Abstract
Urethral duplication is a rare congenital anomaly that can present in various clinical forms according to the plane and extent of duplication. Although some are associated with abnormalities of the external genitalia, others present as mild condition which is incidentally found. Nine cases of complete and incomplete types of urethral duplication have been reported in the Korean literature. We report the clinical presentation and management of four cases of various types of urethral duplication in boys.
REFERENCES
1.Haleblian G., Kraklau D., Wilcox D., Duffy P., Ransley P., Mushtaq I. Y-type urethral duplication in the male. BJU Int. 2006. 97:597–602.

2.Seo YH., Jung SY., Shim JM., Kang SS., Park JI. A case of inverted Y-type congenital urethral duplication. Korean J Urol. 2000. 41:788–90.
4.Huang CC., Wu WH., Chai CY., Wu TC., Chuang JH. Congenital prepubic sinus: a variant of dorsal urethral duplication suggested by immunohistochemical analysis. J Urol. 2001. 166:1876–9.

5.Woodhouse CR., Williams DI. Duplications of the lower urinary tract in children. Br J Urol. 1979. 51:481–7.

6.Podesta ML., Medel R., Castera R., Ruarte AC. Urethral duplication in children: surgical treatment and results. J Urol. 1998. 160:1830–3.

7.Arsic D., Qi BQ., Beasley SW. Hedgehog in the human: a possible explanation for the VATER association. J Paediatr Child Health. 2002. 38:117–21.

Fig. 1.
Patient 1 who presented with complete duplication of the bladder and urethra. (A) Urethral opening in mid-dorsum of the penis (black arrow) and indentation of the coronal glans. (B) Dorsal curvature at rest. (C) Magnetic resonance imaging showing fluid and air-filled accessory bladder (white arrow) anterior to the native bladder. (D) Excision of the dorsal accessory urethra. (E) Apparent dorsal curvature with artificial erection. (F) Correction of the dorsal curvature after ventral plication.

Fig. 3.
Patient 3 (A) concealed penis (B) accessory dorsal urethral meatus found in the dorsal glans when the foreskin was retracted for penoplasty (black arrow).

Fig. 4.
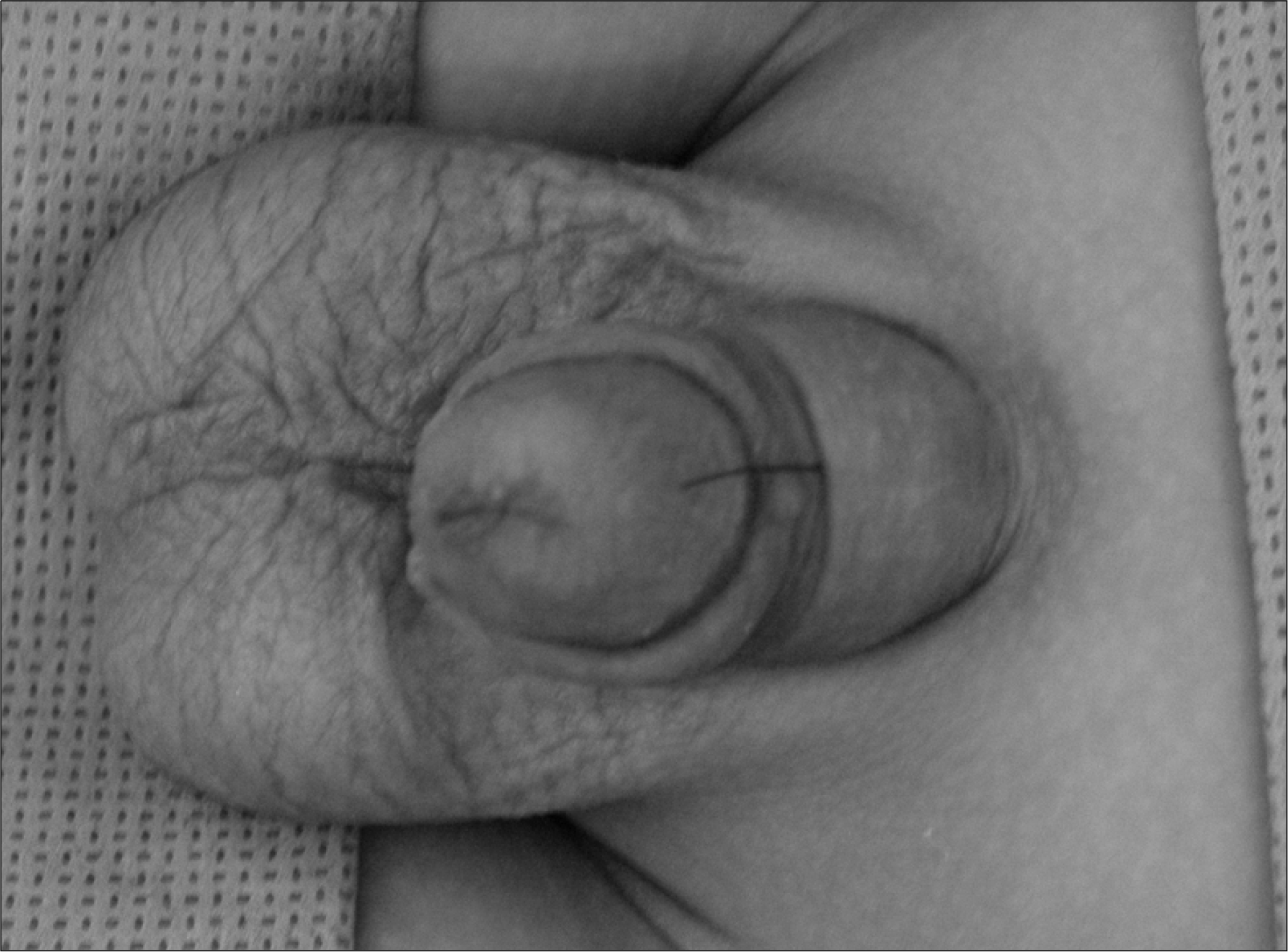
Patient 4 presenting (A) with a normal urethral orifice at the tip of the glans, as well as a (B) dorsal urethral opening at the dorsal penile base (black arrow).
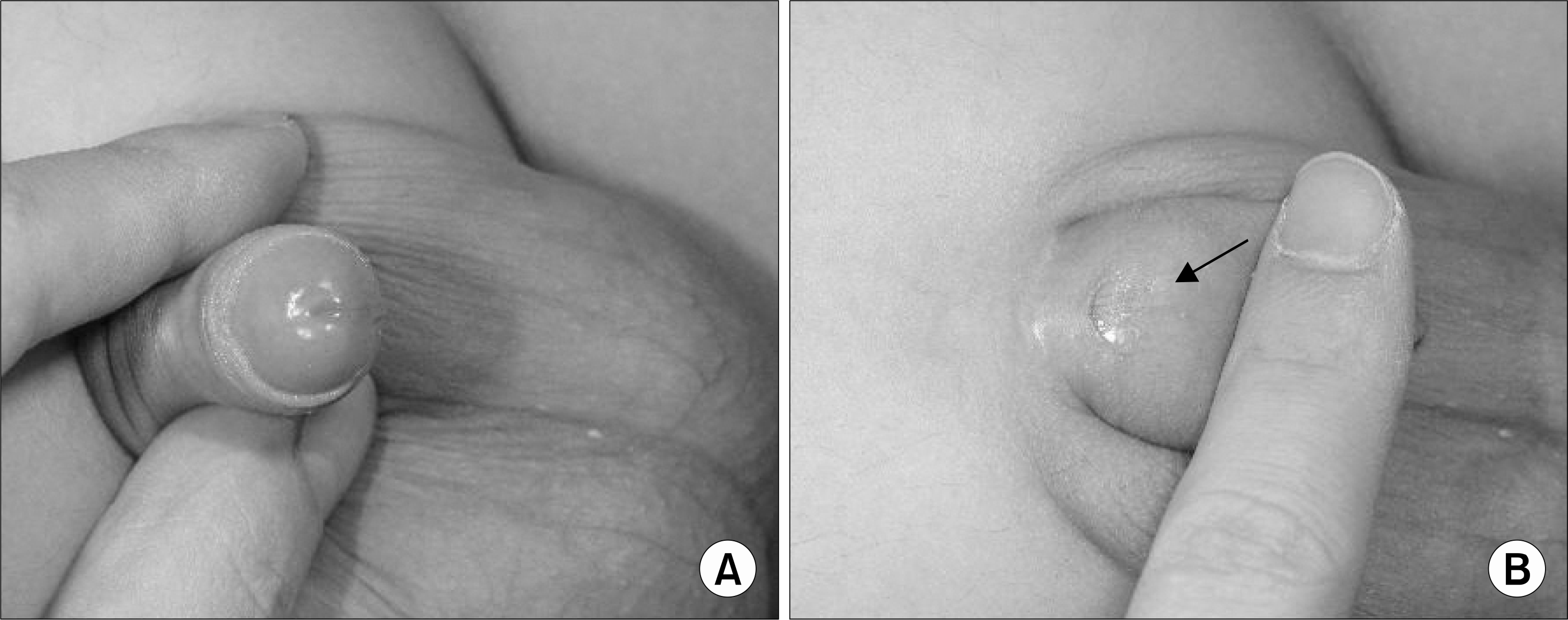
Table 1.
Clinical data of patients with urethral duplication
Table 2.
Effmann classification of urethral duplication3




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download