Abstract
Objective
This study was performed to compare the pharmacokinetics of methotrexate (MTX) in unruptured ectopic pregnancy according to the injection route.
Methods
Between May 2005 and August 2009, thirty-five patients of unruptured ectopic pregnancy in Chungbuk National University Hospital were treated medically either by intramuscular (IM) or intraamniotic (IA) injection of MTX according to the presence of fetal heart beat. Serum concentration of MTX was measured by fluorescent immunoassay using the blood samples withdrawn serially after its injection.
Results
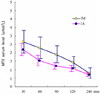
The peak plasma MTX level was achieved at the 30-minute after injection sample in both groups. The mean peak plasma level of MTX in IM group was significantly higher than that of IA in 60-minute (2.296±0.64 umol/L vs 1.535±0.31 umol/L; p<0.006), 90-minute (1.9±0.51 umol/L vs 1.225±0.21 umol/L; p<0.002), and 240-minute (1.443±0.33 umol/L vs 1.077±0.18 umol/L; p<0.011) samples. The mean pretreatment plasma β-hCG level was significantly higher in IA group, both tubal pregnancy (48,405±37,811.7 IU/L vs 18,452.05±19,205.34 IU/L; p<0.007) and cervical pregnancy (94,574.2±45,037.1 IU/L vs 42,446±34,778.12 IU/L; p<0.037), than those of IM group. But neither plasma MTX level nor pretreatment β-hCG level were related to the treatment outcome.
Conclusion
The plasma level of MTX increased rapidly in both IM and IA groups; the peak level reached at 30 minutes, and decreased to less than 1 umol/L after 240 minutes. Moreover, it was higher in IM group than IA group. Nevertheless, IA injection may be useful in patients who had high β-hCG level or fetal heart beat, which are not usually indicated to medical treatment.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 2
Average MTX serum level according to the route of administration. IM: intramuscular, IA: intraamniotic.
References
1. Jeong EH, Hong SH, Park YJ, Ji IW, Kim HS. Pharmacokinetics of methotrexate after intraamniotic injection for non-surgical treatment of unruptured ectopic pregnancy. Chungbuk Med J. 2006. 16:173–179.
2. Stovall TG, Ling FW, Smith WC, Fellcer RF, Rasco BJ, Buster JE. Methotrexate treatment of unruptured ectopic pregnancy: a report of 100 cases. Obstet Gynecol. 1991. 77:749–753.
3. Cannon L, Jesionowska H. Methotrexate treatment of tubal pregnancy. Fertil Steril. 1991. 55:1033–1038.
4. Kojima E, Abe Y, Morita M, Ito M, Hirakawa S, Momose K. The treatment of unruptured tubal pregnancy with intratubal methotrexate injection under laparoscopic control. Obstet Gynecol. 1990. 75:723–725.
5. Hung TH, Shau WY, Hsieh TT, Hsu JJ, Soong YK, Jeng CJ. Prognostic factors for an unsatisfactory primary methotrexate treatment of cervical pregnancy: a quantitative review. Hum Reprod. 1998. 13:2636–2642.
6. Kang EJ, Kim HJ, Kim MH, Cho EN, Kim HJ. Conservative treatment of cervical pregnancy with MTX followed by therapeutic curettage. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 2001. 44:1483–1487.
7. Jeong EH, Ahn CS. Single-dose methotrexate: non-surgical treatment of unruptured ectopic pregnancy. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 1996. 39:1485–1488.
8. Schiff E, Tsabari A, Shalev E, Mashiach S, Bustan M, Weiner E. Pharmacokinetics of methotrexate after local tubal injection for conservative treatment of ectopic pregnancy. Fertil Steril. 1992. 57:688–690.
9. Fernandez H, Lelaidier C, Bourget P, Frydman R, Ville Y. Treatment of unruptured tubal pregnancy with methotrexate: pharmacokinetic analysis of local versus intramuscular administration. Fertil Steril. 1994. 62:943–947.
10. Sin SK, Yoon TJ, Hong SH, Kim YB, Ji IW, Jeong EH, et al. Conservative treatment of viable cervical pregnancy with intra-amniotic methotrexate. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 2001. 44:2031–2035.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print







 XML Download
XML Download