Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of a terpene mixture compared with alpha-blocker in patients with chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS).
Materials and Methods
Patients diagnosed with CPPS were included in this study. The patients were randomly placed into three groups. Group 1 was treated with levofloxacin alone (36 patients), group 2 was treated with levofloxacin and alfuzosin (33 patients), and group 3 was treated with levofloxacin and terpene mixture (34 patients) for 8 weeks. The National Institutes of Health Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI) was evaluated in patients in each group at the beginning of the study and after 8 weeks of treatment.
Results
Pain domain, urinary domain, quality of life domain, and total score on the NIH-CPSI were not significantly different at the initial visit. After treatment with each medication, improvements on the pain domain and total score of the NIH-CPSI were better in group 3 than in group 1 or group 2 (p<0.05). Improvement on the urinary domain of the NIH-CPSI was better in group 2 than in group 1 or group 3 (p=0.014). Changes in the quality of life domain of the NIH-CPSI were not significant among the three groups.
Figures and Tables
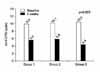 | Fig. 1Mean value of the National Institute of Health Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI) pain domain score (potential of 21 points) at the beginning of the study and after 8 weeks of treatment in each group. |
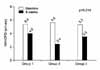 | Fig. 2Mean value of the National Institute of Health Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI) urinary domain score (potential of 10 points) at the beginning of the study and after 8 weeks of treatment in each group. |
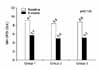 | Fig. 3Mean value of the National Institute of Health Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI) quality of life domain score (potential of 12 points) at the beginning of the study and after 8 weeks of treatment in each group. |
References
1. Alexander RB, Propert KJ, Schaeffer AJ, Landis JR, Nickel JC, O'Leary MP, et al. Ciprofloxacin or tamsulosin in men with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a randomized, double-blind trial. Ann Intern Med. 2004. 141:581–589.
2. Krieger JN, Nyberg L Jr, Nickel JC. NIH consensus definition and classification of prostatitis. JAMA. 1999. 282:236–237.
3. Nickel JC, Nyberg LM, Hennenfent M. Research guidelines for chronic prostatitis: consensus report from the first national institutes of health international prostatitis collaborative network. Urology. 1999. 54:229–233.
4. Lee CB, Ha US, Lee SJ, Kim SW, Cho YH. Preliminary experience with a terpene mixture versus ibuprofen for treatment of category III chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. World J Urol. 2006. 24:55–60.
5. Bartoletti R, Cai T, Mondaini N, Dinelli N, Pinzi N, Pavone C, et al. Prevalence, incidence estimation, risk factors and characterization of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome in urological hospital outpatients in Italy: results of a multicenter case-control observational study. J Urol. 2007. 178:2411–2415.
6. Woo YN. Prostatitis. Korean J Urol. 1994. 35:575–585.
7. Kirby RS. Nickel JC, editor. Surgical considerations in the management of prostatitis. Textbook of prostatitis. 1999. Oxford: ISIS Medical Media Ltd;346–364.
8. Roberts RO, Lieber MM, Rhodes T, Girman CJ, Bostwick DG, Jacobsen SJ. Prevalence of a physician-assigned diagnosis of prostatitis: The Olmsted County Study of Urinary Symptoms and Health Status Among Men. Urology. 1998. 51:578–584.
9. Ku JH, Kim ME, Lee NK, Park YH. The prevalence of chronic prostatitis-like symptoms in young men: a community-based survey. Urol Res. 2001. 29:108–112.
10. Moon TD, Hagen L, Heisey DM. Urinary symptomatology in younger men. Urology. 1997. 50:700–703.
11. Mehik A, Hellstrom P, Lukkarinen O, Sarpola A, Jarvelin M. Epidemiology of prostatitis in Finnish men: a population-based cross-sectional study. BJU Int. 2000. 86:443–448.
12. Shoskes DA, Hakim L, Ghoniem G, Jackson CL. Long-term results of multimodal therapy for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. J Urol. 2003. 169:1406–1410.
13. McNaughton Collins M, MacDonald R, Wilt TJ. Diagnosis and treatment of chronic abacterial prostatitis: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2000. 133:367–381.
14. Nickel JC, Pontari M, Moon T, Gittelman M, Malek G, Farrington J, et al. A randomized, placebo controlled, multicenter study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of rofecoxib in the treatment of chronic nonbacterial prostatitis. J Urol. 2003. 169:1401–1405.
15. Goto T, Makinose S, Ohi Y, Yamauchi D, Kayajima T, Nagayama K, et al. Diffusion of piperacillin, cefotiam, minocycline, amikacin, and ofloxacin into the prostate. Int J Urol. 1998. 5:243–246.
16. Nickel JC, Downey J, Johnston B, Clark J, Canadian Prostatitis. Predictors of patient response to antibiotic therapy for the chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a prospective multicenter clinical trial. J Urol. 2001. 165:1539–1544.
17. Mo KI, Lee KS, Kim DG. Efficacy of combination therapy for patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a prospective study. Korean J Urol. 2006. 47:536–540.
18. Donker PJ, Ivanovici F, Noach EL. Analyses of the urethral pressure profile by means of electromyography and the administration of drugs. Br J Urol. 1972. 44:180–193.
19. Barbalias GA, Nikiforidis G, Liatsikos EN. Alpha-blockers for the treatment of chronic prostatitis in combination with antibiotics. J Urol. 1998. 159:883–887.
20. Cheah PY, Liong ML, Yuen KH, Teh CL, Khor T, Yang JR, et al. Initial, long-term, and durable responses to terazosin, placebo, or other therapies for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Urology. 2004. 64:881–886.
21. Youn CW, Son KC, Choi HS, Kwon DD, Park K, Ryu SB. Comparison of the efficacy of antibiotic monotherapy and antibiotic plus alpha-blocker combination therapy for patients with inflammatory chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Korean J Urol. 2008. 49:72–76.
22. Nickel JC, Narayan P, McKay J, Doyle C. Treatment of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome with tamsulosin: a randomized double blind trial. J Urol. 2004. 171:1594–1597.
23. Ryu YG, Kim HJ, Park HJ. The efficacy of alfuzosin for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome in young and middle aged patients. Korean J Urol. 2007. 48:858–862.
24. Dedhia RC, McVary KT. Phytotherapy for lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol. 2008. 179:2119–2125.
25. Siller G. Effect of rowatinex capsules on the stone fragments formed by extracorporeal shock-wave lithotripsy. Magyar Urol. 1998. 10:139–146.
26. Zhou JY, Tang FD, Mao GG, Bian RL. Effect of alpha-pinene on nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B in THP-1 cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2004. 25:480–484.
27. Park TJ, Park YS, Lee TG, Ha H, Kim KT. Inhibition of acetylcholine-mediated effects by borneol. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003. 65:83–90.
28. Juergens UR, Stober M, Vetter H. Inhibition of cytokine production and arachidonic acid metabolism by eucalyptol (1.8-cineole) in human blood monocytes in vitro. Eur J Med Res. 1998. 3:508–510.
29. Minnery CH, Getzenberg RH. Benign prostatic hyperplasia cell line viability and modulation of jm-27 by doxazosin and ibuprofen. J Urol. 2005. 174:375–379.
30. Bak CW, Yoon SJ, Chung H. Effects of an α-blocker and terpene mixture for pain control and spontaneous expulsion of ureter stone. Korean J Urol. 2007. 48:517–521.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download