Abstract
Purpose
We evaluated the incidence and impact of vesico-ureteral reflux (VUR) on renal function after a radical cystectomy and the use of orthotopic bladder substitutes, using refluxing and antirefluxing type uretero-intestinal anastomosis.
Materials and Methods
Sixty-five patients (124 renal units) had undergone a radical cystectomy with an ileal orthotopic substitute and received postoperative follow-up for longer than 12 months. For these patients, we evaluated the presence and grade of VUR using voiding cystourethrography (VCUG) and measured the individual glomerular filtration rate99mtechnetium diethy-(GFR) of the corresponding renal units using a lenetetraminepentaacetic acid (DTPA) renal scan. According to the urinary diversion (refluxing or antirefluxing methods), we analyzed the incidence of VUR and the impact of VUR on renal function. The mean follow-up time was 52 months (range 13 132 months) after surgery.
Results
The incidence of VUR was higher in the refluxing anstomosis group (group R, 60.3%) of patients than in the antirefluxing group of patients (group NR, 21.7%) (p=0.001). However, the mean GFR was not significantly different (72.5ml/min/m2 for group R patients, 76.4ml/min/ m2 for group NR patients, respectively). Between the refluxing and nonrefluxing renal units, no significant difference of GFR was also noted (38.3ml/min/m2 versus 37.7ml/min/m2). When GFR was stratified by the duration of the diversion, it was not significantly different (38.2, 36.2, and 41.7ml/min/m2 at 12 24, 25 48 and > 48 months, p>0.05, respectively) regardless of the diversion methods. The degree of reflux was not related to the renal function.
Conclusions
Although there was a higher incidence of VUR in the refluxing type than in the antirefluxing type of orthotopic bladder substitutes, VUR developing after a radical cystectomy does not significantly alter renal function regardless of its severity or the methods and duration of the diversion. (Korean J Urol 2007;48:933–937)
References
2. Shaaban AA, Mosbah A, Abdel-Latif M, Mohsen T, Mokhtar AA. Outcome of patients with continent urinary reconstruction and a solitary functioning kidney. BJU Int. 2003; 92:987–92.

3. Hautmann RE, Abol-Enein H, Hafez K, Haro I, Mansson W, Mills RD, et al. Urinary diversion. Urology. 2007; 69(1 Suppl):17–49.

4. Kristjansson A, Abol-Enein H, Alm P, Mokhtar AA, Ghoneim MA, Mansson W. Long-termrenal morphology and function following enterocystoplasty (refluxing or antireflux anastomosis): an experimental study. Br J Urol. 1996; 78:840–6.
5. Pantuck AJ, Han KR, Perrotti M, Weiss RE, Cummings KB. Ureteroenteric anastomosis in continent urinary diversion: longterm results and complications of direct versus nonre-fluxing techniques. J Urol. 2000; 163:450–5.

6. Shaaban AA, Abdel-Latif M, Mosbah A, Gad H, Eraky I, Ali-El-Dein B, et al. A randomized study comparing an antireflux system with a direct ureteric anastomosis in patients with orthotopic ileal neobladders. BJU Int. 2006; 97:1057–62.

7. Studer UE, Danuser H, Thalmann GN, Springer JP, Turner WH. Antireflux nipples or afferent tubular segments in 70 patients with ileal low pressure bladder substitutes: longterm results of a prospective randomized trial. J Urol. 1996; 156:1913–7.

8. Studer UE, Zingg EJ. Ileal orthotopic bladder substitutes. What we have learned from 12 years' experience with 200 patients. Urol Clin North Am. 1997; 24:781–93.
9. Thoeny HC, Sonnenschein MJ, Madersbacher S, Vock P, Studer UE. Is ileal orthotopic bladder substitution with an afferent tubular segment detrimental to the upper urinary tract in the long term? J Urol. 2002; 168:2030–4.

10. Hautmann RE, de Petriconi R, Gottfried HW, Kleinschmidt K, Mattes R, Paiss T. The ileal neobladder: complications and functional results in 363 patients after 11 years of followup. J Urol. 1999; 161:422–7.

11. Hollowell CM, Christiano AP, Steinberg GD. Technique of Hautmann ileal neobladder with chimney modification: interim results in 50 patients. J Urol. 2000; 163:47–51.

12. Abol-Enein H, Ghoneim MA. Functional results of orthotopic ileal neobladder with serous-lined extramural ureteral reimplantation: experience with 450 patients. J Urol. 2001; 165:1427–32.

13. Stein JP, Dunn MD, Quek ML, Miranda G, Skinner DG. The orthotopic T pouch ileal neobladder: experience with 209 patients. J Urol. 2004; 172:584–7.

14. Kristjansson A, Mansson W. Renal function in the setting of urinary diversion. World J Urol. 2004; 22:172–7.

15. Minervini A, Boni G, Salinitri G, Mariani G, Minervini R. Evaluation of renal function and upper urinary tract morphology in the ileal orthotopic neobladder with no antireflux mechanism. J Urol. 2005; 173:144–7.

16. Jung JU, Sohn DW, Cho YH. Alteration in renal function for patients with ileal conduit and ileal orthotopic neobladder. Korean J Urol. 2006; 47:1065–8.

17. Kristjánsson A, Wallin L, Månsson W. Renal function up to 16 years after conduit (refluxing or antireflux anastomosis) or continent urinary diversion. 1. Glomerular filtration rate and patency of uretero-intestinal anastomosis. BJU Int. 1995; 76:539–45.
Fig. 1.
The mean GFR does not differ among the renal units with or without VUR when stratified by the duration of diversion. GFR: glomerular filtration rate, VUR: vesico-ureteral reflux.
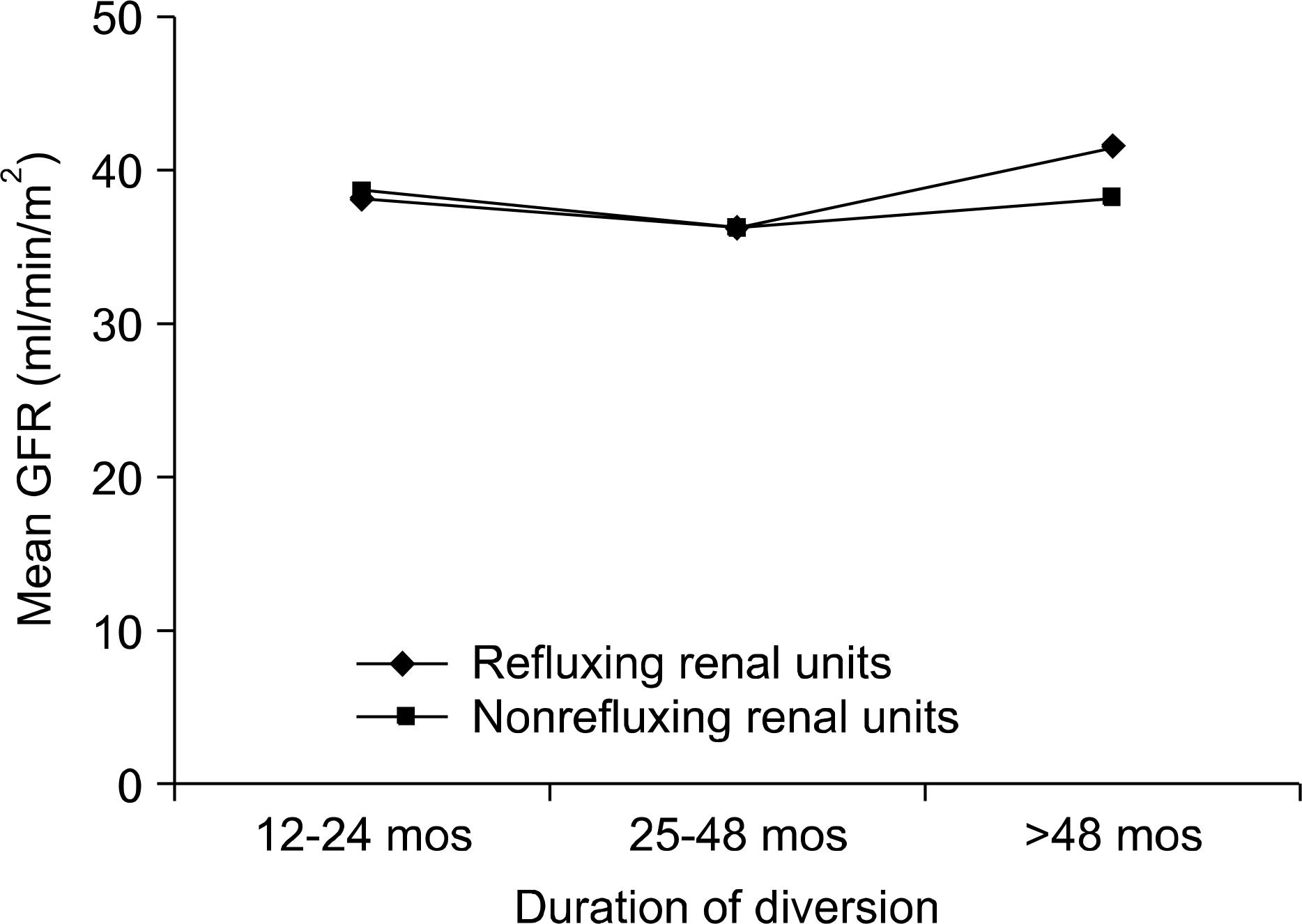
Table 1.
Patient characteristics
Table 2.
Incidence of VUR and postoperative GFR between the two groups




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download