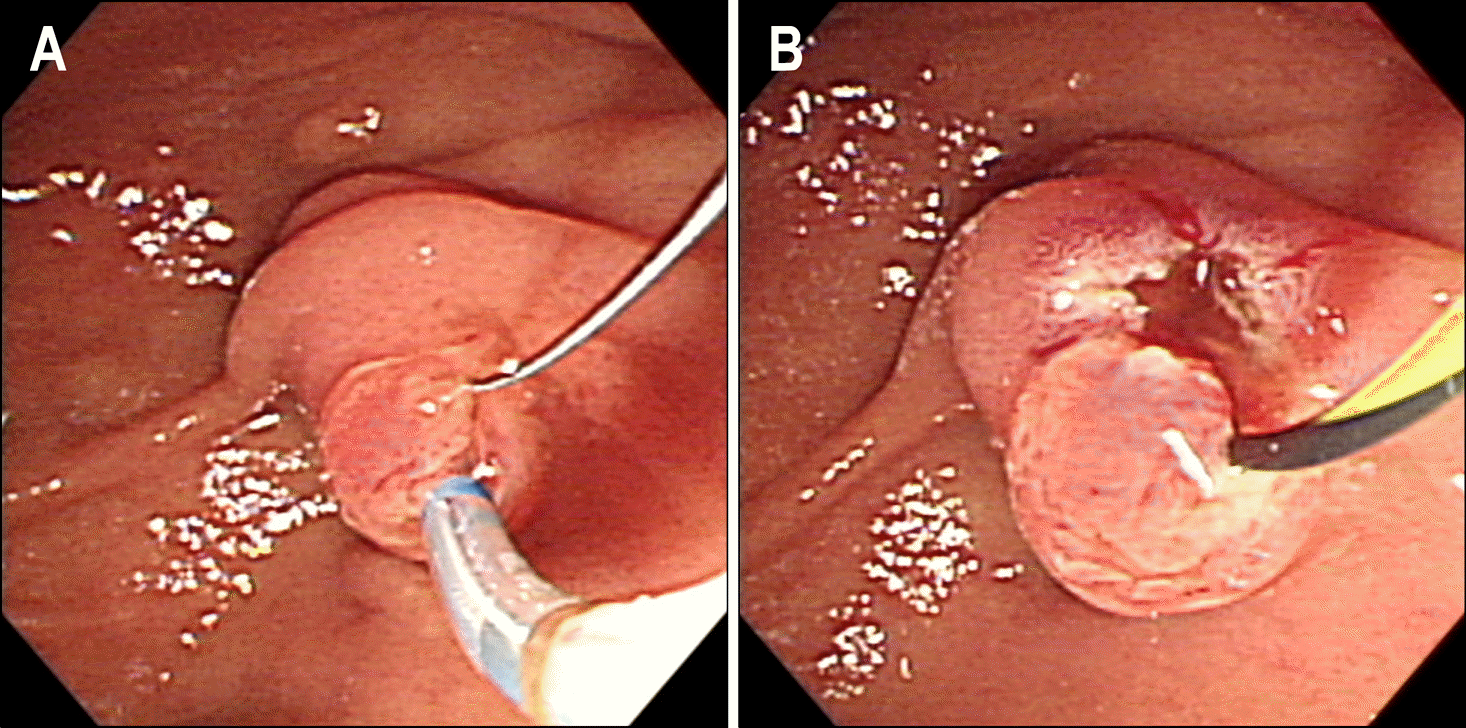
 | Fig. 2.Endoscopic retrograde cho-langiopancreatography findings. (A) Major duodenal papilla looked normal. (B) Pancreatogram showed unremarkable finding. (C) Sphincter of Oddi manometry was performed with a catheter placed in-side the main pancreatic duct. (D) After withdrawal of the manometry device, pancreatic stent (5Fr 3 cm) was placed. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download