Abstract
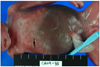
Listeriosis is an infectious disease caused by Listeria monocytogenes, a gram positive, facultatively anaerobic bacterium. Listeriosis occurs primarily in newborn infants, elderly patients, immunocompromised patients and pregnant women. One third of the patients are pregnant women, and complications of this disease include miscarriage, stillbirth and preterm labor. We experienced a case of listeriosis in a singleton pregnancy at 23rd week of gestation that presented with fever, chill, lower abdominal pain, backache, and eventually resulted in fetal death in utero. Autopsy results of the stillborn baby, as well as blood and amniotic fluid culture of the mother confirmed Listeria monocytogenes infection. Proper antibiotics therapy thereafter led to clear recovery of the infected mother. We report this case with a brief review of literature.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Skogberg K, Syrjänen J, Jahkola M, Renkonen OV, Paavonen J, Ahonen J, et al. Clinical presentation and outcome of listeriosis in patients with and without immunosuppressive therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 1992. 14:815–821.

2. Mead PS, Slutsker L, Dietz V, McCaig LF, Bresee JS, Shapiro C, et al. Food-related illness and death in the United States. Emerg Infect Dis. 1999. 5:607–625.

3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Preliminary FoodNet data on the incidence of infection with pathogens transmitted commonly through food--10 states, 2007. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2008. 57:366–370.
4. Mylonakis E, Paliou M, Hohmann EL, Calderwood SB, Wing EJ. Listeriosis during pregnancy: a case series and review of 222 cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 2002. 81:260–269.
11. Chi JG. Listeriosis in a Stillborn Fetus (An Autopsy Case). Seoul J Medi. 1989. 30:181–188.
14. Linnan MJ, Mascola L, Lou XD, Goulet V, May S, Salminen C, et al. Epidemic listeriosis associated with Mexican-style cheese. N Engl J Med. 1988. 319:823–828.

15. Olsen SJ, Patrick M, Hunter SB, Reddy V, Kornstein L, MacKenzie WR, et al. Multistate outbreak of Listeria monocytogenes infection linked to delicatessen turkey meat. Clin Infect Dis. 2005. 40:962–967.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download