Abstract
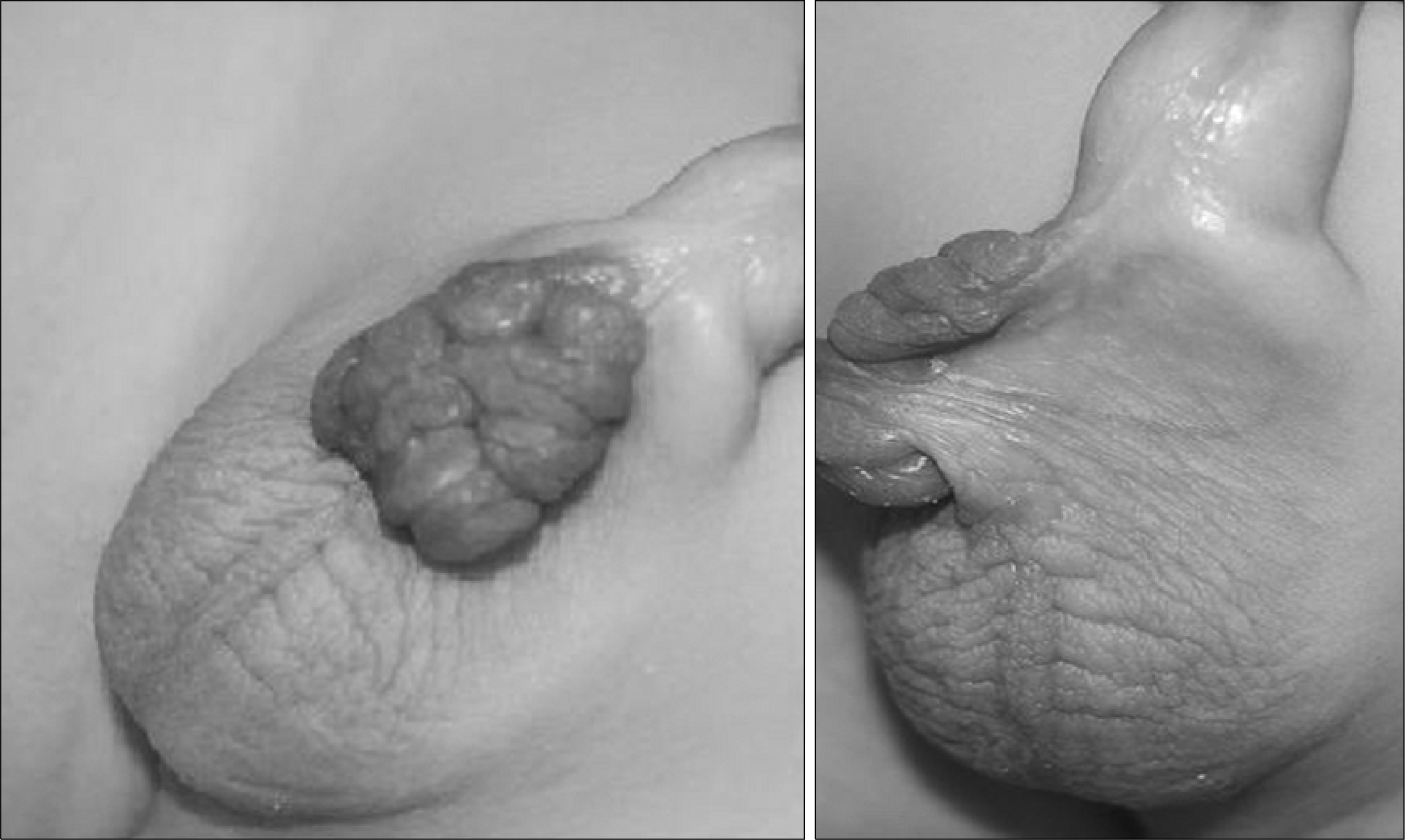
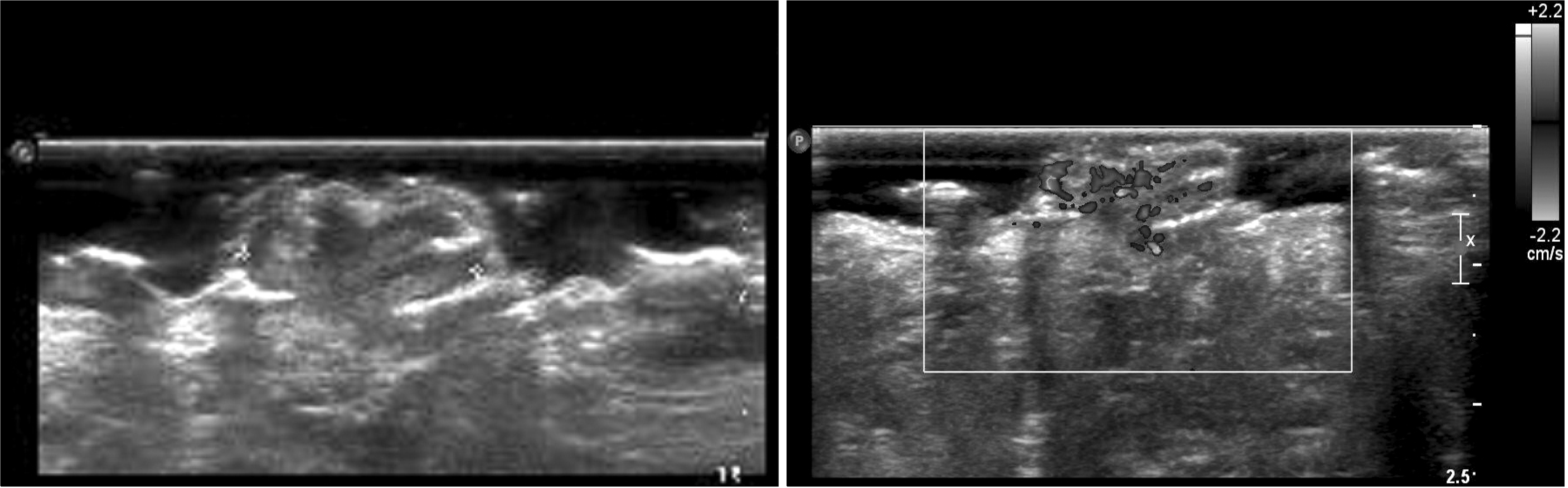
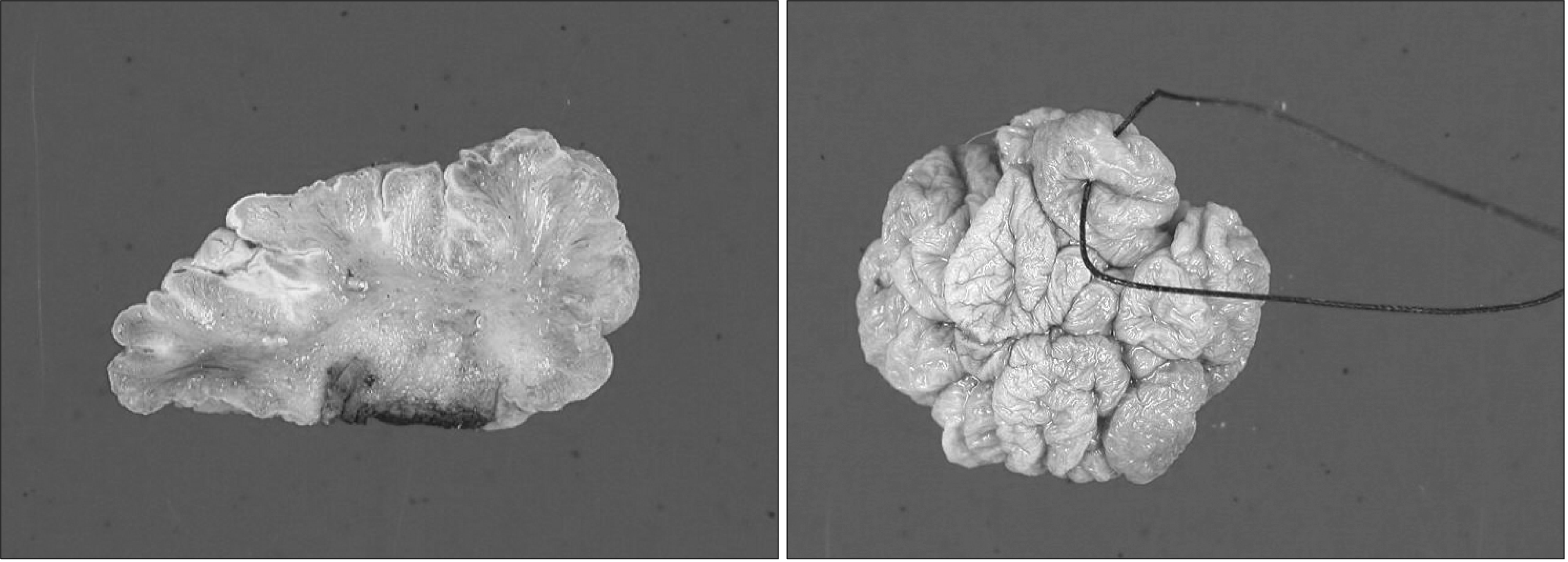
Fibroepithelial polyps are benign, easily treated, and tumors with a good prognosis in the urinary tract. Congenital fibroepithelial polyps of the external genitalia are rarely reported. We report a case of a congenital fibroepithelial polyp of the penoscrotal junction in an 18-month-old boy. The fibroepithelial polyp was noted at birth with continuous grow. The fibroepithelial polyp was soft, dark-red in color, non-tender, and had a cockscomb shape. We treated the fibroepithelial polyp with simple excision and the histopathologic finding was a fibroepithelial polyp without a malignant component.
References
1. Musselman P, Kay R. The spectrum of urinary tract fibroepithelial polyps in children. J Urol. 1986; 136:476–7.

2. Turgut M, Yenilmez A, Can C, Bildirici K, Erkul A, Ozyürek Y. Fibroepithelial polyp of glans penis. Urology. 2005; 65:593.

3. Yildirim I, Irkilata C, Sumer F, Aydur E, Ozcan A, Dayanc M. Fibroepithelial polyp originating from the glans penis in a child. Int J Urol. 2004; 11:187–8.

4. Tekdogan UY, Canakli F, Aslan Y, Han O, Gungor S, Atan A. Bilateral ureteral fibroepithelial polyps and review of the literature. Int J Urol. 2005; 12:98–100.

5. Fetsch JF, Davis CJ Jr, Hallman JR, Chung LS, Lupton GP, Sesterhenn IA. Lymphedematous fibroepithelial polyps of the glans penis and prepuce: a clinicopathologic study of 7 cases demonstrating a strong association with chronic condom catheter use. Hum Pathol. 2004; 35:190–5.

6. Natsheh A, Prat O, Shenfeld OZ, Reinus C, Chertin B. Fibroepithelial polyp of the bladder neck in children. Pediatr Surg Int. 2008; 24:613–5.

7. Jallouli M, Trigui L, Gargouri A, Mhiri R. Vaginal polyp in a newborn. Eur J Pediatr. 2008; 167:599–600.

8. Demircan M, Ceran C, Karaman A, Uguralp S, Mizrak B. Urethral polyps in children: a review of the literature and report of two cases. Int J Urol. 2006; 13:841–3.

9. Agir H, Sen C, Cek D. Squamous cell carcinoma arising from a fibroepithelial polyp. Ann Plast Surg. 2005; 55:687–8.

10. From L, Assad D. Neoplasms, pseudoneoplasms and hyperplasias of the dermis-acrochordon. Freedberg IM, editor. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 5th ed.New York: McGowan-Hill;1999. p. 1166–7.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download