Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of 8 weeks of 0.2mg tamsulosin medication on the erectile and ejaculatory functions of patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Materials and Methods
108 patients with BPH and they were without prostate cancer and neurogenic bladder were included in this study. Initial evaluations included a thorough history, digital rectal exam, urinalysis, serum prostate-specific antigen, uroflowmetry (UFM), post void residual urine measurement, transrectal ultrasound, International Prostatic Symptom Score (IPSS) and an International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) and ejaculatory function questionnaire. After 4 and 8 weeks of medication, we analyzed the differences of these parameters at each week.
Results
The mean age of the patients was 61.3±9.0 years old and their prostate volume was 35.7±21.3ml. The IIEF erectile function (EF) domain score showed no statistically significant difference after medication. However, the orgasmic function domain score showed a significant decrease from 16.3±9.3 to 15.7±9.6 at the 4th and 8th week. Regarding the ejaculatory function, when the patients were divided into two groups according to the EF domain score (<10, ≥11), the score of the ejaculatory volume showed a tendency to decrease from 2.5±1.0 to 2.2±1.2 (p=0.07), and the score for satisfaction about ejaculation was decreased from 3.0±1.2 to 2.5±1.5 (p=0.01) in the larger EF domain group after 8 weeks of treatment. The IPSS score and UFM parameters improved significantly after medication (p<0.05).
Figures and Tables
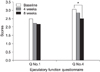 | Fig. 1Ejaculatory function score in 78 patients with an erectile function (EF) domain score more than 11. Q No. 1, ejaculatory function question number 1; Q No. 4, ejaculatory function question number 4; 4 weeks, 4 weeks after tamsulosin 0.2mg medication; 8 weeks, 8 weeks after tamsulosin 0.2mg medication, Values are shown as means. *p<0.05 compared with the baseline by a paired sample t-test. |
References
1. Narayan P, Lepor H. Long-term, open-label, phase III multi-center study of tamsulosin in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 2001. 57:466–470.
2. Lepor H. Tamsulosin Investigator Group. Long-term evaluation of tamsulosin in benign prostatic hyperplasia: placebo-controlled, double-blind extension of phase III trial. Urology. 1998. 51:901–906.
3. Lee E, Lee C. Clinical comparison of selective and non-selective alpha 1A-adrenoreceptor antagonists in benign prostatic hyperplasia: studies on tamsulosin in a fixed dose and terazosin in increasing doses. Br J Urol. 1997. 80:606–611.
4. Hisasue S, Furuya R, Itoh N, Kobayashi K, Furuya S, Tsukamoto T. Ejaculatory disorder caused by alpha-1 adrenoceptor antagonists is not retrograde ejaculation but a loss of seminal emission. Int J Urol. 2006. 13:1311–1316.
5. Hellstrom WJ, Sikka SC. Effects of acute treatment with tamsulosin versus alfuzosin on ejaculatory function in normal volunteers. J Urol. 2006. 176:1529–1533.
6. van Dijk MM, de la Rosette JJ, Michel MC. Effects of alpha (1)-adrenoceptor antagonists on male sexual function. Drugs. 2006. 66:287–301.
7. Höfner K, Claes H, De Reijke TM, Folkestad B, Speakman MJ. Tamsulosin 0.4mg once daily: effect on sexual function in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic obstruction. Eur Urol. 1999. 36:335–341.
8. Athanasopoulos A, Gyftopoulos K, Giannitsas K, Fisfis J, Perimenis P, Barbalias G. Combination treatment with an alpha-blocker plus an anticholinergic for bladder outlet obstruction: a prospective, randomized, controlled study. J Urol. 2003. 169:2253–2256.
9. Cho SH, Lee SK. The experience with combination of finasteride and tamsulosin on benign prostatic hyperplasia. Korean J Urol. 2003. 44:1110–1115.
10. Joung JY, Park JK, Park CH, Lee JG, Chung BH, Hong SJ, et al. The role of alpha 1 (a) adrenoceptor antagonist tamsulosin for the treatment of patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia: the effect on lower urinary tract symptoms and nocturia. Korean J Urol. 2006. 47:1–6.
11. Choi WS, Moon KH. The effects of finasteride, tamsulosin and doxazosin therapy on sexual function in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Korean J Urol. 2004. 45:777–782.
12. Berthelson S, Pettinger WA. A functional basis for classification of alpha-adrenergic receptors. Life Sci. 1977. 21:595–606.
13. Kobayashi S, Tang R, Shapiro E, Lepor H. Characterization and localization of prostatic alpha 1 adrenoceptors using radioligand receptor binding on slide-mounted tissue section. J Urol. 1993. 150:2002–2006.
14. Walden PD, Durkin MM, Lepor H, Wetzel JM, Gluchowski C, Gustafson EL. Localization of mRNA and receptor binding sites for the alpha 1a-adrenoceptor subtype in the rat, monkey and human urinary bladder and prostate. J Urol. 1997. 157:1032–1038.
15. Forray C, Bard JA, Wetzel JM, Chiu G, Shapiro E, Tang R, et al. The alpha 1-adrenergic receptor that mediates smooth muscle contraction in human prostate has the pharmacological properties of a cloned human alpha 1c subtype. Mol Pharmacol. 1994. 45:703–708.
16. Goepel M, Krege S, Price DT, Michelotti GA, Schwinn DA, Michel MC. Characterization of α-adrenoceptor subtypes in the corpus cavernosum of patients undergoing sex change surgery. J Urol. 1999. 162:1793–1799.
17. Dausse JP, Leriche A, Yablonsky F. Patterns of messenger RNA expression for α1-adrenoceptor subtypes in human corpus cavernosum. J Urol. 1998. 160:597–600.
18. Krege S, Goepel M, Sperling H, Michel MC. Affinity of trazodone for human penile alpha1- and alpha2-adrenoceptors. BJU Int. 2000. 85:959–961.
19. Becker AJ, Stief CG, Machtens S, Schultheiss D, Hartmann U, Truss MC, et al. Oral phentolamine as treatment for erectile dysfunction. J Urol. 1998. 159:1214–1216.
20. Kaplan SA, Reis RB, Kohn IJ, Shabsigh R, Te AE. Combination therapy using oral alpha-blockers and intracavernosal injection in men with erectile dysfunction. Urol. 1998. 52:739–743.
21. Lepor H, Williford WO, Barry MJ, Brawer MK, Dixon CM, Gormley G, et al. Veterans Affairs Cooperative Studies Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Study Group. The efficacy of terazosin, finasteride, or both in benign prostatic hyperplasia. N Engl J Med. 1996. 335:533–539.
22. Roehrborn CG. Efficacy and safety of once-daily alfuzosin in the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms and clinical benign prostatic hyperplasia: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Urology. 2001. 58:953–959.
23. Michel MC, Bressel HU, Goepel M, Rübben H. A 6-month large-scale study into the safety of tamsulosin. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2001. 51:609–614.
24. Nordling J. Efficacy and safety of two doses (10 and 15mg) of alfuzosin or tamsulosin (0.4mg) once daily for treating symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia. BJU Int. 2005. 95:1006–1012.
25. Schulman CC, Lock TM, Buzelin JM, Boeminghaus F, Stephenson TP, Talja M. Long-term use of tamsulosin to treat lower urinary tract symptoms/benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol. 2001. 166:1358–1363.
26. Kawabe K, Ueno A, Takimoto Y, Aso Y, Kato H. YM617 Clinical Study Group. Use of an alpha1-blocker, YM617, in the treatment of benign prostatic hypertrophy. J Urol. 1990. 144:908–912.
27. Okada H, Kamidono S, Yoshioka T, Okuyama A, Ozono S, Hirao Y, et al. A comparative study of terazosin and tamsulosin for symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia in Japanese patients. BJU Int. 2000. 85:676–681.
28. Kim DS, Chung BH. Translation validity and reliability of the Korean version of the DAN-PSS. Korean J Urol. 2003. 44:871–875.
29. Oh CY, Lee JS, Chung BH. A validation and reliability study for the Korean version of the male sexual health questionnaire. Korean J Urol. 2005. 46:1308–1326.
30. Smith LJ, Mulhall JP, Deveci S, Monaghan N, Reid MC. Sex after seventy: a pilot study of sexual function in older persons. J Sex Med. 2007. 4:1247–1253.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download