Abstract
DNA profiling with sets of short tandem repeat (STR) markers is the most popular method for identifying human DNA in forensics. Identification by STR typing might fail when DNA is degraded or is present in low amounts, such as in disaster victim identification (DVI) samples. In such cases, more information might be obtained by using additional markers such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Multiplex PCR and microarray are convenient techniques to analyze SNP markers. We used an AccuID™ Chip, SNP-based DNA chip manufactured by DNA Link Corporation, to confirm genetic relationship between two human bone samples that had been buried for more than 50 years and blood samples from the alleged descendants of the sources of the bone fragments. The chip combines an Affymetrix resequencing array with a multiplex PCR technology and can genotype hundreds of SNP markers in a single experiment. Genotyping the two bone samples yielded 90.5 and 77 SNP markers. The commonly genotyped markers (61 and 47 SNP loci) in each bone-family pair provided high paternity indices to support the genetic relationships in both cases.
REFERENCES
1. Kim YL, Hwang JY, Kim YJ, et al. Allele frequencies of 15 STR loci using AmpF/STR Identifiler kit in a Korean population. Forensic Sci Int. 2003; 136:92–5.

2. Gross A, To ¨njes A, Kovacs P, et al. Population-genetic comparison of the Sorbian isolate population in Germany with the German KORA population using genomewide S-NP arrays. BMC Genet. 2011; 12:67.

3. Dixon LA, Dobbins AE, Pulker HK, et al. Analysis of artificially degraded DNA using STRs and SNPs-results of a collaborative European (EDNAP) exercise. Forensic Sci Int. 2006; 164:33–44.

4. Kothiyal P, Cox S, Ebert J, et al. An overview of custom array sequencing. Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2009. Chapter7: Unit7.17.

5. Seo SB, Zhang A, Kim HY, et al. Technical note: efficiency of total demineralization and ion-exchange column for D-NA extraction from bone. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2010; 141:158–62.

6. Fung W, Hu Y. Statistical DNA forensics: theory, methods and computation (statistics in practice). New York: John Wiley and Sons, Ltd;2008. p. 47–78.
7. Butler JM, Coble MD, Vallone PM. STRs vs. SNPs: thoughts on the future of forensic DNA testing. Forensic Sci Med Pat. 2007; 3:200–5.

8. Amorim A, Pereira L. Pros and cons in the use of SNPs in forensic kinship investigation: a comparative analysis with STRs. Forensic Sci Int. 2005; 150:17–21.

9. Sobrino B, Brion M, Carracedo A. SNPs in forensic genetics: a review on SNP typing methodologies. Forensic Sci Int. 2005; 154:181–94.

10. Seo SB, Lee HY, Zhang AH, et al. Effects of humic acid on DNA quantification with Quantifiler� Human DNA Quantification kit and short tandem repeat amplification effieicency. Int J Legal Med. 2012; 126:961–8.
Fig. 1.
Sequencing array design. Eight 25-mers are tiled to probe each individual base pair. A single position differs so that each of the four possible nucleotides can be queried on both the sense and antisense strands (a, adapted from reference 4). The probe designed in triplicate provides advantages in the aspect of accuracy, confidence, and reproducibility (b, illustrated by Hyung Jin Yu, DNA Link).
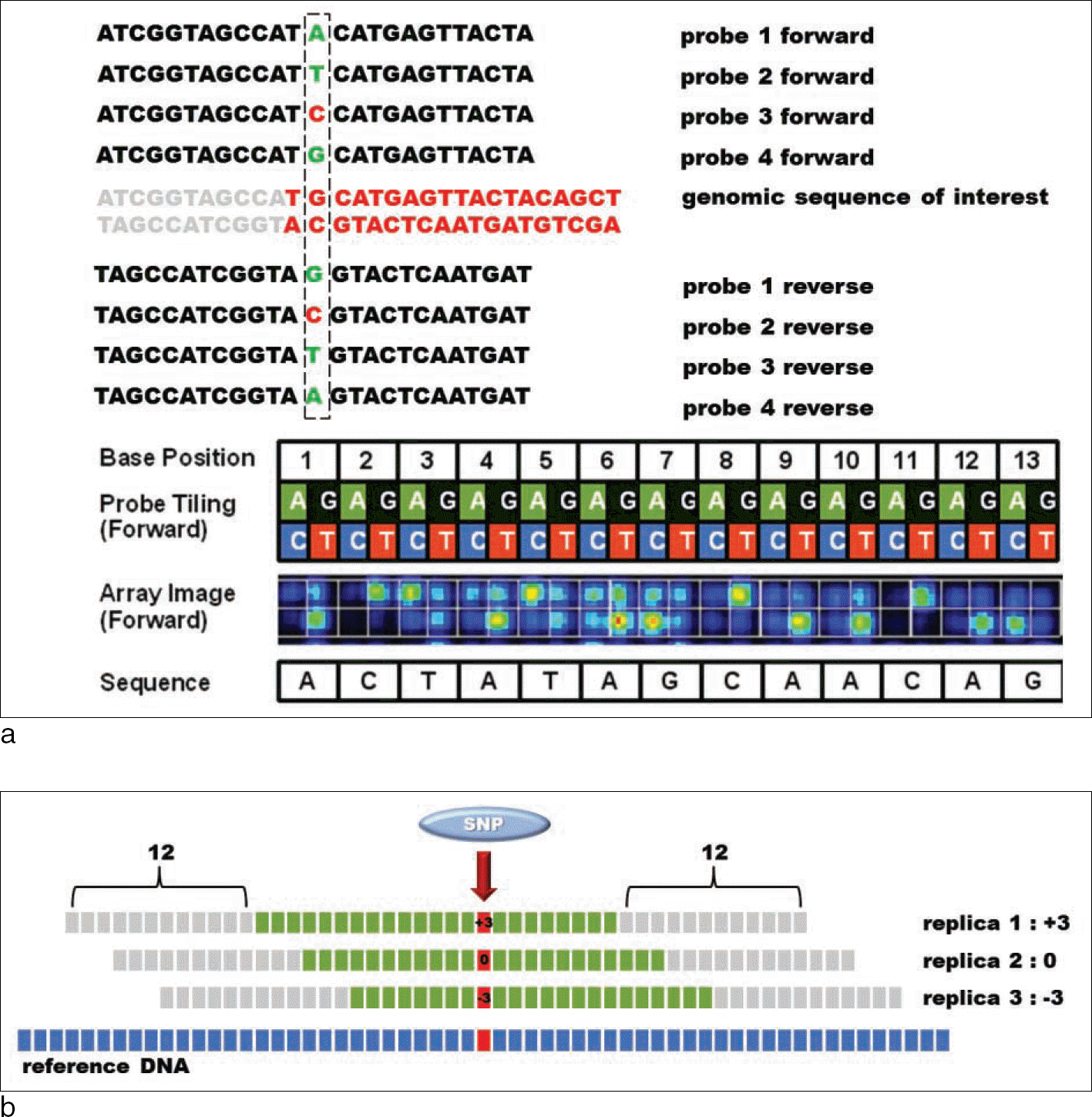
Table 1.
The Average Minor Allele Frequency (MAF) and Fixation Index (Fst) Value of 169 Markers
Table 2.
The Result of SNP Typing Using AccuID™
| Family 1 | Bone 1 | Family 2 | Bone 2 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Typed SNP | 154 | 150 | 87 | 94 | 157 | 152 | 75 | 79 | ||||||
| 61∗ | 47∗ | |||||||||||||
| Untyped SNP | 15 | 19 | 82 | 75 | 12 | 17 | 94 | 90 | ||||||
| 6† | 60† | 9† | 67† | |||||||||||
| Total SNP | 169 | 169 | 169 | 169 | 169 | 169 | 169 | 169 | ||||||
Table 3.
The Result of 169 SNP Typing in all Samples




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download